ENGINEERING-43 RC Series Circuits Lab-16 – ENGR-43 Lab-16
advertisement

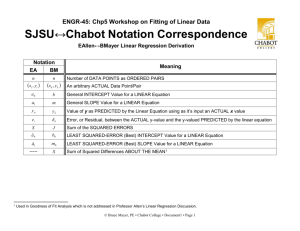
ENGINEERING-43
RC Series Circuits
Lab-16
Lab Data Sheet – ENGR-43 Lab-16
Lab Logistics
Experimenter: Bruce Mayer, PE
Recorder:
Date: 27Feb08
Equipment Used (maker, model, and serial no. if available)
CFG-250
Fluke 8050A DMM
TEK TDS340 Oscope
Knight K-240C LCR Meter, S/N 12001212
Directions
1. Check out
a DMM
an oscilloscope
a Signal/Function Generator.
Cables and Leads
2. Go to the side counter, collect resistors, a capacitor, “bread board”, and leads required to
construct the circuit shown in Figure 1.
3. See the Instructor to use the LCR meter to measure the actual value of the Capacitor
4. Use the DMM to measure the actual value of the Resistor
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 1
Figure 1 • RC Series Circuit.
Vs = 14 Vpp (Vamplitude = 7V) or
Vs = 7V0º
f = per Table I or Table IV.
R = 350-750 Ω (470 Ω nominally).
C = 100 nF (0.1 µF) nominally.
Digital-Meter Actual-Values
R=
C=
0.5258 kΩ
105.3 nF
5. Make the Measurements and Calculations needed to complete Table I.
Reveal the Vs-GND signal on the Scope
Connect CHANNEL-1 between the Vs and GND nodes for the circuit shown in
Figure 1 (measures Vs-GND)
Press the CH1 Button to bring the signal onto the display
Set up the waveform for each frequency using TDS340
Set the Frequency, f: [MEASURE Menu] → [Frequency side menu-1, button-2]
Set the Peak-to-Peak Amplitude, Vpp: [MEASURE Menu] → [Pk-Pk side menu3, button-3]
Confirm the Period, T : [MEASURE Menu] → [Period side menu-1, button-1]
Reveal the Vc-GND signal on the Scope
Connect CHANNEL-2 between R and C (measures Vc-GND)
Press the CH2 Button to bring the signal onto the display
o Both the CH1 and CH2 traces should be simultaneously displayed
Use the Scope to Measure the Capacitor Phase-Difference, , in Terms of TIME
Expand the SEC/DIV scale on the scope to make a maximally precise
measurement of the time-based phase difference
o See the Instructor if you are unsure about this procedure
Measure using the cursors
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 2
o Activate the Vertical-Bar cursors: [CURSOR button] → [Side Menu = V
Bars]
o Use the SELECT button and the GENERAL PURPOSE knob to position
the Left cursor at the peak of the left-most trace.
o Use the SELECT button and the GENERAL PURPOSE knob to position
the Right cursor at the peak of the left-most trace.
o Read the “Δ” measurement in the upper-left corner of the display
Be Sure to Note if LEADS or LAGS the source which is DEFINED to have
ZERO phase angle
Measure Vc,pp using the cursors
o Activate the Horizontal-Bar cursors: [CURSOR button] → [Side Menu =
H Bars]
o Use the SELECT button and the GENERAL PURPOSE knob to position
the top cursor at the peak of the CH2 trace.
o Use the SELECT button and the GENERAL PURPOSE knob to position
the Bottom cursor at the trough of the CH2 trace.
o Read the “Δ” measurement in the upper-left corner of the display
Use The DMM in “TRUE RMS” mode to measure the rms values for V & I
Be sure readjust the amplitude every time the frequency is changed
Table I – Capacitance Measurements
Frequency, f
T
for Vc
Vc,pp
Vc,rms
Ic,rms
1000 Hz
995 μs
54 μs Lag
13.9 Vpp
4.562 Vrms
2.973 mA
3333 Hz
299 μs
43.5 μs Lag
9.20 Vpp
3.183 Vrms
6.742 mA
10000 Hz
99.75 μs
19.3 μs Lag
3.88 Vpp
1.365 Vrms
8.763 mA
6. Perform the Calculations needed to complete Table II
Use the Signal Period and the Capacitor Phase-Difference Time to calculate the
capacitor phase ANGLE, , in DEGREES (°) relative to the base-line value for Vs:
LEAD
360
sec
T sec
LAG
Using measured values calculate: XC = −Vrms/Irms
From measured Vrms & Irms values Calculate C from the expression for XC
|XC| = 1/(C)
Use the calculation and the LCR meter data to determine the % for the Capacitor as
C-% = 100x(Ccalc – CLCR)/CLCR
Table II – Capacitance Calculations
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 3
Frequency, f
for Vc
|XC|
Ccalc
C-%
1000 Hz
−19.44°
1534 Ω
0.1037 μF
−1.52%
3333 Hz
−52.2°
472.1 Ω
0.1011 μF
−3.99%
10000 Hz
−69.48°
155.7 Ω
0.1022 μF
−2.94%
7. Use the Digital-Meter Actual Values for R & C, and the rms & scope measurements to
complete Table III. Specifically CALCULATE the
Capacitor impedance, Zc (specify in RECTANGULAR form):
Zc
1
j
1
1
j
jX c , LCR Note that X c
jC C
C
C
Single-loop phasor circuit current Ic using Ohm’s law (specify Ic in POLAR form):
Ic
Vs
Vs
Z series R Z c
Single-loop phasor Voltage across the Capacitor, Vc, by the Voltage Divider method
(specify Vc in POLAR form):
Vc Vs
Zc
Zc
Vs
Z series
R Zc
All Phase Angles MUST stated in degrees (°)
To Calculate the Δ%’s, Let “Q” = Ic or Vc, then:
Q%
Q
2 Brms
Brms
Table III – Impedance-Based Calculations
Frequency, f
Zc
Ic
Vc
Ic-%
Vc-%
1000 Hz
−j1511.4Ω
4.374mA70.82°
6.611V−19.18°
+4.03%
+2.47%
3333 Hz
−j453.5Ω
10.08mA40.78°
4.572V−49.22°
+5.72%
+1.57%
10000 Hz
−j151.14Ω
12.79mA16.04°
1.934V−73.96°
+3.21%
+0.19%
8. Make the Measurements and Calculations needed to complete Table IV
Use the Scope to measure Vc,pp
Use the Scope MATH menu MEASURE DIRECTLY VR,pp
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 4
Press the MATH button
o On the side menu press button-2 to activate the Ch1-Ch2 measurement
With the MATH WaveForm selected Press the MEASURE Button
o On the side menu press the button needed to activate the Pk-Pk
function
Use the Scope to measure the TIME-based phase difference, , for Vc as was done in
step 5
Expand the SEC/DIV scale on the scope to make a maximally precise
measurement of the time-based phase difference
Using determine the Capacitor Phase Angle in DEGREES (°)
Table IV – Series RC Potential Measurements Sweep
Frequency, f
Vs,pp
Vc,pp (Vpp)
VR,pp (Vpp)
for Vc
for Vc
100 Hz
14V0º
13.92
680 mVpp
40 μs Lag
−1.44°
400 Hz
14V0º
13.76
2.08
60 μs Lag
−8.64°
1250 Hz
14V0º
12.88
5.6
59 μs Lag
−26.55°
2.5 kHz
14V0º
10.64
9.2
48.5 μs Lag
−43.65°
8.0 kHz
14V0º
4.96
13.12
24.2 μs Lag
−69.7°
25.0 kHz
14V0º
1.74
13.88
9.6 μs Lag
−86.4°
80 kHz
14V0º
540 mVpp
13.95
3.06 μs Lag
−88.13°
Note: Low frequencies such as 100Hz can be difficult to measure
9. Use MATLAB or EXCEL to create two SemiLog plots of the data contained in Plot the Data
Table IV. In both plots the frequency, f, will be plotted on the Logarithmic scale
Plot-1
Independent variable = log(f)
TWO dependent variables on the same plot: Vc,pp and VR,pp
Plot-2
Independent variable = log(f)
Dependent variable =
Attach both plots to this lab report
ANALYZE the trends shown in the plots, and comment on the physical CAUSE of the
observed trends
HINT: Consider the Behavior of the Circuit in these extreme cases
o →0
o →∞
10. Return all lab hardware to the “as-found” condition
Run Notes/Comments
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 5
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 6
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 7
MATLAD Code Used to Create the Plots
% Bruce Mayer, PE * 15May10
% ENGR43 * Lab-16 RC Series Ckt Plots
% file = ENGR43_Lab16_RCckt_Plots_1005.m
%
% DATA from Lab-16 Sheet
f = [100
400
1250
2500
8000
25000
80000]
Vc = [13.9200 13.7600 12.8800 10.6400
4.9600
.7400 0.5400]
Vr = [0.6800 2.0800 5.6000 9.2000 13.1200 13.8800 13.9500]
q = [0.6800
2.0800
5.6000
9.2000
13.1200
13.8800
13.9500]
%
% Vc & Vr plot
semilogx(f,Vr, '--mo', f, Vc,':bs' ), grid, legend('Vr','Vc'),
xlabel('frequency (Hz)'), ylabel('Vc & Vr (Vpp)'),...
title('ENGR43 Lab-16 Voltage-Drop vs. Freqency for Series RC
Circuit')
disp('Showing Vc & Vr plot - hit ANY KEY to continue')
pause
%
disp('Showing Phase-Angle plot')
semilogx(f,q, '--mo' ), grid, xlabel('frequency (Hz)'), ylabel('Phase
Angle. \phi (°)'),title('ENGR43 Lab-16 Phase-Angle vs. Freqency for
Series RC Circuit')
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 8
ENGR43 Lab-16 Voltage-Drop vs. Freqency for Series RC Circuit
14
12
Vc & Vr (Vpp)
10
8
6
Vr
Vc
4
2
0 2
10
10
3
10
frequency (Hz)
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 9
4
10
5
ENGR43 Lab-16 Phase-Angle vs. Freqency for Series RC Circuit
0
-10
-20
Phase Angle. (°)
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90 2
10
10
3
10
frequency (Hz)
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 10
4
10
5
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 11
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 12
x
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 13
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 14
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 15
© Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291237631 • Page 16