CCNA v3.0 Semester 3 Chapter 3 Study Guide
advertisement

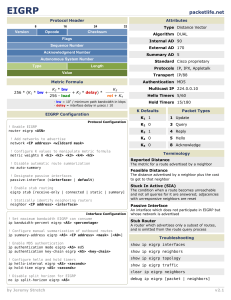
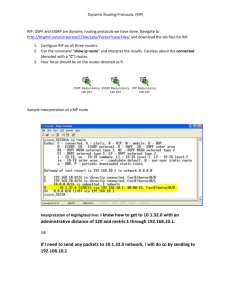
CCNA v3.0 Semester 3 Chapter 3 Study Guide 3.1 EIGRP Concepts 3.1.1 What aspects of IGRP have been improved upon in EIGRP 3.1.1 Explain the differences in metrics used by IGRP and EIGRP 3.1.1 How can an IGRP metric be converted into a EIGRP metric? 3.1.1 How do hop counts differ between the 2 protocols? 3.1.1 What configuration must be the same for IGRP and EIGRP to interoperate? 3.1.1 How does EIGRP treat routes learned from IGRP 3.1.1 How does IGRP deal with external routes? 3.1.2 What tables are maintained by EIGRP 3.1.2 Which is the most important table & what is its function 3.1.2 Which command lets you view the neighbouring routers? 3.1.2 How does the router learn about its neighbours? 3.1.2 What is the hold time? 3.1.2 Where does the information in the topology table originate? 3.1.2 Define feasible distance 3.1.2 What is a successor? 3.1.2 How many successor routes are permitted? 3.1.2 What is a feasible successor 3.1.3 How does EIGRP differ from simple distance vector routing protocols? 3.1.3 How does EIGRP conserve bandwidth? 3.1.3 What is a bounded update? 3.1.3 Which routed protocols does EIGRP support? 3.1.4 Describe the use of hello packets by EIGRP 3.1.4 Why does EIGRP use RTP as its transport layer protocol? 3.1.4 Describe DUAL 3.1.4 How does DUAL recalculate a route if a route becomes unavailable? 3.1.5 What is the destination address of EIGRP hello packets 3.1.5 What is the hold time? 3.1.5 Describe the different packets used by EIGRP 3.2 Configuring EIGRP 3.2.1 Which command enables EIGRP 3.2.1 3.2.1 3.2.2 3.2.2 3.2.3 3.2.3 3.2.3 3.2.6 What step is important when configuring serial links? Which command is used? Which additional command is recommended by Cisco when configuring EIGRP Which command would you use so that routes are not summarised at the classful boundary? Which command allows you to manually enter a summary route? Which command displays the eigrp neighbour table? Which command displays all the feasible successors Which command displays all routes What happens when a link goes down? 3.3 Troubleshooting Routing Protocols 3.3.1 What is the purpose of show commands? 3.3.1 3.3.2 3.3.2 3.3.3 3.3.3. 3.3.3 3.3.4 3.3.5 3.3.5 What is the purpose of debug commands? What is a common problem associated with RIP v1 Which command displays information about RIP routing transactions Which commands allow you to verify IGRP configuration? Which command allows you to verify IGRP operation? Which command allows you to view routing update information? Why should the hold-time value in a show ip eigrp neighbors command output normally be a value of 10 to 15. Which command allows you to troubleshoot OSPF adjacency problems? What information is displayed by the debug ip ospf events command? Show commands monitor installation and normal behaviour. They show the status of a router and display neighbouring routers. They provide information about traffic, error messages, troubleshooting data RIP v1 does not support VLSM and does not advertise routes using VLSM correctly Router#debug ip rip Router#debug show runningconfiguration Router#show ip protocols Router#show ip route Router#debug ip igrp events Hellos are sent every 5 seconds and expire after 15. Router#Show ip ospf neighbor Adjacencies, flooding information, designated router selection, Shortest path first calculation