Anisotropic MOT for Nonlinear Optical Studies
advertisement

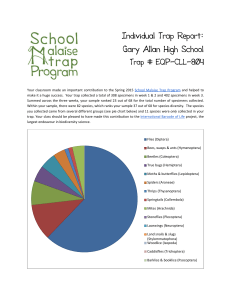
Anisotropic MOT for Nonlinear Optical Studies Joel A. Greenberg, Marcos Oria*, Daniel J. Gauthier Quantum Electronics Lab, Physics Department, Duke University Optics: Introduction Trap Characteristics 3 cm Vacuum Trapping Goals: • Develop a simple MOT geometry to produce an anisotropic, high density trap • Use the MOT to study nonlinear optical effects 1cm Mirror y Cell x z Probe Experimental Setup Magnets θ Cooling + − • Two reflected beams ( σ - σ ) for trapping (3cm x 2cm) • Retroreflected off-axis beams for cooling (lin lin; d=1cm) à Cooling beams also act as pump beams • Probe along axis of MOT Magnets: • Length: ~3 cm Radius: 0.3 mm à Aspect Ratio 100:1 • Optical Depth ~12 (e-OD) • Density 2x109 atoms/cm3 • Temperature ~20µK 3cm Why Use Off-Axis Cooling Beams? Citations 1) M. Vengalatorre, W. Rooijakkers, M. Prentiss. PRA 66, 053403 (2002) 2) J. Guo, P.R. Berman, B. Dubetsky, G. Grynberg. PRA 46, 1426 (1992) 3) A.M.C. Dawes, L. Illing, S. M. Clark, and D. J. Gauthier, Science 308, 672 (2005) Funding US Army Research Office (grant # W911NF-05-1-0228), DARPA (grant # Contract PO #412785-G-2) 400 300 200 100 z velocity Cooling beams along z axis with different forward:backward cooling beam power ratios Recoil-Induced Resonance - 2- 1 0 1 2 3 RIR Gain z position 150 125 100 75 50 25 - 2- 1 0 1 2 3 z velocity Rotation of Cooling Beams: Gives less confinement along trap axis à Longer Trap Gives more cooling in the z direction à Colder Trap *Permanent Address: UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DA PARAÍBA DEPARTAMENTO DE FÍSICA LABORATÓRIO DE FISICA ATÔMICA E LASERS RIR Model Fit Model[2] Data 0.8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 -1 -500 0.6 Abs (arb) z position - 2- 1 0 1 2 3 • Can localize trap in z direction by beam misalignment • Atomic population can be transferred quickly θ = 0 rad - 2- 1 0 1 2 3 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 Trap Localization/Transfer 1cm Transmission 175 150 125 100 75 50 25 # of atoms (arb) • Magnets external to vacuum • Trap location 5 mm above magnets • 4 oppositely poled µ metal cores (5x5x0.1 cm) [1] • 200 turns for each magnet • No need to cool magnets (Iouter/Iinner = 2, Iouter ~300 mA) • Typical gradient: ∇ B= 10 G/cm ; Max ∇B= 30 G/cm • Uses a simple vacuum system (p ~10-9 T) • Rb supplied via getter (trap runs with getter off) • Homemade cell constructed with AR coated windows (3 cm cube) • Cell base is gold mirror to produce beam geometry • No magnetic compression currently used θ = π /10 rad # of atoms (arb) 1cm # of atoms (arb) MAGNETS # of atoms (arb) CELL Results/Future Work • 2D Model (x-z plane) to determine effect of beam geometry • Atoms with vz injected into trap with cooling beams off z axis • Considers: - 2 level atom - Classical trajectories - Gaussian beam profile - Absorption due to trap - Perfect trapping in x-y plane -300 -100 ν (kHz) 100 300 500 0.4 0.2 0 - 0.2 - 0.4 - 0.6 - 0.8 • RIR gain of 650% • Trap run in steady state ν (arb) - 0.4 0 0.4 0.8 • Fit used for determining T Future Work • Look for instabilities and optical pattern formation[3] • Look for collective spatial atomic behavior for enhanced nonlinear response • Look at RIR in strong probe regime for multiphoton effects