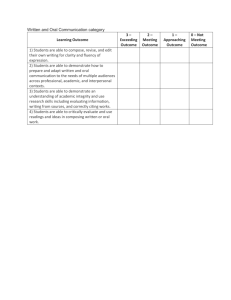
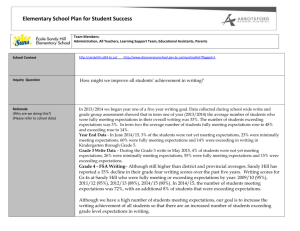
Document 11496024
advertisement

® Tax Handbook 2012 Tax Handbook 2012 An Information Guide This page is intentionally left blank Tax Handbook 2012 Preface This handbook attempts to cater the needs of the various post budget queries forthcoming by our clients. We have attempted to apprise them with a comprehensive explanation of the implications and effect that this Finance Bill has brought about. The handbook encompasses the amendments in the Income Tax Ordinance, Sales Tax Act, Federal Excise Act, Customs Act and Miscellaneous Laws. The applicable amendments in the laws after enactment are effective from July 1, 2012 unless otherwise specified. The commentary should be read in conjunction with the applicable sections of respective Ordinances, Acts and Rules along with the text of the Finance Bill 2012. This commentary attempts to provide a general guideline and thus should not be considered as a conclusive and enforceable document. Professional advice should be sought before acting on any amendment in the Finance Bill or on our comments. We hope that this handbook enhances your perception of Budget 2012-13. For better understanding and convenience, we have also drafted a Tax Planning Guide appended to this handbook. This handbook is the property of Horwath Hussain Chaudhury & Co. and is compiled for the exclusive use of its clients and employees. No part of this handbook may be reproduced except with prior permission of Horwath Hussain Chaudhury & Co. Although best efforts have been made to ensure accuracy of the information in this handbook, any errors and omissions are regretted. Lahore June 02, 2012 www.crowehorwath.pk This page is intentionally left blank Tax Handbook Contents Chapter Page General Budget ‘12-13 1-4 Commentary on the Finance Bill 2012 Highlights 5-7 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Schedules First Second Third Fourth Fifth Seventh Eighth 9-16 16-19 20-21 21 21 21 22 22 Sales Tax Act, 1990 Schedules Sixth Schedule Notable Notifications 23 23 24-26 Federal Excise Act, 2005 Schedules First Notable Notifications 27-29 30 Customs Act, 1969 Notable Notifications Miscellaneous Laws 31-32 33-34 35-36 Tax Planning Guide 2012 Income Tax Sales Tax Capital Value Tax 37-47 48-49 50 2012 This page is intentionally left blank Tax Handbook 2012 Budget, 2012-2013 Budget, 2012-2013 Salient Features of the Budget 2012-2013 The salient features of the budget 2012-13 are as follows: The total outlay of budget 2012-13 is Rs. 3,203 billion (Rs. 3,110 billion: 2011) showing an increment of 3%. The resource availability during 2012-13 has been estimated at Rs. 2,719 billion (Rs. 2,171 billion: 2011) showing an increment of 25%. The net revenue receipts for 2012-13 have been estimated at Rs. 1,775 billion (Rs. 1,328 billion: 2011) indicating an increment of 34%. The provincial share in federal revenue receipts is estimated at Rs. 1,459 billion (Rs. 1,209 billion: 2011) during 2012-13 showing an increment of 21%. The net capital receipts for 2012-13 have been estimated at Rs. 478 billion (Rs. 525 billion: 2011) showing a decrease of 9%. The external receipts in 2012-13 are estimated at Rs. 387 billion (Rs. 226 billion: 2011) showing an increment of 71%. The overall expenditure during 2012-13 has been estimated at Rs. 3,203 billion (Rs. 3,110 billion: 2011) of which the current expenditure is Rs. 2,612 billion (Rs. 2,632 billion: 2011) and development expenditure is Rs. 591 billion (Rs. 478 billion: 2011). The share of current expenditure Rs. 2,612 billion (Rs. 2,632 billion: 2011) is 82%, (85% : 2011) of the total budgetary outlay for 2012-13. The expenditure on General Public Services is estimated at Rs. 1,877 billion, (Rs 1,898 billion: 2011) which is 72% (72% : 2011) of the current expenditures. The size of Public Sector Development Programme (PSDP) for 2012-13 is Rs. 873 billion (Rs 734 billion: 2011), while for other Development expenditures an amount of Rs. 154 billion (Rs. 122 billion: 2011) has been allocated. This shows an increment of 19% and 26%, respectively. The provinces have been allocated an amount of Rs. 513 billion (Rs. 430 billion: 2011) from Public Sector Development Programme (PSDP) showing an increment of 19%. An amount of Rs. 10 billion (Rs.10 billion: 2011) has been allocated to Earthquake Reconstruction and Rehabilitation Authority (ERRA) in the PSDP 2012-13. 01 Budget, 2012-2013 Comparative Budgetary Position 2012-2013 & 2011-2012 Receipts 2012-2013 2011-2012 (Rs. in Billion) (Rs. in Billion) 2,503.58 2,024.57 730.33 512.19 3,233.91 2,536.76 (1,458.92) (1,208.62) 1,774.99 1,328.14 Net Capital Receipts (B) 477.78 525.50 External Resources (C) 386.87 226.15 79.55 90.74 483.81 939.20 3,203.00 3,109.73 Tax Revenue (FBR) Non Tax Revenue Gross Revenue Receipts Less: Provincial Share in Taxes Net Federal Revenue Receipts (A) Estimated Provincial Surplus (D) Bank Borrowings (E) Total Resources (A+B+C+D+E) 02 Tax Handbook 2012 Budget, 2012-2013 Expenditures 2012-2013 2011-2012 (Rs. in Billion) (Rs. in Billion) 1,876.84 1,898.03 545.39 510.18 Public Order and Safety Affairs 70.16 61.85 Economic Affairs 53.64 72.24 Environment Protection 0.74 0.60 Housing and Community Amenities 1.86 1.65 Health Affairs and Services 7.85 6.65 Recreation, Culture and Religion 6.25 5.37 47.87 45.21 1.34 30.13 2,611.94 2,631.91 360.00 303.66 76.77 52.40 436.77 356.06 154.29 121.76 3203.00 3,109.73 General Public Services Defence Affairs and Services Education Affairs and Services Social Protection Current Expenditures (A) Development Expenditure (B) Federal Government Provincial Government Other Development Expenditure (C) Total Expenditures (A+B+C) 03 Budget, 2012-2013 Breakup of Receipts 14.92% 12.08% 2.48% 55.42% 15.10% Revenue Receipts (Net) Capital Receipts (Net) External Resources Estimated Provincial Surplus Bank Borrowings Breakup of Expenditures 0.24% 1.49% 0.20% 0.04% 11.24% 2.40% 4.82% 58.60% 17.03% 0.06% 0.02% 2.19% 1.67% Defence Affairs and Services Housing and Community Amenities Education Affairs and Services Other Development Expenditures Public Order and Safety Affairs General Public Services Social Protection Economic Affairs Health Affairs and Services Development Expenditures (PSDP) 04 Environment Protection Recreation, Culture & Religon Dev. Loans and Grants to Province Tax Handbook 2012 Commentary The Finance Bill, 2012 This page is intentionally left blank Tax Handbook Finance Bill Highlights 2012 Finance Bill Highlights Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to define National Clearing Company Limited and assigns it the role of withholding agent. Concept of 'Total Income' income rationalized. Notional benefit on concessional loan by employers to employees to the extent of Rs. 500,000 shall be exempt from tax. Tax on capital gains from short selling of immovable property has been imposed. Additional amount received on delayed refunds to be treated as 'Income from Other Sources'. Provisions relating to setting off of losses in case of AOPs have been rationalized. Limits for determination of tax credit on investment in listed shares and life insurance have been relaxed. Tax credits have been extended to industrial undertakings as a relief to combat industrial crises. The Commissioner (Appeals) empowered to grant stay against tax demand for 30 days. Commissioner (Appeals) is no more bound to dispose of an appeal within 4 month time limit. Appellate Tribunal empowered to grant stay against recovery of tax demand for 180 days. Commercial Importers, Traders and Exporters have been provided an alternative option to be taxed under Normal Tax Regime. The Bill seeks to make manufacturer a withholding agent in respect of supplies made to distributors, dealers and wholesalers. Taxpayer Honor Card Scheme has been introduced providing privilege to active taxpayers. Flat rate of default surcharge at 18% p.a. prescribed. Tax free threshold of daily cash withdrawals from banks has been increased from Rs. 25,000 to Rs. 50,000. NCCPL has been empowered to collect advance tax from members of stock exchanges. Exemption threshold for salary income and business income has been increased to Rs. 400,000. Slabs of total income have been reduced and uniform and progressive rates for computing tax liability have been introduced for both individuals and AOPs. Rates of tax on disposal of securities frozen for two years. Relief has been provided to both individual and AOP retailers by reducing rate of turnover tax applicable to them from 1% to 0.5%. Tax on goods transport vehicles has been increased from Re. 1 to Rs. 5 per Kg of the laden weight. Tax for passengers transport vehicles plying for hire has been increased from Rs. 100 per seat per annum to Rs. 500 per seat per annum. Advance tax to be paid on registration of motor vehicles (1,301cc to 1,600cc) has been increased from Rs. 16,875 to Rs. 25,000. Exemption, subject to certain conditions, has been provided on amount received from income payment plan out of accumulated balance of Pension Accounts. Reduced rate of 3% shall be sanctioned to importers only at the production of exemption certificate. Intra group profit on debt and dividends shall be exempt from tax if group companies opt to be taxed under group taxation. Exemption from applicability of capital gains tax extended. Initial Allowance on building reduced from 50% to 25%. An alternative option for payment of tax at the rate of 40% of profits and gains net of royalty has been provided to Petroleum Exploration and Production Companies. Dividends received by banks from money market funds and income funds are to be taxed at the rate 25% in Tax Year 2013 and at the rate of 35% in Tax Year 2014 and onwards. 05 Finance Bill Highlights Sales Tax Act, 1990 The Finance Bill harmonized the procedure for tax assessment and recovery of tax not levied or short levied or erroneously refunded. Uniform rate of sales tax @16% made applicable and higher sales tax rates from standard rate of 16% eliminated. Supplies against international tenders exempted that are currently treated as zero rated. Nomenclature of certain existing HS Codes revised to align coding with World Customs Organization (WCO). Exemption on locally produced cotton seeds oil withdrawn. Sales Tax rate on import and supplies of black tea reduced from 16% to 5%. Certain zero-rated items included in exempt items list. Federal Excise Act, 2005 Rate of duty enhanced on locally produced cigarettes. Rate of duty reduced by Rs. 100 per metric ton on cement. Duty on lubricant oil, certain cosmetic items and perfumes withdrawn. Duty in respect of air travel rationalized. Services provided by asset management company and companies providing insurance cover for livestock have been exempted from duty. Exemption on viscose staple fiber withdrawn. Customs Act, 1969 En route pilferage of transit goods has regarded as smuggle. Additional functionary directorates have been introduced for effective functional enforcement. Punishment of whipping eliminated and punishment on computer related offences introduced. Powers of adjudicating authorities Collectors, Superintendent and Principal Appraiser extended and jurisdiction of monetary limit of each level of authority redefined. Departmental appeals allowed for officers before Collector (Appeals) and Appellate Tribunal. Concept of e-auction of goods introduced. Custom duty in respect of shredded tyre scrap for cement manufacturers and raw materials of printing and stationery items has been reduced. The maximum tariff rate has been reduced from 35% to 30%. 06 Tax Handbook 2012 Finance Bill Highlights Miscellaneous Laws Capital value of shares of a public listed company acquired by a person has been exempted from CVT. Cantonment Board not to be included in the definition of urban area. For residential flats and commercial immovable area, the rate of CVT has been decreased to 2% of the recorded value if the value of the immovable property is recorded. Maximum rate of cess for gas infrastructure development companies has been increased. Certain provisions of the Finance Bill, 2012 are to be immediately applicable with effect from June 2, 2012. 07 This page is intentionally left blank 08 Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 'National Clearing Company Limited' Defined Section 2(35A) National Clearing Company Limited (NCCPL) was incorporated in 2001 to manage and operate the National Clearing & Settlement System (NCSS). The capital market of Pakistan has a triangular foundation comprising of the stock exchanges, Central Depository Company and NCCPL. NCCPL is playing a significant role in the capital market of Pakistan. The Operations of NCCPL are governed by the following: NCCPL Regulations, 2003 NCSS Procedures, 2003 Clearing House (Registration and Regulations) Rules, 2005 By virtue of the Finance Bill, 2012 the definition of NCCPL has been sought to be inserted as a company incorporated under the Companies Ordinance, 1984 and licensed as 'Clearing House' by the Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan. Concept of 'Total Income' Rationalized Section 10, 53(IA), 9 The Bill seeks to rationalize an inclusive concept of 'total income' that includes: Person's income under all heads of income for the year, and Person's income exempt from tax under any of the provisions of the Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 By virtue of proposed amendment in the definition of total income, whereby the exempt income has been included in the scope of total income and, therefore, the superfluous provision envisaged under subsection (1A) of Section 53 captioned as Exemptions and tax concessions under the Second Schedule is sought to be omitted. Pursuant to amendment in the definition of 'total income', Section 9 captioned as 'Taxable income' is sought to be amended. It would result in including the person's income under all heads of income for the year except exempt income. Concessional Loans by Employers to Employees Section 13(7), (14) Presently the loan advanced by an employer to an employee on soft terms is considered as perquisite for the employee and it is added to the taxable income of the employee based on benchmark interest rate policy given under the provisions of the law. By virtue of the Finance Bill, 2012, the employer may disburse a loan of upto Rs. 500,000 to an employee free of interest or at a rate lower than the benchmark rate. Thus, notional benefit on loan amount of upto Rs. 500,000 would not be treated as taxable perquisite for an employee. This is a good move to incentivize employees whereby small loans are advanced by employers to employees for their financial assistance. In an another move the Bill seeks to cap the benchmark rate of interest for concessional loans as 10% instead of aligning it with benchmark rate that has pitched upto 13%. Taxability of Capital Gain on Sale of Immovable Property Section 37(1A) The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to introduce the policy of taxing gains on disposal of real estate. Taxing the real estate sector is very much confusing in the Country and according to research reports a huge foreign direct investment (FDI), flow of foreign remittances and a phenomenal rise in banking growth in the past years helped significant investment in the real estate sector but the revenue contribution from this sector was negligible due to legal issues. The Bill proposes a new tax policy for the property sector with an aim to broaden the tax base and impose tax on those earning huge profits in this sector. 09 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 The Bill seeks to tax the gains arising on sale of immovable property held for a period less than two years under the head capital gains at the following rates: Period for which Immovable Property is Held Rate of Tax Up to 1 year 10% More than 1 year but not more than 2 years 5% Additional Amount Received on Delayed Refunds Section 39,171 In the wake of activating the dormant provisions of law to compensate the taxpayer receiving additional amount on account of delayed refunds, the Bill seeks to tax such amount under the income head of ‘Income from other sources’ so as to charge tax on such compensation. The Bill seeks to replace the fluctuating rate linked with KIBOR for determining the compensation on delayed refunds with the flate rate of 15% per anum. Redundancy in Setting off of Losses in AOP Cases Removed Section 59A By virtue of the Finance Act, 2003, a new section 59A was inserted to provide procedure for set-off of losses in the case of AOPs. Consequent to changes in principles of taxation of AOPs, the redundant references made to the provisions of loss adjustment are sought to be removed so as to bring harmony in the principles of taxation of AOPs. Tax Credit on Investment in Listed Shares and Life Insurance Section 62(2),(3) Tax credit for investment in shares and insurance is worked out using the following formula: (A/B) X C Where A is the amount of tax assessed to the person for the tax year before allowance of any tax credit under Part-X of Chapter III B is the person's taxable income for the tax year and C is the lesser of: a) b) c) Total cost of acquiring the shares or the total contribution or the premium paid by the person 15% of the person's taxable income for the year Rs. 500,000 10 Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 The Bill seeks to enhance the eligible investment amount for tax credit on investment in shares and insurance by the resident persons other than companies in the following manner: Current Proposed 15% of the person's taxable income for the year Rs. 500,000 20% of the person's taxable income for the year Rs. 1,000,000 The Bill seeks to curtail the limit of holding period of shares for reversing the tax credit already availed thereof under the following timeline: Current Proposed Disposal of shares within 36 months of the date of acquisition Disposal of shares within 24 months of the date of acquisition 'Tax Payable' Clarified for Availing of Tax Credit for Investment in BMR Section 65B(1) The Bill seeks to clarify the phraseology of ‘tax payable’ in consonance to availing tax credit on the amount invested for balancing, modernization and replacement (BMR) of plant and machinery shall be allowed as tax credit. The tax payable shall constitue the tax paid under the following regimes: Normal Tax Regime Minimum Tax Regime Final Tax Regime Terminative Date for Availing of Tax Credit for Investment in BMR Extended Section 65B(4) By virtue of Finance Act, 2010 some relief measures for recession stricken industry and a tax credit for BMR costs incurred by corporate sector was provided @ 10% in the tax year of its incurrence. This concession had been made available in-between the Tax Years 2011 to 2015. The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to extend the terminative date of availing the tax credit upto the Tax Year 2016 and the credit amount is also sought to be doubled i.e. at 20% of the tax payable. Tax Credit for Newly Established Industrial Undertakings Section 65D In the wake of dampening industrial crisis in the country the Federal Government, as a relief measure for new investment, introduced tax credit for new industrial undertakings vide Finance Act, 2011 on fulfilling the following pre-requisites: A new corporate taxpayer establishes a new industrial undertaking for manufacturing in Pakistan between the first day of July, 2011 and 30th day of June, 2016 Industrial undertaking is managed by a company registered under the Companies Ordinance, 1984 The industrial undertaking is not formed by the splitting up or reconstruction or reconstitution The industrial undertaking is set up with 100% equity owned by the company The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to include and clarify the following in order to avail the tax credit: Corporate dairy farming is proposed to be treated as an industrial undertaking 100% equity raised through issuance of new shares for cash consideration Short term financing obtained from banking companies for the purposes of meeting working capital requirements shall not disqualify the taxpayer from claiming tax credit under this section Industrial undertaking is proposed to be treated to have been setup on the date on which the industrial undertaking is ready to go into production, whether trial-run production or commercial production 11 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Tax Credit for Equity Investment in Existing Established Industrial Undertakings Section 65E By virtue of Finance Act, 2011 the Federal Government, as a relief measure for an investment, introduced a tax credit for equity investment in existing established industrial undertakings. The amount of the tax credit is equal to 100% of the tax payable and is allowed to such company for new investment made on or after first day of July, 2011, for a period of five years or commencement of commercial production, whichever is later. The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to include and clarify the following in order to avail the tax credit: Corporate dairy farming to be treated as an industrial undertaking 100% equity raised through issuance of new shares Equity investment for expansion project and for a new project 100% tax credit whereby separate books of accounts are maintained for an expansion project or a new project otherwise the tax credit shall be such proportion of the tax payable as is the proportion between the new equity and the total equity including new equity The plant and machinery is installed at any time between July 1st, 2011 and the 30th June, 2016 New equity means the fresh issue of shares and shall not include loans obtained from shareholders or directors Short term financing obtained from banking companies for the purposes of meeting working capital requirements shall not disqualify the taxpayer from claiming tax credit under this section In case of tax credit for equity investment for expansion in Industrial unit, the newly introduced section 65E is meant to provide tax credit on investment by a company with 100% equity investment in BMR, or for expansion of the plant and machinery already installed, in an industrial undertaking set up in Pakistan before July 1, 2011 subject to the fulfillment of laid down conditions. Tax credit shall be allowed on the basis of proportion that such equity investment bears to the total investment in the company. The tax credit shall be allowed if the plant and machinery is purchased and installed at any time between July 1, 2011 and June 30, 2016 and amount of tax credit shall be allowed against the tax payable by the taxpayer in respect of the tax year in which the plant or machinery is purchased and installed and for the subsequent four years. FBR Empowered to Make Rules for Determination of Cost of an Asset and Consideration Received Section 76, 77 The Bill seeks to empower FBR to make rules for determination of cost of any asset and determination of consideration received for any asset. Special Provision Relating to Capital Gain Tax on Disposal of Listed Securities Section 100B The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to insert a special provision relating to Capital Gain Tax, which states that tax on Capital Gains on disposal of listed securities shall be computed, determined, collected and deposited in accordance with the rules laid down in Eighth Schedule. This section shall not apply to the following persons or class of persons, namely: a) b) c) d) e) A mutual fund A banking company, a non-banking finance company, an insurance company A modaraba A “foreign institutional investor” being a person registered with NCCPL as a foreign institutional investor Any other person or class of persons notified by the Board 12 Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Anomaly in Pakistan-Source Dividend Income Removed Section 101B The proposed insertion seeks to include ‘remittance of after tax profit of a branch of a foreign company operating in Pakistan’ as a Pakistan-source income. The Finance Act, 2008 amended the inclusive definition of dividend income to include remittance of after tax profit of a branch of a foreign company operating in Pakistan; however, reference to Pakistan source income was overlooked under the scope of geographical source of income. This anomaly is sought to be removed by elaborating the Pakistan-source dividend as: Dividend paid by a resident company Remittance of after tax profit of a branch of a foreign company operating in Pakistan Phraseology of 'Tax Payable or Paid' for Minimum Tax Applicability Clarified Section 113 The Bill seeks to clarify that tax payable or paid does not include tax already paid or payable in respect of deemed income which comes under the Final Tax Regime in ascertaining the minimum tax liability . In Budget speech, the Finance Minister announced the incentive of reduction in minimum tax rate from 1% to 0.5% but relevant amendments are missing under the provisions of the Finance Bill, 2012 and to that extent needs to be clarified. Profit/Loss for Revised Return Section 114(6)(c) The Bill proposes that the revised return ought to reflect the profit amount or loss amount as determined or ascertained under best judgment assessment, amended order, revision order, provisional assessment, appellate order or rectified order. Limitation Period for Examination of Return Extended Section 120(6) The Finance Bill, 2012 proposes to extend the limitation of examination of return by further 180 days. Presently in case the return of income is not complete, the Commissioner has the powers to serve a notice for furnishing of certain documents uptill the close of the financial year in which the return is furnished. Ex-parte Assessment Effectuated Section 121(1) By virtue of proposed insertion the Bill seeks to elaborate that the ex-parte assessment would have an overriding effect on the deemed assessment on the basis of original return or revised return filed thereof. Amendment of Provisional Assessment Section 122(1)(5A) The proposed insertion seeks to include the provisional assessment in the scope of amendment of assessment. The Bill further seeks to omit the redundant references for amending assessments made under the Repealed Income Tax Ordinance. The Bill also seeks to empower the Commissioner to undertake such enquiries as he deems fit for amending an order. Compliance Requirement for Invalidating of Provisional Assessment for Corporate Taxpayers Explained Section 122C (2) Proviso The Bill proposes to insert a new proviso to envisage the compliance requirement for invalidating the provisional assessment made in the case of corporate taxpayers whereby the return of total income along with audited accounts or final accounts are filed electronically during the time limitation of sixty days. Time Limitation for Tax Demand Stay by Commissioner (Appeals) Prescribed Section 128(1A) The proposed insertion seeks to envisage the powers of the Commissioner (Appeals) against the recovery of tax levied under the Ordinance and period of stay has been provided for 30 days. 13 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Time Limitation for Disposal of the Appeal by Commissioner (Appeals) Withdrawn Section 129(5)(6)(7) The Bill proposes to withdraw the provisions of time limitation of four months for disposal of an appeal by the Commissioner (Appeals) as well as to withdraw the relating conditions laid down for implementation of such time limitation. Appointment of An Accountant Member of ATIR Section 130(4)(ii) The proposed amendment seeks to curtail the minimum experience requirement for appointment of an Accountant Member of Appellate Tribunal Inland Revenue from five years to three years. Eligibility Criterion for Appointment of Chairperson of Inland Revenue Appellate Tribunal Section 130(5) The Bill seeks to remove the compulsive condition of appointment of a judicial member as a chairperson of Inland Revenue Appellate Tribunal. The proposed omission empowers the Government to appoint a chairperson either from accountant members or judicial members. Tax Demand Stay by Appellate Tribunal Section 131(5) The proposed substitution seeks to remove the ambiguous multiple time limitation periods against stay of recovery of tax with a single provision of stay against tax recovery for 180 days in aggregate and in case stay by high court is already granted then the availed time thereof would be excluded from the given time period of 180 days. Option to Commercial Importers, Traders & Exporters For Assessment under Normal Tax Regime Sections 148(7), 153(1)(a), 154(4) and 169 Clauses (41A), (41AA) and (41AAA) of Part IV of the Second Schedule At present, different sectors are operating under the Final Tax Regime (FTR) and finally discharge their tax liabilities under that regime. For example, commercial importers are paying 5% withholding tax; exporters 1%; suppliers 3.5%. Under that system taxes collected or deducted at source are treated as a final tax liability in respect of such amounts. The proposed changes would result in maintenance of books of account to record each and every business transaction which would ultimately promote documentation. In this way, taxpayer will either have to pay higher rate of withholding tax for not maintaining books of accounts or pay lower rate under normal tax regime and file income tax returns. To bring them at par with the taxpayers operating under normal tax regime the right of carry forward of losses and other related provisions will remain applicable if such option is availed. However, in order to opt in the newly introduced scheme the minimum tax liability in respect of such income shall not be less than: 60% of tax collected at the import stage 70% of tax deducted at source on such supplies 50% of the tax collected at the time of realization of export proceeds and indenting commission 14 Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Payments to Non-residents & to PE of Non-residents Sections 152, 153 In an effort to remove the anomalous placement of withholding taxes provisions applicable to nonresidents and to Permanent Establishment (PE) of a nonresident have been rearranged to make the implications of the provisions more clear and unambiguous. The Bill proposes the insertion of a new subsection to rearrange the withholding tax provisions whereby a person making a payment for advertisement services to a nonresident media person relaying from outside Pakistan shall deduct tax from the gross amount paid at the rate of 10%. This was previously covered under section 153A which is now being replaced. The Bill further seeks that deduction of tax from payment of insurance premium or re-insurance premium to a nonresident shall not apply in case of written approval of the Commissioner to the effect that such amount is taxable to a PE of the nonresident in Pakistan. The proposed omission of references in Section 153 regarding payments to a PE of a non-resident on account of sale of goods, rendering of or providing of services or execution of a contract are intended to be placed in Section 152; however, no such corresponding reference has been made to Section 152. Manufacturers Liable to Collect Tax at Source from Traders and Distributors Section 153A Withholding tax on payments for goods, services and contracts is one of the major contributors to the Government Exchequer and over the period of time frequent amendments have been brought in under the relevant provisions of law. Right from the promulgation of the Ordinance numerous amendments have been made to the withholding provisions and in eventuality has resulted into some ambiguities in its application. In an attempt to broaden tax base manufacturers have been given the role of withholding tax agent to collect the required amount of withholding tax at the time of sale to distributors, dealers and wholesalers at the proposed tax rate of 1% of the gross amount of their sales. Taxpayer Card Scheme Introduced Section 181B In an attempt to boost the morale of active taxpayers the proposed insertion of a new section seeks to introduce a 'Taxpayer Honour Card Scheme' to privilege active taxpayers. Voluntarily Penalty Payment Prescribed Section 182(2) The Finance Bill, 2012 proposes to insert a proviso to prescribe that where the taxpayer admits his default he may voluntarily pay the amount of penalty due thereon. Default Surcharge to be Determined on Flat Rate Basis Section 205 The Finance Bill, 2012 proposes to introduce a flat rate of default surcharge at the rate of 18% per annum contrary to the prevailing varying rate that is linked with the KIBOR. The Bill further seeks to provide relief in the amount of default in consequent to appeal orders. Hierarchical Arrangement of Tax Authorities Section 207(3)(3A) The Bill seeks to make all the tax authorities subordinate to FBR. The Bill proposes to arrange hierarchical order of income tax authorities to name the subordinates of Chief Commissioner of Inland Revenue. Condonation of Time Limit Section 214A The Bill seeks to insert an explanation to the provision of condonation of time limit to elaborate the jurisdictional powers of authorities to condone the time limit with respect to powers vested with them. 15 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Functionary of Directorate General (Intelligence and investigation), Inland Revenue Established Section 230 In line with similar functionaries working under the auspices of 'Inland Revenue' under Sales Tax and FED the proposed insertion seeks to induct the DG Intelligence and Investigation authority under hierarchical arrangement as to be notified by the Government. Limit of Cash Withdrawal from a Bank Section 231A Finance Bill 2012 seeks to enhance the daily cash withdrawal limit attracting the deduction of withholding tax from Rs. 25,000 to Rs. 50,000. However, the rate of withholding tax has not been changed. Collection of Tax by a Stock Exchange Section 233A(1)(d) The Bill seeks to restrict the Stock Exchanges registered in Pakistan to act as a withholding agent from collecting advance tax from its members in respect of trading of shares and financing of carryover trades in share business. The restriction to collect advance tax from members on trade of shares has been reinforced in the Finance Bill, 2012 as it was also provided in the Finance (Amendment) Ordinance, 2012. Collection of Tax by NCCPL Section 233AA The Bill seeks to introduce a new section whereby it proposes NCCPL to collect advance tax from the members of stock exchanges registered in Pakistan in respect of margin financing in share business at the rate of 0.01% of value of shares. First Schedule Uniform Rates of Tax for Business Individuals and Association of Persons Part 1 Division 1 Clause 1 The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to revive the older pattern whereby the individuals, other than the salaried class, and AOPs were taxed at the same slab rates. The Finance Bill, 2010 introduced a flat rate of 25% applicable on all AOPs. The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to restore the common slab rates used by both the individuals, other than the salaried class, and the AOPs and revised the rates and slabs as under: Current Rates of Tax for Individuals Applicable on Taxable income Taxable income not exceeding Rs. 350,000 Proposed Rates of Tax for Individuals and AOPs Applicable on Taxable income 0% Taxable income not exceeding Rs. 400,000 0% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 350,000 but not exceeding Rs. 500,000 7.5% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 400,000 but not exceeding Rs. 750,000 10% of the amount exceeding Rs. 400,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 500,000 but not exceeding Rs. 750,000 10% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 750,000 but not exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 Rs. 35,000 + 15% of the amount exceeding Rs. 750,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 750,000 but not exceeding Rs. 1,000,000 15% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 but not exceeding Rs. 2,500,000 Rs. 147,500 + 20% of the amount exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 1,000,000 but not exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 20% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 2,500,000 Rs. 347,500 + 25% of the amount exceeding Rs. 2,500,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 25% 16 Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Rates of Tax for Salaried Taxpayers Part 1 Division 1 Clause 1A The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to reduce the slab rates applicable on salaried individuals. Existing 17 slabs are proposed to be reduced to 5 as under: Current Rates of Tax for Salaried Taxpayers Proposed Rates of Tax for Salaried Taxpayers Applicable on Taxable income Applicable on Taxable income Taxable income not exceeding Rs. 350,000 0% Taxable income not exceeding Rs. 400,000 0% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 350,000 but not exceeding Rs. 400,000 1.50% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 400,000 but not exceeding Rs. 750,000 5% of the amount exceeding Rs. 400,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 400,000 but not exceeding Rs. 450,000 2.50% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 750,000 but not exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 Rs. 17,500 + 10% of the amount exceeding Rs. 750,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 450,000 but not exceeding Rs. 550,000 3.50% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 but not exceeding Rs. 2,500,000 Rs. 92,500 + 15% of the amount exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 550,000 but not exceeding Rs. 650,000 4.50% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 2,500,000 Rs. 242,500 + 20% of the amount exceeding Rs. 2,500,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 650,000 but not exceeding Rs. 750,000 6.00% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 750,000 but not exceeding Rs. 900,000 7.50% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 900,000 but not exceeding Rs. 1,050,000 9.00% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 1,050,000 but not exceeding Rs. 1,200,000 10.00% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 1,200,000 but not exceeding Rs. 1,450,000 11.00% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 1,450,000 but not exceeding Rs. 1,700,000 12.50% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 1,700,000 but not exceeding Rs. 1,950,000 14.00% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 1,950,000 but not exceeding Rs. 2,250,000 15.00% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 2,250,000 but not exceeding Rs. 2,850,000 16.00% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 2,850,000 but not exceeding Rs. 3,550,000 17.50% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 3,550,000 but not exceeding Rs. 4,550,000 18.50% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 4,550,000 20% 17 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Taxability of Salary Income Sr. No 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Average Tax Rate Tax Liability for the Tax Year 2012 Taxable Salary Pre-Budget Post-Budget Increase / (Decrease) Pre-Budget Post-Budget Rs. Rs. Rs. Rs. % % 350,000 400,000 450,000 550,000 650,000 750,000 900,000 1,050,000 1,200,000 1,450,000 1,700,000 1,950,000 2,250,000 2,850,000 3,550,000 4,550,000 5,551,000 0 6,000 11,250 19,250 29,250 45,000 67,500 94,500 120,000 159,500 212,500 273,000 337,500 456,000 621,250 841,750 1,110,200 0 0 2,500 7,500 12,500 17,500 32,500 47,500 62,500 87,500 122,500 160,000 205,000 312,500 452,500 652,500 852,700 0 (6,000) (8,750) (11,750) (16,750) (27,500) (35,000) (47,000) (57,500) (72,000) (90,000) (113,000) (132,500) (143,500) (168,750) (189,250) (257,500) 0% 1.5000% 2.5000% 3.5000% 4.5000% 6.0000% 7.5000% 9.0000% 10.0000% 11.0000% 12.5000% 14.0000% 15.0000% 16.0000% 17.5000% 18.5000% 20.0000% 0% 0% 0.5556% 1.3636% 1.9231% 2.3333% 3.6111% 4.5238% 5.2083% 6.0345% 7.2059% 8.2051% 9.1111% 10.9649% 12.7465% 14.3407% 15.3612% Tax liability has been worked out without taking into account the marginal tax relief. Graphical Representaion 1,200,000 1,000,000 800,000 600,000 400,000 200,000 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 18 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Rate of Tax on Retailers Part 1 Division 1A The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to reduce tax rate applicable on retailers, both individuals and AOPs, having turnover of upto Rs. 5 million in a tax year from 1% to 0.50%. Rate of Tax Applicable on Capital Gains on Disposal of Securities Part 1 Division VII The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to make editorial changes to enhance clarity and seeks to freeze the tax rates for Tax Years 2011 to 2014 that have already been introduced by the Finance (Amendment) Ordinance, 2012. Tax rates proposed by the Finance Bill are as under: Period for which Securities are Held Tax Year Existing Rates Proposed Rates Less than 6 months 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 10% 10% 12.5% 15% 17.5% 10% 10% 10% 10% 17.5% More than 6 months but less than 12 months 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 7.5% 8% 8.5% 9% 9.5% 10% 7.5% 8% 8% 8% 9.5% 10% Rate of Tax on Capital Gains on Disposal of Immovable Property Part 1 Division VIII The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to charge tax on capital gains in respect of disposal of immovable properties on the following rates: Period for which Immovable Property is Held Up to 1 year More than 1 year but less than 2 years Rate of Tax 10% 5% Collection of Tax from Distributors, Dealers and Wholesalers Part IIA The Finance Bill seeks to collect tax from distributors, dealers and wholesalers at 1% of the gross amount of their sales. Part IV Tax on Motor Vehicles Division III & Division VII The Bill seeks to enhance tax rates on motor vehicles as under: For goods transport vehicle, tax is proposed to be increased from Re. 1 to Rs. 5 per kilogram of the laden weight; For passenger transport vehicles plying for hire with registered seating capacity of 20 persons or more, the tax is proposed to be increased from Rs. 100 per seat per annum to Rs. 500 per seat per annum; and Advance tax levied at the time of registration of a new 1301cc to 1600cc locally manufactured motor vehicle is proposed to be enhanced from Rs. 16,875 to Rs. 25,000. 19 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Second Schedule Exemptions & Tax Concessions The Second Schedule relates to specific exemptions granted in respect of total income; reduction in tax rates; reduction in tax liability and exemption from specific provisions. The Bill proposes to exempt or extend the scope of exemptions in respect of the following sources of income: Part I Exemptions from Total Income Amounts Received from Income Payment Plan out of Accumulated Balance of Pension Accounts Clause 23B & 23C The Bill seeks to exempt from tax the amounts received as monthly installment from income payment plan invested out of the accumulated balance of an individual pension account with a pension fund manager or an approved annuity plan etc. as specified in Voluntary Pension System Rules, 2005, provided the accumulated balance is invested for 10 years. It also seeks to exempt the withdrawal of accumulated balance from approved pension fund that represents the transfer of balance of approved provident fund to the said approved pension fund under the Voluntary Pension System Rules, 2005. Donations to Specified Institutions Clause 61(ia) & Clause 66(xxvii) The Bill seeks to extend the exemption on donation paid to The Citizen Foundation as a straight deduction from taxable income . Any income derived by The Citizen Foundation shalll also be exempt. Profits and Gains Derived by a Venture Capital Company & Venture Capital fund Clause 101 The Bill seeks to extend the exemption to profits and gains derived by a venture capital company and venture capital fund registered under the Venture Capital Companies and Funds Management Rules, 2000 beyond 2014. It proposes to extend this exemption by further 10 years upto June 30, 2024. Part II Reduction in Tax Rates Advance Tax from Importers Clause 9A The Bills seeks to correlate the collection of 3% tax from importers only on production of exemption certificate issued by the Commissioner. Part IV Exemptions from Specific Provisions Exemption from Deduction of Tax on Paying Dividends and Profit on Debt Clause 11B & 11C The Bill seeks to introduce new clauses whereby the payment of inter-corporate dividends and inter-corporate profit on debts would not attract the deduction of tax in the hands of company making such payment provided the group companies are subject to group taxation under Section 59AA and 59B of the Income Tax Ordinance, 2001. 20 Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Capital Gains Tax on Disposal of Certain Securities Withdrawn Clause 47B The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to extend the exemption from application of capital gains tax on disposal of securities to National Investment Unit Trust, Collective Investment Scheme, Modaraba, REIT Scheme, Private Equity and Venture Capital Fund, recognized provident fund, approved superannuation fund or approved gratuity fund. Applicability of Advance Tax on Electricity Bill of a Commercial / Industrial Consumer Clause 76 The Bill seeks to withdraw exemption available to manufacturer-cum-exporter industrial undertakings situated in Karachi Export Processing Zone from the collection of advance tax on electricity bills. Third Schedule Initial Allowance and First Year Allowance Part II The Finance Bill seeks to reduce the initial allowance for buildings from 50% to 25%. Fourth Schedule Mutual Insurance Companies Rule 6B The Bill seeks to reduce the rates of tax applicable on capital gains on disposal of shares of listed companies, vouchers of Pakistan Telecommunication Corporation, Modaraba Certificates or instruments of redeemable capital and derivative products by mutual insurance associations as under: Period for which Securities are Held Tax Year Existing Rates Proposed Rates Less than 6 months 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 10.0% 12.5% 15.0% 17.5% 17.5% 10.0% 10.0% 12.5% 15.0% 17.5% More than 6 months but less than 12 months 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 8.0% 8.5% 9.0% 9.5% 10.0% 8.0% 8.0% 8.5% 9.0% 9.0% Fifth Schedule Mechanism for Computation of Tax on Profits and Gains Petroleum Exploration and Production Companies Rule 4A The Bill seeks to introduce a new rule whereby petroleum exploration and production companies may opt to pay tax at the rate of 40% of their profit and gains net of royalty derived by them. However, they may opt to do so upon withdrawing pending appeals, references and petitions filed by them and paying the entire outstanding tax liability created under the Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 upto the tax year 2011 by June 30, 2012. It is pertinent to mention that the Bill proposes that this option is available for one time only and would be irrevocable. 21 Income Tax Ordinance, 2001 Seventh Schedule Rules for the Computation of the Profits and Gains of a Banking Company and Tax Payable Thereon Dividends Received from Money Market Funds and Income Funds Rule 6 The Bill seeks to enhance the tax rates on dividends received from money market funds and income funds to 25% for the Tax Year 2013. The tax rate is proposed to be raised further to 35% in the Tax Year 2014 for the ongoing period. Eighth Schedule Rules for the Computation of Capital Gains on Listed Securities The Bill seeks to introduce Eighth Schedule dealing with the rules for the computation of capital gains on listed securities. This Schedule proposes the structural and procedural details that would be followed by NCCPL in calculating capital gains and issuing certificate to taxpayers in respect of their capital gains subject to tax. Manner and basis of computation of capital gains and tax thereon: NCCPL shall issue an annual certificate to the taxpayer on the prescribed form in respect of capital gains subject to tax for a financial year. However, on request of a taxpayer or if required by the Commissioner, NCCPL shall issue a certificate for a shorter period within a financial year. Above mentioned certificate shall be filed along-with the return of income. NCCPL shall furnish to the Board within 30 days of end of each quarter, a statement of capital gains and tax computed thereon in that quarter. Capital Gains computed under this Schedule shall be charged to tax at the rate applicable in Division VII of Part I of First Schedule. Enquiries as to source of Investment shall not be made: If a person has made investment in listed securities prior to introduction of this Ordinance and the amount remains invested for a period of 45 days upto June 30, 2012 and he has filed a statement of investment with the Commissioner along with a Return of Income and wealth Statement for the Tax Year 2012. If a person has made investment in listed securities from the date of coming into force of this Ordinance till 30th June, 2014 and the amount remains invested for a period of 120 days and the tax on capital gains has been duly discharged and he has filed a statement of investment with the Commissioner alongwith a Return of Income and wealth Statement for the Tax Year 2012. Rates for CGT for the Tax Years 2013 and 2014 Division VII Part I First Schedule The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to freeze the rate of tax for two years. Proposed rate of tax shall be as follows: Holding Period Tax Year Present Rate Proposed Rate Less than six months 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 10% 10% 12.5% 15% 17.5% 10% 10% 10% 10% 17.5% More than six months but less than twelve months 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 7.5% 8% 8.5% 9% 9.5% 10% 0% 7.5% 8% 8% 8% 9.5% 10% 0% Twelve months or more 22 Tax Handbook 2012 Sales Tax Act, 1990 Sales Tax Act, 1990 Assessment of Tax and Recovery of Short Levied or Erroneously Refunded Tax Section 11 and Section 36 In view of concurrence in procedural application of Section 11 and Section 36, the proposed amendment seeks to merge these provisions under Section 11 and seeks to omit Section 36. The new placement of these provisions of law would harmonize the procedure for assessment of Sales Tax and streamline the provisions of law. The proposed amendment further aims at the following changes: Time limit for issuance of show cause notice, in case of tax not levied or short levied or refunded due to any inadvertence, error or misconstruction, has been enhanced from three years to five years from relevant date. Officer of Inland Revenue is proposed to make his decision in 120 days from the date of issuance of show cause notice; however, this period can be further extended by 90 days and the maximum period which can be excluded from the time period mentioned earlier, due to adjournment or stay, has also been extended by 60 days. Uniformity in Standard Sales Tax Rate of 16% S.R.O. 594(1)/2012 seeks to rescind S.R.O. 644 (I)/2007 S.R.O. 644 (I)/2007 whereby items which were charged at 19.5% and 22% would be charged at a uniform rate of 16%. Sixth Schedule (Table 1) Implementation of Revised HS Code - 2012 The Bill proposes to implement revised HS code - 2012 of the World Customs Organization (WCO) by substituting 18 PCT headings in column 3 of Table 1 of Sixth Schedule with 23 new PCT headings. HS codes are revised in view of technological and trade developments after every five years. These changes are of technical nature and will have no effect on rates to be applied and procedures to be followed. Zero Rating Category Substitution with Exemption Category Fifth Schedule & Sixth Schedule (Table 2) The Bill proposes to substitute zero rating on supplies made against international tenders with exempt supplies by omitting it from Fifth Schedule and including it in Table 2 of Sixth Schedule. Withdrawal of Exemption for Cotton Seed Oil Sixth Schedule (Table 2) The Bill proposes to withdraw exemption on cotton seed oil. 23 Sales Tax Act, 1990 Notable Notification S.R.O. 589(I)/2012 This S.R.O. seeks to make amendments, additions or substitution in Sales Tax Rules 2006. A brief summary of significant proposed amendments, additions or substitution is as under: Rule Ref. Description of proposed amendments, additions or substitution Rule 5, sub rule(1), clause C It proposes to authorize the FBR to transfer the registration of a registered person or any business of a registered person to an area of jurisdiction where the place of business or registered office or manufacturing unit is located. Rule 7, sub rule(3) A new sub rule (4) is introduced which states that change of nature of business from individual to AOP or corporate person shall be allowed when: Transfer of individual business from any person to his spouses or children or change in nature of business from individual to AOP Change of nature of business from AOP to corporate entity provided directors in the corporate entity are the same persons who were members of AOP For both cases mentioned above change shall be allowed by LRO after receiving verified documents from RTO. Whereby transfer of business or change in nature of business is due to any other reason, a new Sales Tax Registration Number shall be issued. Rule 12 Sub rules (1), (2), (3), (4) and (5) are substituted resultantly giving powers to Commissioner or Board, instead of Collector, to suspend the registration or black list a person if they have reasons to do so. Rule 50B Rule 50B has been substituted which describes the procedure to be followed to avail the exemption facility for supply of locally produced goods against international tender. Procedure is same as was for availing zero rated facility, under rescinded rule, with one exception that the facility of exemption has been restricted to goods which become part of project to be completed or goods to be supplied. Rule 50C It is substituted with new rule to replace "zero rated" with "exempt". This change has been made with an aim to hold illegal refunds. S.R.O. 590(I)/2012 The S.R.O. seeks to remove requirement for commercial importers of computer hardware and parts to pay minimum value addition Tax @ 10%. S.R.O. 591(I)/2012 Through amendments made by this S.R.O. import and supply of polyethylene and polypropylene by registered manufacturer for manufacture of mono filament yarn and who makes exempt supplies of net cloth to green house farming shall be exempt, earlier they were zero rated. 24 Tax Handbook 2012 Sales Tax Act, 1990 S.R.O. 592(I)/2012 This S.R.O. seeks to make following changes in Sales Tax Special Procedure Rules 2007: Sub rule(2) of rule 58E is omitted which would result in importers who do not claim any refund of excess input tax also being subject to audit. Rules of Chapter XI has been substituted with new rules, in new rules Sales Tax rates has been revised with a view to increase revenue, detail of such revision is as below: Rule Ref. Sales Tax Payable By Existing Sales Tax Rate Proposed Sales Tax Rate 58 H Every steel-melter, steel re-roller and composite unit of aforesaid (having single electricity meter) Rs. 6 per unit of electricity consumed. Rs. 8 per unit of electricity consumed. 58 H (4) Ship breakers Rs. 848 per metric ton. Rs. 6,700 per metric ton. 58 Ha (2) Steel melters (generating electricity using gas generators) Rs. 1,972 per hundred cubic meter or HM3 Rs. 1,900 per hundred cubic meter or HM3 58 Ha (2) Re-rolling mills (self generated electricity) Rs. 38,964 per inch of mill size Rs. 51,822 per inch of mill size 58 I (1) Re-roller Rs. 5,526 per metric ton Rs. 7,349 per metric ton 58 I (2) Registered person Rs. 5,960 per metric ton Rs. 8,387 per metric ton 58 I (3) Downstream Industry Rs. 6,306 per metric ton Rs. 9,651 per metric ton 58 I (4) Registered Person Rs. 5,628 per metric ton Rs. 7,740 per metric ton 58 I (5) Un-registered buyer Rs. 780 per metric ton Rs. 1040 per metric ton Registered person Rs. 7,308 per metric ton (registered person) Rs. 780 per metric ton (other than registered person) Rs. 9,651 per metric ton (registered person) Rs. 1,040 per metric ton (other than registered person) 58 I (6) Un-registered person A new rule 58MC has been inserted which states that steel melters and re-rollers who also supply stainless steel products other than billets, ingots and re-rolled MS products shall follow standard Sales Tax procedures and fixed taxes under this chapter shall not be applicable to them. S.R.O. 595(I)/2012 This S.R.O. seeks to make following amendments in S.R.O. 551(1)/2008: Raw material, component and subcomponents imported for using the in manufacture of goods to be supplied against international tenders are removed from list of exempted goods. Waste paper, re-meltable scrap, sprinkler equipment, drip equipment and spray pumps including supplies thereof have been exempted from the ambit of Sales Tax. 25 Sales Tax Act, 1990 Revision in Sales Tax Rates Following new S.R.Os are introduced which seek to amend the old rates as given below: S.R.O Description Previous Rate/Amount Proposed Rate/Amount 604(I)/2012 Import of soya bean as mentioned in S.R.O 313(I)/2006 7% 6% 608(I)/2012 Import and supplies of black tea 16% 5% 605(I)/2012 Import of rapeseed and sunflower seed 15% 14% 597(I)/2012 Billets and Ingots Rs. 55,000 & Rs. 60,000 respectively Rs. 65,000 & Rs. 60,000 respectively (This has also been set at minimum value) 602(I)/2012 Re-meltable scrap, sprinkler, drip equipment cotton seed oil 0% Exempt Exempt 0% 26 Tax Handbook 2012 Federal Excise Act, 2005 Federal Excise Act, 2005 First Schedule (Table I) Federal Excise Duty on Excisable Goods Revised The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to revise rates of FED for certain excisable goods aligned with given pricing threshold as under: Relevant Reference in Schedule Description of Goods Headings/SubPresent Rates headings Number Proposed Rates 9 Locally produced cigarettes if their retail price exceeds Rs. 22.86 per ten cigarettes. 24.02 65% of retail price (if retail price exceeds Rs. 21 per 10 Cigarettes) 65% of retail price (if retail price exceeds Rs. 22.86 per 10 Cigarettes) 10 Locally produced cigarettes if their retail price exceeds Rs. 13.36 per ten cigarettes but does not exceeds Rs. 22.86 per ten cigarettes. 24.02 Rs. 6.04 per 10 cigarettes + 70% per incremental rupee or part thereof (if retail price exceed Rs. 11.50 but does not exceed Rs. 21 per 10 Cigarettes) Rs. 7.02 per 10 cigarettes + 70% per incremental rupee or part thereof. 11 Locally produced cigarettes if their retail price does not exceed Rs. 13.36 per ten cigarettes. 24.02 Rs. 6.04 per 10 cigarettes (if retail price does not exceed Rs. 11.50 per 10 Cigarettes) Rs. 7.02 per 10 cigarettes 13 Portland cement, aluminous cement, slag cement, super sulphate cement and similar hydraulic cements, whether or not coloured or in the form of clinkers. 25.23 Rs. 500 per Metric ton Rs. 400 per Metric ton First Schedule (Table I) Federal Excise Duty on Excisable Goods Withdrawn The Finance Bill, seeks to withdraw the FED charged on the following items: Relevant Reference in Schedule Description of Goods Headings/Subheadings Number Present Rates Proposed Rates 22 Lubricating oil in packs not exceeding 10 liters. 2710.1951 10% per Liter Nil 23 Lubricating oil in packs exceeding 10 liters. 2710.1952 10% per Litre Nil 24 Lubricating oil in bulk (vessels, bouzerslorries etc). 2710.1953 Rs. 7.15 per Liter Nil 25 Lubricating oil manufactured from reclaimed oils or sludge or sediment, subject to the condition if sold in retail packing or under brand names the words manufactured from reclaimed oil or sludge or sediment should be clearly printed on the pack. Respective headings Rs. 2 per Liter Nil 27 Federal Excise Act, 2005 Relevant Reference in Schedule Description of Goods Headings/Subheadings Number Present Rates Proposed Rates 27 Base lube oil 2710.1993 Rs. 7.15 per Liter Nil 42 Perfumes and toilet waters. 3303.0000 10% of retail price if packed in retail packing and 10% ad valorem if in bulk Nil 43 Beauty or make-up preparations and preparations for the care of the skin (other than medicaments), including sunscreen or sun tan preparations; manicure or pedicure preparations 33.04 10% of retail price if packed in retail packing and 10% ad valorem if in bulk Nil 44 Preparation for use on the hair excluding herbal hair oil and kali mehndi. 33.05 10% of retail price if packed in retail packing and 10% ad valorem if in bulk Nil 45 Pre-shave, shaving or after shave preparations, personal deodorants, bath preparations, depilatories and other perfumery, cosmetic or toilet preparations, not elsewhere specified or included; prepared room deodorizers, whether or not perfumed or having disinfectant properties (excluding agarbatti and other odoriferous preparations which operate by burning). 33.07 10% of retail price if packed in retail packing and 10% ad valorem if in bulk Nil 50 Filter rods for cigarettes 20% ad val. Nil 5502.0090 Pricing Mechanism for Cigarettes Rationalized The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to insert new conditions regarding variant of the existing brand of cigarettes, in order to avoid FED evasion. The Bill seeks to restrict the manufacturer or importer of cigarette to introduce or sell new cigarette brand variant of the existing brand family at a price lower than the price of the existing variant cigarettes after the announcement of 2012-13 Budget. The Bill also seeks to introduce a provision by virtue of which, a new brand of cigarette could not be sold at a price which is more than 5% lower, than the price of a Most Popular Price Category (MPPC). 28 Tax Handbook 2012 Federal Excise Act, 2005 FED Increased on Air Tickets First Schedule (Table II) The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to revise the FED on international air travel as enumerated below: Relevant Reference in Schedule Headings/Subheadings Number Description 3(a) Services provided or rendered in respect of travel by air of the passenger within the territorial jurisdiction of Pakistan. 9803.1000 3(b) Services provided or rendered in respect of travel by air of the passenger embarking on international journey from Pakistan 9803.1100 (i) Economy and economy plus (ii) Club, business and first class Present Rates Proposed Rate of FED 16% of the charges plus rupees twenty per ticket 16% of the charges plus rupees sixty per ticket Rs. 3,240 for Economy and economy plus and four thousand two hundred and forty rupees for club, business and first classes, for passengers embarking from SAARC region, UAE (Middle East), Saudi Arabia, Africa, Afghanistan. Rs. 3,840 Rs. 4,240 for economy and economy plus classes and five thousand seven hundred and forty rupees for club, business and first classes. Rs. 6,840 Exemption Granted on Services Relating to Livestock Insurance and Asset Management Companies The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to amend the Table-II in third schedule to grant exemptions on services in respect of livestock insurance and asset management companies Relevant Reference in Schedule Description of Services Headings/Sub-headings Number 7 Livestock insurance 9813.1600 8 Services provided by Asset Management Companies with effect from 1st of July, 2007. Respective Headings 29 Federal Excise Act, 2005 Notable Notifications: Withdrawal of FED Exemption S.R.O. 599(I) / 2012 This S.R.O. seeks to amend Table in S.R.O. 474(I) / 2009, dated June 13, 2009 to withdraw exemptions in respect of following: Relevant Reference in Schedule Description of Goods Headings/Sub-headings Number Restored Rate of Duty 48 Viscose staple fibre Respective Headings 10% ad val. FED on Air Tickets Rationalized S.R.O. 600(I) / 2012 This S.R.O. proposes to amend Rule 41A of Federal Excise Rules 2005 by withdrawing excise duty on services provided by aircraft operators in respect of travel by air of passengers embarking for Pakistan from anywhere in the world. By virtue of this S.R.O. excise duty chargeable on all international air tickets issued by airlines or through their agents for international journey terminating in Pakistan has been withdrawn. This S.R.O. proposed to substitute existing sub-rule (7) with a new rule as follow: Existing sub-rule(7) Proposed sub-rule(7) An air ticket issued for international travel covering more than one destination on flights operated by one or more airlines shall be chargeable to excise duty by the airline issuing the ticket and shall be charged at the rate of excise duty applicable for the farther destination in terms of distance from Pakistan. Where an airline operating in Pakistan uplifts passengers from Pakistan for another airline, the liability to charge, collect and pay Federal Excise Duty with respect to such passengers, shall be of the uplifting airline. As excise duty on international travel to Pakistan has proposed to be withdrawn, so such excise duty will not be called as Air Travel Tax (ATT). S.R.O. 603(I) / 2012 This S.R.O rescinds 6 notifications already issued by Federal Government of Pakistan. A brief summary of the S.R.Os rescinded, matters discussed in them and the effect of rescission thereof is given hereunder: Rescinded S.R.O Subject Matter of the S.R.O Effect of Rescission S.R.O. 807(I)/2005 Rebate given of Federal Excise Duty, paid on base oil used in the manufacture of the motor lubricating oil for different automobiles Rebate withdrawn S.R.O. 671(I)/2006 Fixing the minimum price of lubricating oil in packs at US$ 2 per litre for the purpose of assessment of excise duty at import stage (PCT headings 2710.1951 and 2710.1952) Price determination as per normal procedure S.R.O. 777(I)/2006 Rates of excise duty chargeable on the tickets issued for the services of travel by air on international journey originating from Pakistan to SAARC countries, Middle East, Saudi Arabia, Afghanistan, Europe, Far East, China, USA, Canada, Australia and South America Rates withdrawn S.R.O. 949(I)/2006 Exempting the import and supply of solvent oil (PCT heading 2710.1150) for manufacture of shoe adhesives subject to certain conditions Exemption withdrawn S.R.O. 1229(I)/2007 Exempting special Excise Duty levied on the tractor parts by registered vendors to the manufacturers of agricultural tractors Exemption withdrawn S.R.O 47(I)/2012 Levying FED on facilities for travel services at specified rates Rates withdrawn 30 Tax Handbook 2012 Customs Act, 1969 Customs Act, 1969 Definition of 'Smuggle' Broadened Section 2 (s) The Finance Bill, 2012 proposes to insert “en route pilferage of transit goods” in definition of 'smuggle' in an effort to curb en route pilferage for evading duties. Additional Functionary Directorates Established Section 3AA, 3BB, 3BBB, 3CC The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to introduce new additional functionary directorates for the purposes of jurisdictional administrative division evident from the assigned nomenclature. The new proposed directorates are: Directorate General of Transit Trade Directorate General of Reform and Automation Directorate General of Risk Management Directorate General of Intellectual Property Rights Enforcement Board Empowered to Change Pakistan Customs Tariff Coding Section 18E The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to authorize the Board to make changes in the Pakistan Customs Tariff, specified in the First Schedule to the Customs Act, 1969 merely for the purposes of aligning statistical suffix of the Pakistan Customs Tariff (PCT) codes with World Customs Organization (WCO). Punishment for Certain Offences Altered Section 156(1) The Finance Bill, 2012 proposes the following amendments in provisions for punishment for following offences: Punishment Serial No. Applicable to The punishment, of whipping under this section, to be totally eliminated. Serial No. 8(i), 89(i) and 92 of Section 156(1) General The punishment, for transferring certain classes of goods subject to prescribed conditions and transit of goods across Pakistan to a foreign territory, to be enhanced by including imprisonment for a term of up to 5 years. Serial No. 64 of Section 156(1) Section 128 & Section 129 Prosecution to those instances where attempts are made to make unauthorized access or to interfere with Custom Computerized System or to make unauthorized use of unique user identifier by any person, be enhanced. Serial No. 101, 102 and 103 of Section 156(1) Sections 155I, 155J and 155K 31 Customs Act, 1969 Adjudicating Jurisdiction and Powers of the Officers Changed Section 179(1) The Finance Bill, 2012 proposes revision in the jurisdiction and powers of the officers of Customs in terms of amount of duties and other taxes involved thereby. S. No. Adjudicating Authority Existing Limit Proposed Limit (i) Collector - without limit (ii) Additional Collector without limit not exceeding Rs. 3,000,000 (iii) Deputy Collector not exceeding Rs. 800,000 not exceeding Rs. 1,000,000 (iv) Assistant Collector not exceeding Rs. 300,000 not exceeding Rs. 500,000 (v) Superintendent - not exceeding Rs. 50,000 (vi) Principal Appraiser - not exceeding Rs. 50,000 Departmental Appeals Allowed before Collector (Appeals) & Appellate Tribunal Section 193(1), 194 A The Finance Bill, 2012 proposes that officer of Customs aggrieved by any decision or order passed by officer of Customs below the rank of Additional Collector may also prefer an appeal to Collector (Appeals) within thirty days of the date of communication to him of such decision or order. The Finance Bill, 2012 proposes that any person or officer of Customs may prefer to file an appeal to the Appellate Tribunal against any order passed by any officer of Customs not below the rank of Additional Collector under section 179. Electronic Auction for Sale of Goods Allowed Section 201 In the wake of growing trend of e-trading, the Bill proposes to allow the mode of disposal of goods through electronic auctions. Rewards for Meritorious Conduct Section 202 B The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to introduce the system of award for those officers and informers who render meritorious conduct in cases involving evasion of Custom duty and taxes and confiscation of goods after the realization of whole or part of duty and taxes involved. The procedure of such reward is proposed to be introduced by the Board by notification in the Official Gazette. Condonation of Time Limit Section 224 The Finance Bill, 2012 proposes to authorize the authorities to condone the time limit in complying with the procedural requirement whereby the delay is beyond the control of the concerned person. 32 Tax Handbook 2012 Customs Act, 1969 Notable Notifications Rates of Duty Reduced on Certain Items S.R.O. 574(I)/2012 This S.R.O. seeks to amend Table-I of S.R.O. 567(I)/2006, dated June 5, 2006. By virtue of this S.R.O. Custom duty on following items shall be levied at reduced rate specified hereunder against each item. S. No. PCT Code 23A 4004.0020 44A 3215.1190 3215.1990 3701.3020 4802.5700 9612.1010 3215.1990 Description Present Rate Proposed Rate Condition Shredded tyre scrap 20% 10% If imported by cement manufacturers Black ink Colour ink CTP plates Fully sensitized cheque paper weighing 40 g/m2 or more but not more than 150 g/m2 Red bleed through ribbons for dot matrix printers Anti-forgery security printing ink 20% 20% 10% 20% 10% 10% 5% 10% If imported by Printing Industry 20% 10% 20% 10% The notification also seeks to restrict the concession of Customs duty at 0% only to ambulances having following features: Rear panel and rear step Stretcher of 8 feet length in case of hiace type vehicles and 6 feet in case of mini-van type vehicles Folding seats for 2-4 persons Oxygen supply system with cylinder Rotary lamp and siren Fire extinguisher Hooks for intravenous infusion giving sets / bottles Small cabinet for medicines Nebulizer, room light, examination light, wiring switch sockets 12Volt Water resistant floor Suction unit Suspension system of base vehicle to be spring and shock absorber type and not exclusively of leaf spring type Permanent markings as ambulance on the front and rear of the vehicle The S.R.O. further seeks to amend Table-III of S.R.O. 567(I) / 2006 dated June 5, 2006 by reducing the rate of Customs duty from 10% to 5% on 87 pharmaceuticals ingredients. 33 Customs Act, 1969 Exemption on Certain Items Withdrawn S.R.O. 577(I)/2012 This S.R.O. seeks to amend S.R.O. 482(I) / 2009, dated June 13, 2009 by substituting certain items in the table for levy of regulatory duty on import of goods. S. No. Proposed Rate of Regulatory Duty Betel Nuts Areca nuts (Betel nuts) 10% ad valorem Smoking tobacco, whether or not containing tobacco substitutes in any proportion Water pipe tobacco specified in Subheading Note 1 of Chapter 24 of the First Schedule to the Customs Act, 1969 15% ad valorem Other (Newly Inserted) 15% ad valorem PCT Code Existing 1 0802.8000 6 2403.1100 6A 2403.1900 Description Notification under Free Trade Agreements Rearranged S. No. Revising SRO (New) SRO Revised Description 1 S.R.O. 582(I)/2012 S.R.O. 659(I)/2007 Substituted Table-I and Table-II in respect of certain items imported into Pakistan from Peoples Republic of China under Free Trade Agreement (FTA) 2 S.R.O. 583(I)/2012 S.R.O. 1261(I)/2007 Substituted Table-I and Table-II in respect of certain items imported into Pakistan from Malaysia under Free Trade Agreement (FTA) 3 S.R.O. 584(I)/2012 S.R.O. 1296(I)/2005 Substituted Table-I and Table-II in respect of certain items imported into Pakistan from Peoples Republic of China under Free Trade Agreement (FTA) 4 S.R.O. 585(I)/2012 S.R.O. 558(I)/2004 Substituted Table-I and Table-II in respect of certain items produced in and imported from Islamic Republic of Iran or the Republic of Turkey and SAARC countries imported into Pakistan under Free Trade Agreement (FTA) 5 S.R.O. 586(I)/2012 S.R.O. 570(I)/2005 Substituted Table-I and Table-III and Table-IV in respect of certain items imported into Pakistan from Sri Lanka under Free Trade Agreement (FTA) DTRE Scheme Rationalized S.R.O.601(I)/2012 This S.R.O. seeks to amend rule No. 297 and 305 of Custom Rules, 2001 by attaching condition that DTRE facility shall be available to persons who manufacture and export goods in accordance with the prevalent value-addition of the relevant industry, only if the value addition is not less than 15%, and goods imported shall be utilized within twelve months, instead of twenty four months from the date of approval of DTRE application. 34 Tax Handbook 2012 Miscellaneous Laws Capital Value Tax (CVT) Exemption of CVT on Shares of Public Listed Company Section 7(1) The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to reinforce the amendments introduced in the Finance (Amendment) Ordinance, 2012, by virtue of which a person shall not be liable to pay CVT on the capital value of shares of public listed company acquired by him. Further, Cantonment Board and the rating areas as defined under the Urban Immovable Property Act, 1985 are proposed to be excluded from the definition of 'urban area' under CVT law. Revision in rates of CVT on Residential Flats of any Size and Commercial Immovable Property Situated in Urban Areas Section 7(2) The Bill proposes to apply CVT on following rates on the above-cited properties. Category S.No Residential flats Commercial immovable property Description of Property Rate of CVT 1 Where the value of immovable property is recorded 2% of recorded value or value as per DC rate Whichever is higher 1a Where the value of immovable property is not recorded Rs. 100 per square feet of the covered areas of the immovable property or value as per DC rate Whichever is higher 2 Where the value of immovable property is recorded 2% of recorded value of the landed area or value as per DC rate Whichever is higher 2a Where the value of immovable property is not recorded Rs. 100 per square feet of the landed area or value as per DC rate Whichever is higher 2b Where the immovable property is a constructed property Rs. 10 per square feet of the constructed area in addition to the value worked out above Whichever is higher 35 Miscellaneous Laws Gas Infrastructure Development Cess Act, 2011 The Second Schedule Increase in Rates of Cess Section 3(1) The Finance Bill, 2012 seeks to increase the maximum rate of cess as follows: S.No Sector 1 Fertilizer - Feed Stock (except for fertilizer plants having fixed price contracts) 2 Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) (a) Region - I Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Baluchistan & Potohar Region (Rawalpindi, Islamabad & Gujarkhan) (b) Region - II Sindh & Punjab (excluding Potohar Region) Existing Cess Proposed Cess (Rs./MMBTU) (Rs./MMBTU) 197 300 141 300 79 200 3 Industrial (including Captive Power) 13 100 4 WAPDA/KESC/GENCOs 27 100 5 Independent Power Plants (IPPs) 70 100 Declaration under the Provisional Collection of Taxes Act, 1931 The provision of the Finance Bill, 2012 regarding the following matters shall be immediately applicable with effect from 2nd June, 2012: Service of show cause notice on a person for payment of tax or charge not levied, short levied or erroneously refunded, under the Sales Tax Act, 1990, due to inadvertence, error, misconstruction or by reason of collusion or a deliberate act Change in the rate of FED on cigarette and cement and withdrawal of FED on certain items specified in the First Schedule to the Federal Excise Act, 2005 Customs tariff as provided in the First Schedule to the Customs Act, 1969 36 Tax Handbook 2012 Tax Planning Guide For Corporations & Individuals This page is intentionally left blank Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax Income Tax Who is Required to File a Return of Income? Following persons are required to furnish a return of income for a tax year: every company every AOP individual whose taxable income for the year exceeds Rs. 400,000 any non-profit organization any person who has been charged to tax in respect of any of the two preceding tax years claims a loss carried forward under the Income Tax Ordinance for a tax year owns immovable property with a land area of 250 sq. yards or more, or owns any flat located in areas falling within the municipal limits existing immediately before the commencement of Local Government laws in the provinces, or area in a Cantonment, or the Islamabad Capital Territory. The following are excluded from this category: • • • • widows orphans below the age of 25 years disabled persons non-resident Pakistanis in case of ownership of immovable property owns immovable property with a land area of 500 square yards or more located in a rating area owns a flat having covered area of 2,000 square feet or more located in a rating area owns a motor vehicle having engine capacity above 1000cc has obtained National Tax Number has industrial and commercial electricity connection and the amount of annual utility bills exceed Rs. 1,000,000 Who is Required to File Wealth Statement? Every resident taxpayer filing a return of income whose declared or assessed income is Rs. 1,000,000 or more Every resident taxpayer filing statement under FTR and has paid tax of Rs. 35,000 What Year End Can a Taxpayer Adopt? Class of Person Tax Year Type Companies, Association of persons and Individuals Normal Tax Year July 01 to June 30 Sugar Special Tax Year October 01 to September 30 Banking and Insurance Companies Special Tax Year January 01 to December 31 Ginners, Rice huskers, Oil mills Special Tax Year September 01 to August 31 Shawl manufacturers Special Tax Year April 01 to March 31 37 Year End Income Tax When to File the Return of Income? Status Year End Date of Filing Tax Year Salaried Individual & Non-corporate Taxpayer (falling under FTR) June 30, 2012 August 31, 2012 2012 Other Individual & AOP June 30, 2012 September 30, 2012 2012 Company (including falling under FTR) June 30, 2012 December 31, 2012 2012 Company September 30, 2012 September 30, 2013 2013 Company December 31, 2012 September 30, 2013 2013 Who is Required to Pay Advance Tax? Every business individual whose latest assessed taxable income excluding the presumptive tax income is more than Rs. 500,000 Every Association of Person Every Company When to Pay Advance Tax by an Individual? Individuals have to pay advance tax within 15 days after the close of each quarter. When to Pay Advance Tax by an AOP or Company? Period Quarter Payment Date 1st of July to 30th September September quarter On or before the 25th of September 1st October to 31st December December quarter On or before the 25th of December 1st January to 31st March March quarter On or before the 25th March 1st April to 30th June June quarter On or before the 15th of June 38 Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax Rate of Tax for Business Individuals and AOPs The basic exemption limit for business individuals and AOPs is Rs. 400,000 and the varying slab rates range from 10% to 25% as under: Income Brackets Rates Taxable income not exceeding Rs. 400,000 0% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 400,000 but not exceeding Rs. 750,000 10% of the amount exceeding Rs. 400,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 750,000 but not exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 Rs. 35,000 + 15% of the amount exceeding Rs. 750,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 but not exceeding Rs. 2,500,000 Rs. 147,500 + 20% of the amount exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 2,500,000 Rs. 347,500 + 25% of the amount exceeding Rs. 2,500,000 Special Rebates To Senior Citizens A rebate of 50% of the tax payable is allowed to senior citizen who has attained the age of 60 years or above, provided his total income excluding FTR income does not exceed Rs. 1,000,000. To Teachers and Researchers A further rebate of 75% of taxpayable on salary income is allowed to a full time teacher or a researcher, employed in a non profit education or research institution recognized by a Board of Education or Higher Education Commission including Government training and research institution. Minimum Tax Minimum tax is applicable to a resident company, AOP (having turnover more than 50 million) and individuals (having turnover more than 50 million) at the rate of 1% (in budget speech 2012, rate is proposed to be reduced to 0.5%) of turnover even if the business sustain losses except a company which has declared gross loss before depreciation and other inadmissible expenses. 39 Income Tax Rate of Tax for Salaried Individuals The basic exemption limit for salaried individuals is Rs. 400,000 and the varying slab rates range from 5% to 25% as under: Income Brackets Rates Taxable income not exceeding Rs. 400,000 0% Taxable income exceeding Rs. 400,000 but not exceeding Rs. 750,000 5% of the amount exceeding Rs. 400,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 750,000 but not exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 Rs. 17,500 + 10% of the amount exceeding Rs. 750,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 but not exceeding Rs. 2,500,000 Rs. 92,500 + 15% of the amount exceeding Rs. 1,500,000 Taxable income exceeding Rs. 2,500,000 Rs. 242,500 + 20% of the amount exceeding Rs. 2,500,000 Marginal Tax Relief for Salaried Taxpayers Where the total income of the taxpayer marginally exceeds the maximum slab limit, the income tax payable shall be the tax payable upto the maximum of the slab exceeded plus tax on marginal amount as under: Income Bracket Marginal Taxable Amount Where total income: Does not exceed Rs. 550,000 20% Does not exceed Rs. 1,050,000 30% Does not exceed Rs. 2,250,000 40% Does not exceed Rs. 4,550,000 50% Exceeds Rs. 4,550,000 60% 40 Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax Tax on Rental Income In case of non-corporate taxpayers: Gross Amount of Rent Rate of Tax Where the gross amount of rent: Does not exceed Rs. 150,000 Nil Exceeds Rs. 150,000 but does not exceed Rs. 400,000 5.00% of the gross amount exceeding Rs. 150,000 Exceeds Rs. 400,000 but does not exceed Rs. 1,000,000 Rs. 12,500 plus 7.50% of the gross amount exceeding Rs. 400,000 Exceeds Rs. 1,000,000 Rs. 57,500 plus 10.00% of the gross amount exceeding Rs. 1,000,000 In Case of Corporate Taxpayers Gross Amount of Rent Rate of Tax Where the gross amount of rent: Does not exceed Rs. 400,000 5.00% of the gross amount of rent Exceeds Rs. 400,000 but does not exceed Rs. 1,000,000 Rs. 20,000 plus 7.50% of the gross amount exceeding Rs. 400,000 Exceeds Rs. 1,000,000 Rs. 65,000 plus 10.00% of the gross amount exceeding Rs. 1,000,000 41 Income Tax Allowances and Tax Credit Section Particulars Concession Maximum Limit 60 Zakat Straight income deduction N/A 61 Charitable Donation Straight income deduction / Tax credit Lower of amount of donations or: 30% of taxable income in case of individual and AOP 20% of taxable income in case of company 62 Investment in Shares and Insurance Tax credit Resident person other than company shall be allowed Lower of: total cost of acquiring shares / insurance premiums paid 20% of taxable income Rs. 1,000,000 63 Approved Pension Fund Tax credit Lower of: total contribution or premium paid by individual 20% of taxable income 64 Profit on Debt or Share Tax credit Lower of: total profit paid 50% of taxable income Rs. 750,000 65A If 90% of sales by the manufacturer are made to sales tax registered persons Tax credit 2.50% of tax payable 65B Balancing, modernization and replacement of plant & machinery from July 1, 2011 to June 30, 2016 Tax credit 20% of tax payable 65C Enlisting a company on stock exchange Tax credit 15.00 % of tax payable 65D Equity Investment Tax credit Equal to 100% of tax payable (Conditions apply) 65E Equity Investment Tax credit Equal to 100% of tax payable attributable to new expansion (Conditions apply) 42 Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax Tax Rates for Companies Company Tax Rate Banking Company 35% Public Company (other than a banking company) 35% Private Company (other than a banking company) 35% Small Company having turnover upto Rs. 250 million 25% Fixed Tax on Turnover in Case of Individual and AOPs Category Rate In case of individual or AOP being retailer and having turnover upto Rs. 5,000,000 0.5% of turnover as final tax In case of individual or AOP being retailers having turnover Exceeding Rs. 5,000,000 but does not exceed Rs. 10,000,000 Rs. 25,000 plus 0.5% of the turnover exceeding Rs. 5,000,000 Exceeding Rs. 10,000,000 Rs. 50,000 plus 0.75% of the turnover exceeding Rs. 10,000,000 Individual and AOP retailer cannot claim any adjustment of withholding tax collected or deducted under any head during the year Rate of Tax on Capital Gains on Disposal of Immovable Property Period for which Immovable Property is Held Up to 1 year More than 1 year but less than 2 years Rate 10% 5% 43 Income Tax Third Schedule (Part I) Tax Depreciation Rates Description Rate Building (all types) 10% Furniture (including fittings) Machinery and plant (not otherwise specified) Motor vehicles* (all types) Ships, technical or professional books 15% Computer hardware including printer, monitor and allied items Machinery and equipment used in manufacturing of I.T. products Aircraft and aero engines 30% Below ground installations 100% Offshore platform and production installations 20% A ramp built to provide access to person with disabilities, not exceeding Rs. 250,000 each 100% Third Schedule (Part II) Depreciation Allowance Description Section Rate Initial allowance 23 25% (For buildings) 50% (Other eligible assets) First year allowance 23A 90% First year allowance (in case of alternate energy projects) 23B 90% 44 Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax Penalties Default Rate of Penalty Failure to file any return of income 0.1% of tax payable per day subject to minimum Rs. 5,000 & maximum 25% of tax payable Failure to pay any tax (other than a penalty) In case of first default In case of second default additional penalty In case of third and subsequent defaults additional penalty 5% of the amount of tax on default 25% of the amount of tax on default 50% of the amount of tax on default Concealment of income or furnishing of inaccurate particulars of income 25,000 or amount equal to tax sought to be evaded by concealment or furnishing of inaccurate particulars which ever is high Failure to maintain records Rs. 10,000 or 5% of the amount of tax on income whichever is high Making of false or misleading statement Rs. 25,000 or 100% of the amount of tax short fall, whichever is higher Penalty for obstructing the access of comissioner Rs. 25,000 or 100% of the tax involved, whichever is high Penalty for obstructing any Income Tax authority in performance of his official duties Rs. 25,000 Additional Tax Failure to pay tax excluding advance tax pay any penalty pay any other amount of tax under the Income Tax Law pay advance tax collect tax deduct tax deposit tax deducted or collected 18% per annum of amount of default 45 Payment of commission to petrol pump operators 156A Payment on account of approved pension fund Prize on prize bonds, winning from raffle, lottery or cross word puzzle Prize on winning of quiz & prize offered by companies for promotion on sales 156 156B Income from Property Exports Foreign exchange proceeds on account of indenting commission Manufacturers to collect tax at source from traders and distributors 155 154 153A Average rate of tax 10% 10% 20% As per slabs 1% 5% 1% 6% Payment to resident company on account of: 153 20% 5% 10% 20% 15% 6% 6% Execution of Contract (other than supply of goods & rendering of services) Payment to Non-Resident on account of: Royalty, fee for technical services to a non-resident Person Execution of Contract (other than for supply of goods & rendering of services) Contract for construction, assembly, installation projects, supervisory activities and advertisement services Other payments to non-resident except payment to foreign news agencies, syndicate services & non-resident contributing having no permanent establishment in Pakistan Profit on Debt On payment of insurance or re-insurance premium Payments to non-resident media persons 152 After Deduction of Zakat 10% 10% 10% 10% 10% 10% 2% 6% Profit on Debt: National saving deposit including DSC, under national saving scheme Profit on TFCs Profit on banking account or deposit Profit on security Profit on Post Office Saving Account Profit on security issued by Federal Government, Provincial Government or Local Authority 151 10% Average rate of tax Rendering of Services: Passenger transport services & News print media services Other services Dividends 150 1.5% 3.5% 1% Income from Salary 149 5% 3% 2% 1% Standard Tax Rates Sale of Goods: Sale of rice, cotton seed or edible oil Sale of any other goods Sale of edible oil to manufacturer of cooking & vegetable ghee mills Imports: Commercial imports Raw material imports by an industrial undertaking Pulses Fiber fabrics (other than of cotton), capital goods, cement, coal, mobile phones, sugar, gold, silver, wheat raw, wood, medical surgical & dental equipment, certain medicines & vaccines, broadcasting equipment, urea fertilizer etc. Nature of Payment/Transaction 148 Section/ Sub-section of I.Tax Ord. Deduction/Collection of Tax at Source Final Final Final Final Final Final Final except for listed companies Minimum Final except for manufacturercum-supplier & listed companies Final Final Final Adjustable Final except for imports for self use by manufacturers Adjustable/ Final Discharge 25% of accumulated balance Nil Nil Rs. 150,000 (In case of non-corporate taxpayer) Nil Nil Rs. 10,000 Rs. 25,000 Nil Interest on investment up to Rs. 150,000 is exempt in case of National Saving Scheme and TFCs and where installment is less than Rs. 1,000 per month Nil Rs. 400,000 Subject to certain exclusion Exemption Limit Pension fund manager Every person selling petroleum products Payer Federal Govt., Provincial Govt. Local Authority or a company Collector / Authorized dealer in foreign exchange Payer Government Company, a registered AOP, foreign contractor or consultant or a consortium or a joint venture, Individual with turnover exceeding 25 million, AOP with turnover exceeding 50 million and exporter of export house Payer Bank / Financial institution Banking Co., Financial Int. Company, Finance Society Federal Government, Provincial Government or Local Authority Payer of Profit Payer Every Employer Custom Authorities Persons Required To Deduct/Collect Tax Monthly Monthly When actually paid Monthly At time of realization When Paid When actually paid When actually paid When credited or paid which ever is earlier When Paid Monthly Statements of Tax Collected/Deducted Income Tax 46 Collection of tax by stock exchange registered in Pakistan on account of: Purchase of shares Sale of shares Tax on motor vehicle Goods transport vehicle of: Ladden weight till 8119 Kg Ladden weight 8120 Kg or more 234 Tax on gas consumption charges of a Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) Station Electricity Consumption Does not exceed Rs. 400 Exceeds Rs. 400 but does not exceed Rs. 600 Exceeds Rs. 600 but does not exceed Rs. 800 Exceeds Rs. 800 but does not exceeds Rs. 1,000 Exceeds Rs. 1,000 but does not exceed Rs. 1,500 Exceeds Rs. 1,500 but does not exceed Rs. 3,000 Exceeds Rs. 3,000 but does not exceed Rs. 4,500 Exceeds Rs. 4,500 but does not exceed Rs. 6,000 Exceeds Rs. 6,000 but does not exceed Rs. 10,000 Exceeds Rs. 10,000 but does not exceed Rs. 15,000 Exceeds Rs. 15,000 but does not exceed Rs. 20,000 Exceeds Rs. 20,000 Telephone subscriber where the monthly bill exceeds Rs. 1,000 Subscriber of mobile phone and prepaid mobile & telephone cards Sale of units through any electric medium or whatever form Sale of any property or goods by auction / tenders Purchase of air tickets 234A 235 236 236A 236B In case of passenger transport vehicle with seating capacity of: 4 or more person but less than 10 person 10 or more person but less than 20 person 20 or more person Other private motor car with engine capacity of: Upto 1000CC 1001CC to 1199CC 1200CC to 1299CC 1300CC to 1599CC 1600CC to 1999CC 2000CC and above Brokerage and Commission 233 Purchase of motor vehicle manufactured locally with engine capacity: Up to 850CC 851CC to 1000CC 1001CC to 1300CC 1301CC to 1600CC 1601CC to 1800CC 1801CC to 2000CC Above 2000CC 233A Cash withdrawals from bank 231B Nature of Payment/Transaction 231A Section/ Subsection of I.Tax Ord. Final Final / Adjustable 5% 5% 10% 10% 10% N/A N/A Adjustable Rs. 1,000 Adjustable Fully adjustable for companies whereas adjustable upto the extent of tax liability for individuals and AOPs N/A Nil N/A Nil Nil Final Final Nil Rs. 50,000 Adjustable Adjustable Exemption Limit Adjustable/ Final Discharge 0 Rs. 80 Rs. 100 Rs. 160 Fully adjustable for companies Rs. 300 whereas adjustable upto the extent Rs. 350 of tax liability for individuals and Rs. 450 AOPs Rs. 500 Rs. 650 Rs. 1,000 Rs. 1,500 At 5% (Industrial consumer) At 10% (Commercial consumer) 4% Rs. 750 Rs. 1250 Rs. 1750 Rs. 3000 Rs.4,000 Rs. 8000 Rs. 25 per seat Rs. 60 per seat Rs. 500 per seat Rs. 5 Per Kg of laden weight Rs. 1200 Per Annum After 10 years from 1st registration 0.01% 0.01% 10% Rs. 7,500 Rs. 10,500 Rs. 16,875 Rs. 25,000 Rs. 22,500 Rs. 16,875 Rs. 50,000 0.2% Standard Tax Rates Person making sale Person making sale by auction Person preparing mobile and phone bills and person selling prepaid cards Person preparing Electricity bills Person making consumption bill Excise and Taxation Department Stock exchange Payer Registering Authority Every banking company Persons Required To Deduct/Collect Tax At time of realization of sale proceeds At time of realization Monthly Monthly Monthly Annually At time of payment When actually paid At time of registration When cash is with drawn Statements of Tax Collected/Deducted Tax Handbook 2012 Income Tax 47 Sales Tax Sales Tax Sales Tax Applicability Sales Tax is applicable at the rate of 16% of the value of: Taxable supplies made by a registered person Goods imported into Pakistan Filing of Sales Tax Return The sales tax return is to be filed within 15 days from the close of month by the registered persons Sales Tax Registration Threshold Annual Turnover of Taxable Supply Manufacturers or Producers More than Rs. 2.5 million Up to Rs. 2.5 million Sales Tax Exempt u/s 13 Retailer Wholesalers (including Dealers) and Distributors Importers and Exporters More than 50 million Making Taxable Supply Sales Sales Tax Tax GST @ 16% on manufacturer, importers & wholesalers Exporters fall under zero-rated category (@ 0%) Retailers fall under special procedure for payment of sales tax 48 Rs. 10,000 or 5% of amount of tax involved whichever is higher Rs. 5,000 or 3% of amount of tax involved whichever is higher Penalty of Rs. 5,000 Rs. 10,000 or 5% of tax involved whichever is higher Required to enrol / register himself and fails to do so Fails to maintain records On receipt of 1st notice 2nd notice 3rd notice Twice of the amount of penalty for the said offence Repetition of an offence for which a penalty is provided under this Act Rs. 25,000 Failure to submit summary of sale and purchase invoices required under this Act Such person shall, further be liable, upon conviction by the Special Judge, to imprisonment for a term which may extend to one year, or with fine which may extend to an amount equal to the loss of tax involved, or with both. Rs. 25,000 or 100 % of amount of tax involved whichever is higher Rs. 25,000 or 10% of amount of tax involved whichever is higher Violates any embargo placed on removal of goods in connection with recovery of tax Rs. 5,000 Rs. 10,000 Rs. 50,000 Non production of record Rs. 10,000 due to failure to furnish the information required by Board Rs. 5,000 or 3% of tax involved whichever is higher Contravenes any provision of this Act for which no specific penalty is provided and fails to fulfil conditions prescribed in a Notification Fails to make payment in the manner prescribed in Section 73 knowingly and without lawful authority gains access to the computerized system unauthorizedly uses or discloses or publishes information obtained from the computerized system falsifies any record or information stored in the computerized system knowingly or dishonestly damages or impairs the computerized system knowingly or dishonestly damages or impairs any duplicate tape or disc or other storage medium unauthorizedly uses unique user identifier of any other registered fails to comply with or contravenes security of unique user identifier Rs. 25,000 or 100% of tax involved whichever is higher Makes or files false documents, statements and declaration Destroys or alters the record Denies or obstructs authorised officer to access record and to perform his duties Commits, causes to commit or attempts to commit tax fraud Denies or obstructs Sales Tax Officer posted to business premises to access record and to perform his duties If any person * No penalty shall be imposed, if miscalculation is made first time during the year. * Certain defaults attract imprisonment along with penalty. Refer to Section 33 of the Sales Tax Act for complete reference of penalties. *Default Surcharge at the rate KIBOR plus 3% per annum of the tax due would be imposed in the case of inadmissible input tax credit or refund and on nonpayment of tax and such tax would be calculated on the basis of period of default. Rs. 5,000 or 3% of amount of tax involved whichever is higher Rs. 10,000 or 5% of amount of tax involved whichever is higher Fails to notify change in nature of supply Fails to issue invoice Un-authorisely issues invoice Fails to deposit tax *Repeats erroneous calculation If return is filed in 15 days of due date than penalty of Rs. 100 for each day of default Penalty of Rs. 5,000 Fails to furnish return within due date Penalties Tax Handbook 2012 Sales Tax 49 Capital Value Tax (CVT) Capital Value Tax Certificates / Instruments of Redeemable Capital Capital Value Tax is levied on the transactions of certificates or any instrument of redeemable capital as under: Purchase Rate of CVT Collected by Modaraba certificates or any instrument of redeemable capital Purchase of shares of a public company listed on a registered Stock Exchange 0.02% of purchase value Personal responsible for registering or attesting the tranfer of asset. Personal responsible for registering or attesting the tranfer of asset. 0.01% of purchase value CVT on Real Estate Transactions Capital Value Tax is leviable on the real estate transactions of sale and purchase in the following manner: Nature of Transaction Rate of CVT Residential immovable property (other than flats) situated in urban area, measuring at least 500 square yards or one kanal whichever is less Where the value of Immovable property is recorded 2 % of the recorded value Where the value of immovable property is not recorded Rs.100 per square yard of the landed area Where the immovable property is a constructed property Rs.10 per square feet of the constructed area in addition to the value worked out above Commercial immovable of any size situated in urban area Where the value of immovable property is recorded 2 % of the recorded value of land Where the value of immovable property is not recorded Rs.100 per square feet of the landed area Where the immovable property is a constructed Rs.10 per square feet of the constructed area in property addition to the value worked out above Residential flats Where the value of immovable property is recorded 2 % of the recorded value Where the value of immovable property is not recorded Rs.100 per square feet of the covered area 50 Tax Handbook Disclaimer: 2012 Horwath Hussain Chaudhury & Co. is a member of Crowe Horwath International, a Swiss verein (Crowe Horwath). Each member firm of Crowe Horwath is a separate and and independent legal entity. Horwath Hussain Chaudhury & Co. and its affiliates are not responsible or liable for any acts or omisssions of Crowe Horwath or any other member of Crowe Horwath specifically disclaim any and all responsibility or liability for acts or omissions of Crowe Horwath or any Crowe Horwath member. ©2012 Horwath Hussain Chaudhury & Co. This page is intentionally left blank