Solvent-free particle surface modification using amino acid L-Leucine during milling... improved dry powder dispersion
advertisement

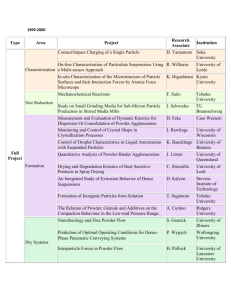
Solvent-free particle surface modification using amino acid L-Leucine during milling for improved dry powder dispersion Kuriakose Kunnath, Z. Huang, R. Dave New Jersey Institute of Technology Inhalation therapy requires the efficient powder de-agglomeration and dispersion in addition to a very fine particle size (<5 µm). Unfortunately, milling of pharmaceutical powders, which is required to achieve the right size range, leads to formation of large agglomerates with poor dispersion after inhalation. In this work, using KCl as a surrogate material, milling and surface coating was done in a Fluid Energy Mill (FEM) to produce particles suitable for inhalation. Several different coating materials were investigated and it was found that L-Leucine, a naturally occurring amino acid, offers similar powder dispersibility performance even at the fine particle sizes used in inhalation