Soil Erosion by Water: Processes & Runoff Models
advertisement

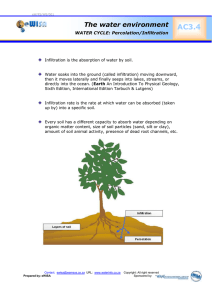
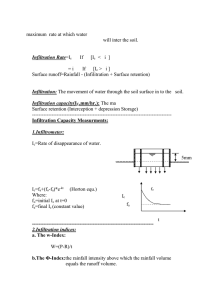
Soil erosion by water EROSION Detachment – particle/aggregate loosened from surface Entrainment – initiation of motion by flow TRANSPORT Rill – concentrated overland flow Inter-rill (sheetwash) – diffuse overland flow Detachment Raindrop impact Bioturbation Frost action Drying Soil Conservation Service “Curve Number” method Empirical relationship between rainfall and runoff 𝑄, dependent upon Curve Number 𝐶𝑁 through the parameter 𝑆 (potential soil retention). 𝑃 − 0.2𝑆 2 𝑄= 𝑃 + 0.8𝑆 𝑆= 𝐶𝑁 − 10 1000 𝑆 may be characteristic of a plot, field, watershed, or region according to terrain, soil type, and land use. Runoff generation Runoff generation depends on antecedent soil moisture conditions, soil infiltration capacity, rainfall intensity. Runoff may be generated either when rainfall intensity exceeds infiltration capacity or when soil is saturated. Green-Ampt Infiltration Approximate physically-based transient infiltration model. 𝑓 𝑡 =𝐾 1+ 𝜓Δ𝜃 𝐹 𝑡 𝐹 𝑡 = 𝐾𝑡 + 𝜓Δ𝜃 ln 1 + 𝐹 𝑡 𝜓Δ𝜃 Where 𝑓(𝑡) and 𝐹(𝑡) are the infiltration rate and net infiltration, respectively. Green-Ampt cont’d Infiltration capacity parameters are strongly sensitive to soil type. Q: How does runoff flux vary with position on a hillslope with uniform soil properties?