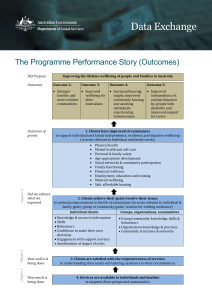
Health & Wellbeing for UK Rail 1
advertisement

Health & Wellbeing for UK Rail Roadmap Workshop 2 7 November, DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Note: Wordle created from participant vision statements Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 1 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Executive Summary This report results from a one-day workshop to map the future of Health & Wellbeing for the UK Rail industry. This is the second of three workshops to develop a roadmap to bring about commitment and understanding for a series of well-planned, effective and prioritised tasks that a diverse range of stakeholders believe will improve health and wellbeing management within the railway and therefore the health and wellbeing of the Rail Workforce and the efficiency of the sector. The workshop was jointly hosted by RSSB and ORR at Central Hall Westminster and benefitted from the insights of 26 experts from across the relevant stakeholder groups. The workshop started with a baseline landscape and outline vision based on the pre-work that had been completed by the vast majority of participants. In setting out a Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail the group showed very strong alignment across all stakeholder groups (see 1.1) in identifying “Better workforce health and physical, social and psychological wellbeing, underpinned by a culture which demonstrates that health at work is everybody's responsibility” as the two key aspects of the Vision. Further factors were also seen to be important: Legal compliance and moving towards broader industry best-in-class; An inclusive and sustainable workforce; Professionalised health and wellbeing provision in Rail; A more efficient and productive railway for the benefit of everyone; Working for the rail industry is a long, productive and attractive career; and An engaged and committed supply chain working together. Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 2 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Executive Summary (continued) Key Trends, Drivers and Stakeholder Perspectives prioritised by the group as having the most influence on the future context for Health and Wellbeing included the following (in order of priority – see section 2 for detail): • Ageing workforce / longer working life • Need to raise Health higher up Corporate Agenda • Social attitudes driving changes in work / life balance • Overcoming entrenched rail culture that health risk ‘not an issue' • Design with roles and people in mind (RTS) • Equipment supplied with health issues managed (e.g. built with ergonomics in mind) • Regulation on health risks, ageing disorders & equality • Better OH Contracts • Rising Obesity • Evaluation of role of fit notes • Technology advances & automation • Need for reliable, timely, consistent & transparent data Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 3 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Executive Summary (continued) The Health and Wellbeing Challenges faced by the Industry (which of course represent Opportunities if addressed) were prioritised as follows (see section 3 for detail): • Poor health management limits ability to work • Management of individual health risks • Lack of individual resilience and adaptability • Fatigue / shift patterns • Stress, Anxiety and Depression • Access for all to quality OH services • Musculoskeletal disorders • Engagement Deficit • Stress (Trauma management following suicides) • Future occupational cancer burden – shift work, DEEE • Presenteeism • Absenteeism Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 4 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Executive Summary (continued) The group then worked to identify and prioritise the key Reponses, Actions and other Enablers that could be pit in place to address these Challenges in the context of future Drivers and Needs (see section 4). The highest priorities were identified as: • Board Level champions provide continued purpose, direction and decision making for industry • Development of cross industry training modules & Education for target groups • H&W best practice guides created • Deliver Employee engagement by operationalising four enablers described by Mcleod and Clarke • Make business case link with Health performance through improved cost benefit analyses and tools • Collaborative industry approach to common issues • All stakeholders (incl. individuals taking ownership) understand roles in making positive changes. • Need for data that is more leading / cross-discipline • Competency frameholders for health and wellbeing line managers • Opportunity for health / safety by design (eg cab ergonomics) • Send signal through franchise programme for H&W • Behaviour & Culture change activities. A number of these priorities were explored in more detail to characterise benefits and identify outline Action Plans for delivery (see section 5) Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 5 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Contents Executive Summary 1. Vision and Roadmap Landscape 2. Trends & Drivers and Stakeholder Perspectives 3. Health & Wellbeing Challenges & Opportunities 4. Responses & Enablers 5. Detailed exploration of Responses & Enablers – – Characterisation and Elevator Pitch Outline Action Plan Appendices: A. Participants B. Workshop Feedback C. Detailed exploration of Value Creation Opportunities D. Workshop Process E. Participant Perspectives Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 6 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 1.1. Vision for Health & Wellbeing in UK Rail Vision component Infrastructure TOC FOC 3 6 0 Number of participants in stakeholder group in workshop: Better workforce health and physical, social and psychological wellbeing A culture which demonstrates that health at work is everybody's responsibility Legal compliance and moving towards broader industry best-in-class An inclusive and sustainable workforce Professionalised health and wellbeing provision in Rail A more efficient and productive railway for the benefit of everyone Working for the rail industry is a long, productive and attractive career An engaged and committed supply chain working together Health Rail / Specialist External Body 5 10 Supply Chain Total 2 26 43% 33% 31% 21% 0% 27% 29% 26% 29% 17% 46% 25% 0% 10% 0% 15% 31% 10% 10% 10% 6% 11% 0% 9% 0% 17% 9% 7% 0% 8% 0% 0% 11% 13% 0% 7% 5% 2% 3% 14% 0% 7% 14% 2% 11% 3% 23% 7% Note: Not all stakeholder groups were equally represented. Stakeholder group numbers do not reflect balance of influence across sector Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 7 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 1.2. Roadmap Landscape Headlines Past 2014 Short term 2016 2017 CP4 Trends & Drivers Social 2020 Long term Technological Environmental 24/7/365 working environment Economic Regulation on health risks, ageing disorders & equality Effects of VfM driving behaviours Ageing workforce / longer working life Tax relief for companies that manage health of employees Industry reputation as an attractive place to work Retain the best employees TOCs & FOCs Network Rail Equipment supplied with health issues managed (eg built with ergonomics in mind) Suppliers InfraCos Health Professionals Well-being Occ Health Others / Whole Industry Need for reliable, timely, consistent & transparent data Better OH Contracts Need to raise Health higher up Corporate Agenda Overcoming entrenched rail culture that health risk ‘not an issue' Legal requirements seem remote Effect of work on health Fatigue / shift patterns Fitness for work Musculoskeletal disorders Poor health management limits ability to work Psychological wellbeing Physical wellbeing Evaluation of role of fit notes SEQOHS occ health competency Stress, Anxiety and Depression Management of individual health risks Future occupational cancer burden – shift work, DEEE Stress (Trauma management following suicides) Lack of individual resilience and adaptability Social wellbeing Engagement Deficit Engagement Access for all to quality OH services Opportunity and Access Other Required Responses and Actions Industry leadership Clinical leadership Collaborative industry approach to common issues Board Level champions provide continued purpose, direction and decision making for industry H&W best practice guides created Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Make business case link with Health performance through improved cost benefit analyses and tools Need for data that is more leading / cross-discipline Competency frameholders for health and wellbeing line managers All stakeholders (incl. individuals taking ownership) understand roles in making positive changes. Development of cross industry training modules & Education for target groups Opportunity for health / safety by design (eg cab ergonomics) Specific Interventions Other Enablers Deliver Employee engagement by operationalising four enablers described by Mcleod and Clarke Behavioural change Knowledge People & Skills Research and specialist advice to formulate the basics / strategy Railway conferences allow cross-fertilisation and promotion of best practice Occupational Health and Wellbeing expertise Improved equipment / reduced emissions Voluntary standards improve organisational management of health to agreed levels Standards & Regulation Supply Chain Best practice knowledge transfer Resources (Numbers of professionals) Facilities & Infrastructure Data processing system / shared databases Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page Rail based health standards are reviewed and improved for better outcomes Incentives and penalties? - H&W as a contract criterion 8 2025 CP6 Work-force Sakeholder Perspectives 2019 Social attitudes driving changes in Rising Obesity work / life balance Whole system approach to railway Technology advances management (RTS) & automation Design with roles and people in mind (RTS) Political & Legal inc DfT & ORR Health & Wellbeing Challenges & Opportunities Medium term CP5 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Vision CP7+ 1.3. Roadmap Landscape (See later for more readable detail) Past 2014 Short term 2016 2017 CP4 Dame Carol Black report indicates work is good for you Trends & Drivers Social People as key drivers in business (RTS) Changes in labour market (zero hours contracts; EU migration and legislation?) Worsening living conditions increase demands for better management of health £75m cost of absence Economic Pressure from socioeconomic downturn £140m cost of impairment New Franchising Worker health has a lower profile than worker and passenger safety Sakeholder Perspectives Work-force D&A tests TOCs & FOCs ATOC HEROH Forum VfM Study - Rail industry needs to earn its investment from Gender Occupational Safety and Health good practice (GOSH) Protection of transient workforce Meet franchise requirements OH professionals need a greater understanding of Rail health issues Occ Health Effect of work on health Psychological wellbeing Manage liabilities Need to raise Health higher up Corporate Agenda Legal requirements seem remote Overcoming entrenched rail culture that health risk ‘not an issue' SEQOHS occ health competency Customers do not require strategic input Ensuring employment issues are not medicalised (flexible working, shifts) Stress, Anxiety and Depression Toilet waste on the track HAVS Fatigue / shift patterns Musculoskeletal disorders Hearing loss Improved Employee and Union relations / engagement Professionalised workforce Industry reputation as an attractive place to work International supply chain impacting on H&W of non-GB workforce Equipment supplied with health issues managed (eg built with ergonomics in mind) Future occupational cancer burden – shift work, DEEE Respiratory issues Effects of long-distance commuting Absenteeism Companies re-evaluate health policies Individual underutilised Engagement Deficit Lack of individual resilience and adaptability Individual Burnout Healthier job roles improve engagement Wellbeing sustains engagement H&W perks support recruitment & retention for sustainable railway Match requirements to work undertaken to retain tacit knowledge of ageing workforce Trade Union support Informing policy / standards development for OH H&W best practice guides created Collaborative industry approach to common issues Clinical effectiveness is managed within industry Improved understanding of OH issues in rail by OH practitioners Intended use of data outputs is understood during the planning stage Improved occupational health reports Embrace diversity of workforce Competency frameholders for health and wellbeing line managers Increase employee say in what is happening Health professionals improve health decisions within organisations Make business case link with Health performance through improved cost benefit analyses and tools Companies publish improved health data indicating the progress of the rail industry All stakeholders (incl. individuals taking ownership) understand roles in making positive changes. Diet & Nutrition advice (engage food services) Hazard specific working groups tackle difficult healt h hazards Specific Interventions Better awareness of H&W initiativ es across dispersed workforce Occupational Health and Wellbeing expertise Rehabilitation plans reduce absence costs Guidance enables better contracts developed with OH providers Opportunity for health / safety by design (eg cab ergonomics) Job roles altered to become more engaging Develop and Validate H&W assessment for Railway staff esp. ‘high risk’ workers Regulator's forum Resources (Numbers of professionals) Voluntary standards improve organisational management of health to agreed levels Data processing system / shared databases Industry productivity is enhanced to improve successful outcomes for all. Implement all 10 recommendations in briefing NSARE accreditation to include occupational health? Improved equipment / reduced emissions Facilities & Infrastructure Deliver Employee engagement by operationalising four enablers described by Mcleod and Clarke All trained on health at work as the norm Link reward (or salary sacrifice) to health & wellbeing Risks are proactively addressed Best practice knowledge transfer Education outreach to schools Review frequency of D&A testing Communication leads to access to information for all Behaviour & Culture change activities. Organisational roles take a holistic approach to health rather than functional Send signal through franchise programme for H&W Railway conferences allow crossfertilisation and promotion of best practice Success is measured and reviewed before wider industry roll-out. Development of cross industry training modules & Education for target groups Logistics of remote working Employee health and wellbeing issues also impact passengers Clinical leadership provides direction for development of industry’s health capabilities Guidance is developed to assist railway physicians Industry educational and competence requirements are mapped Awareness of & training for stress issues Leadership creates conditions for change Translate proven health activities from other industries into rail Action based upon sound evidence Health and wellbeing monitoring technology Health data collection supports reasoned decisions to drive change. Need for data that is more leading / cross-discipline Research and specialist advice to formulate the basics / strategy Active life styles / Active life style promotion Increased home working or working at remote locations Sustainable workforce through effective succession planning More effective communication between OH service providers and line managers Better cooperation between medical professionals eg OHS and GPs Behavioural change Need for reliable leading and lagging indicators for ill health Presenteeism Access for all to quality OH services Eyesight & Colour vision Evidence based action Supply Chain Regulation on health risks, UK Railway Recognised as a key contributor to Tax relief for companies that ageing disorders & equality the world wide integrated transport sector (RTS) manage health of employees Reduced NHS results in best companies picking up non-essential health needs of employees Reduced tolerance for lack of action to prevent ill health Government looks to industry to play an increased role in health Alliances between railway organisations drive performance Increasing demands > Capability < Cost for CP6/7 ORR health programme priorities 2014-19 Long term sickness Heart / circulatory disorders Endocrine disorders eg diabetes Board Level champions provide continued purpose, direction and decision making for industry Standards & Regulation The Railway a magnet for talent (RTS) Management of individual health risks Diesel engine exhaust emissions Poor health management limits ability to work Industry leadership People & Skills Whole system approach to railway management (RTS) Stress (Trauma management following suicides) Sleep disorders Avoidance of abuse of support networks Knowledge CP7+ Ageing workforce / longer working life Improved H&W delivers productivity to benefit of all Manual handling of wheelchairs Biological contaminants Other Other Morbidity & cognitiv e decline Evaluation of role of fit notes Better OH Contracts Improvement needed in competency amongst managers Fitness for work Education & Training Vision CP5 charged large savings from H&W and technology A reliable supply chain Need for reliable, timely, consistent & transparent data Ballast dust Employee engagement 2025 Increased demands on contractors long working hours/tighter schedules Health Professionals Reporting and metrics Long term Mismatch between franchise term and whole working life InfraCos Clinical leadership Cost of non compliance to legislation Retain the best employees Large number of contractors (8090K) Extended supply chain changing time / cost / culture demands Suppliers Opportunity and Access Rising Obesity Technology advances & automation Improved medical understanding demands better treatment ISLG OH manifesto Network Rail Well-being Health & Wellbeing Challenges & Opportunities Required Responses and Actions Social attitudes driving changes in work / life balance Highly skilled workforce (RTS) 24/7/365 working environment Workforce and TU expectations for improved H&W Largely male workforce with most employees over 40 There needs to be a cost benefit to health Others / Whole Industry Other Enablers Design with roles and people in mind (RTS) Role of insurance companies Effects of VfM driving behaviours Political & Legal inc DfT & ORR Social wellbeing 2020 Climate change leads to temp rise Environmental Engagement 2019 CP6 Technological Physical wellbeing Medium term CP5 Increasing mechanisation to eliminate hazardous tasks New technology (eg otoacoustic emission testing) Voluntary standards result in the scope of health activities being fully covered Supply chain standards ensure health is integrated into design Supply chain provides tools to reduce harm Regional OH provider centres based at railway premises Smart cards enable the health of employees to be tracked through their working life Rail based health standards are reviewed and improved for better There is an increase in health skills purchased by the organisation Incentives and penalties? - H&W as a contract criterion Note: Deeper colours indicate higher priority items. Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 9 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 2.1 Trends and Drivers Past 2014 Short term 2016 2017 CP4 Dame Carol Black report indicates work is good for you Social Changes in labour market (zero hours contracts; EU migration and legislation?) People as key drivers in business (RTS) Trends & Drivers Worsening living conditions increase demands for better management of health £75m cost of absence Economic Highly skilled workforce (RTS) There needs to be a cost benefit to health TOCs & FOCs Meet franchise requirements Protection of transient workforce Regulation on health risks, ageing disorders & equality The Railway a magnet for talent (RTS) Improved Employee and Union relations / engagement Reduced tolerance for lack of action to prevent ill health Tax relief for companies that manage health of employees Reduced NHS results in best companies picking up non-essential health needs of employees ORR health programme priorities 2014-19 Cost of non compliance to legislation UK Railway Recognised as a key contributor to the world wide integrated transport sector (RTS) Government looks to industry to play an increased role in health management Industry reputation as an attractive place to work Professionalised workforce Mismatch between franchise term and whole working life CP5 charged large savings from H&W and technology ISLG OH manifesto Network Rail Extended supply chain changing time / cost / culture demands Suppliers CP7+ Whole system approach to railway management (RTS) Alliances between railway organisations drive performance and cost Retain the best employees Large number of contractors (80-90K) ATOC HEROH Forum Technology advances & automation Increasing demands > Capability < Cost for CP6/7 Workforce and TU expectations for improved H&W Largely male workforce with most employees over 40 A reliable supply chain Equipment supplied with health issues managed (eg built with ergonomics in mind) International supply chain impacting on H&W of non-GB workforce Increased demands on contractors - long working hours/tighter schedules InfraCos Health Professionals Others / Whole Industry OH professionals need a greater understanding of Rail health issues Evaluation of role of fit notes Better OH Contracts Need for reliable, timely, consistent & transparent data Improvement needed in competency amongst managers Manage liabilities Need to raise Health higher up Corporate Agenda Legal requirements seem remote Customers do not require strategic input Overcoming entrenched rail culture that health risk ‘not an issue' SEQOHS occ health competency Ensuring employment issues are not medicalised (flexible working, shifts) Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 10 Vision Ageing workforce / longer working life Rising Obesity VfM Study - Rail industry needs to earn its investment from government Gender Occupational Safety and Health good practice (GOSH) Worker health has a lower profile than worker and passenger safety 2025 Climate change leads to temp rise Role of insurance companies Effects of VfM driving behaviours Political & Legal inc DfT & ORR D&A tests Long term Morbidity & cognitive decline 24/7/365 working environment New Franchising Pressure from socioeconomic downturn £140m cost of impairment Work-force 2020 Social attitudes driving changes in work / life balance Improved medical understanding demands better treatment Environmental 2019 CP6 Design with roles and people in mind (RTS) Technological Sakeholder Perspectives Medium term CP5 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Improved H&W delivers productivity to benefit of all 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 2.2 Trends & Drivers (1 to 20) Rank 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Driver Timescale Ageing workforce / longer working life long Social attitudes driving changes in work / life balance medium Design with roles and people in mind (RTS) short Regulation on health risks, ageing disorders & equality long Rising Obesity medium to long Technology advances & automation medium 24/7/365 working environment short Effects of VfM driving behaviours short Tax relief for companies that manage health of employees long Whole system approach to railway management (RTS) medium Government looks to industry to play an increased role in health management medium to long Morbidity & cognitive decline long New Franchising short ORR health programme priorities 2014-19 medium Changes in labour market (zero hours contracts; EU migration and legislation?) short UK Railway Recognised as a key contributor to the world wide integrated transport long sector (RTS) £140m cost of impairment Past £75m cost of absence Past Gender Occupational Safety and Health good practice (GOSH) Short Highly skilled workforce (RTS) medium Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 11 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Workshop 18 11 8 8 7 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 3 3 2 2 1 1 1 1 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk % 18% 11% 8% 8% 7% 6% 5% 5% 4% 4% 3% 3% 3% 3% 2% 2% 1% 1% 1% 1% 2.2 Trends & Drivers (cont) Rank 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Driver Timescale People as key drivers in business (RTS) short Pressure from socio-economic downturn short Reduced tolerance for lack of action to prevent ill health long Role of insurance companies short Alliances between railway organisations drive performance and cost improvements medium Climate change leads to temp rise long Cost of non compliance to legislation medium Dame Carol Black report indicates work is good for you short Improved medical understanding demands better treatment medium Increasing demands > Capability < Cost for CP6/7 medium Reduced NHS results in best companies picking up non-essential health needs medium of employees The Railway a magnet for talent (RTS) medium VfM Study - Rail industry needs to earn its investment from government medium Worsening living conditions increase demands for better management of health medium Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 12 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Workshop 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk % 1% 1% 1% 1% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 2.4 Stakeholder Perspectives (1 to 20) Rank 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Needs Timescale Need to raise Health higher up Corporate Agenda short Overcoming entrenched rail culture that health risk ‘not an issue' short Equipment supplied with health issues managed (eg built with ergonomics in mind) medium Better OH Contracts short Evaluation of role of fit notes medium Need for reliable, timely, consistent & transparent data short Industry reputation as an attractive place to work medium Legal requirements seem remote short Retain the best employees medium SEQOHS occ health competency short Improvement needed in competency amongst managers short Increased demands on contractors - long working hours/tighter schedules medium Meet franchise requirements short OH professionals need a greater understanding of Rail health issues short A reliable supply chain medium Ensuring employment issues are not medicalised (flexible working, shifts) short Extended supply chain changing time / cost / culture demands short International supply chain impacting on H&W of non-GB workforce long ISLG OH manifesto short Largely male workforce with most employees over 40 short Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 13 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Workshop 11 9 6 4 4 4 3 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk % 16% 13% 9% 6% 6% 6% 4% 4% 4% 4% 3% 3% 3% 3% 1% 1% 1% 1% 1% 1% 2.4 Stakeholder Perspectives (cont) Rank 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Needs Manage liabilities Mismatch between franchise term and whole working life Professionalised workforce Protection of transient workforce Workforce and TU expectations for improved H&W ATOC HEROH Forum CP5 charged large savings from H&W and technology Customers do not require strategic input D&A tests Improved Employee and Union relations / engagement (inc H&S Reps) Improved H&W delivers productivity to benefit of all Large number of contractors (80-90K) There needs to be a cost benefit to health Worker health has a lower profile than worker and passenger safety Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 14 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Timescale short short medium medium short short medium short short medium long short short short Workshop 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk % 1% 1% 1% 1% 1% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 3.1 Health & Wellbeing Challenges & Opportunities Past 2014 Short term 2016 2017 CP4 Occ Health Stress, Anxiety and Depression Toilet waste on the track Musculoskeletal disorders Manual handling of wheelchairs Physical wellbeing Long term CP6 Diesel engine exhaust emissions Long term sickness Stress (Trauma management following suicides) Active life styles / Active life style promotion Respiratory issues Heart / circulatory disorders Effects of long-distance commuting Need for reliable leading and lagging indicators for ill health Increased home working or working at remote locations Lack of individual resilience and adaptability Individual Burnout Individual underutilised Healthier job roles improve engagement Absenteeism Presenteeism Engagement Access for all to quality OH services Eyesight & Colour vision Opportunity and Access Other 2020 Future occupational cancer burden – shift work, DEEE Biological contaminants Endocrine disorders eg diabetes Social wellbeing 2019 Management of individual health risks Poor health management limits ability to work Sleep disorders Psychological wellbeing Hearing loss HAVS Fatigue / shift patterns Fitness for work Well-being Health & Wellbeing Challenges & Opportunities Ballast dust Effect of work on health Medium term CP5 Engagement Deficit H&W perks support recruitment & retention for sustainable railway Match requirements to work undertaken to retain tacit knowledge of ageing workforce Avoidance of abuse of support networks Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Wellbeing sustains engagement Sustainable workforce through effective succession planning Page 15 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 2025 Vision CP7+ 3.2 Health & Wellbeing Challenges & Opportunities Rank A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T Challenges Timescale Poor health management limits ability to work short Management of individual health risks medium Lack of individual resilience and adaptability medium Fatigue / shift patterns short Stress, Anxiety and Depression short Access for all to quality OH services short Musculoskeletal disorders short Engagement Deficit medium Stress (Trauma management following suicides) short Future occupational cancer burden – shift work, DEEE short Presenteeism medium Absenteeism short Match requirements to work undertaken to retain tacit knowledge of ageing workforce medium Healthier job roles improve engagement medium Need for reliable leading and lagging indicators for ill health medium Sustainable workforce through effective succession planning long Active life styles / Active life style promotion medium Effects of long-distance commuting short Respiratory issues short Endocrine disorders eg diabetes short Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 16 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Workshop 16 14 10 9 9 8 8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 4 3 3 3 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk % 11% 10% 7% 6% 6% 5% 5% 5% 5% 4% 4% 3% 3% 3% 3% 3% 2% 2% 2% 1% 3.2 Health & Wellbeing Challenges & Opportunities Rank U V W X Y Z AA AB AC AD AE AF AG AH AI AJ AK Challenges HAVS Hearing loss Heart / circulatory disorders Increased home working or working at remote locations Avoidance of abuse of support networks Individual underutilised Long term sickness Sleep disorders Wellbeing sustains engagement Ballast dust Biological contaminants Diesel engine exhaust emissions Eyesight & Colour vision H&W perks support recruitment & retention for sustainable railway Individual Burnout Manual handling of wheelchairs Toilet waste on the track Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 17 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Timescale short short short medium short medium medium short medium short short short short long medium short short 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Workshop 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4.1 Responses and Enablers Past 2014 Short term 2016 2017 CP4 Industry leadership Trade Union support Board Level champions provide continued purpose, direction and decision making for industry More effective communication between OH service providers and line managers Required Responses and Actions Better cooperation between medical professionals eg OHS and GPs Evidence based action H&W best practice guides created Increase employee say in what is happening Competency frameholders for health and wellbeing line managers Other Enablers Occupational Health and Wellbeing expertise People & Skills Supply Chain Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 18 Regulator's forum Resources (Numbers of professionals) Voluntary standards improve organisational management of health to agreed levels Guidance enables better contracts developed with OH providers Job roles altered to become more engaging Implement all 10 recommendations in briefing Education outreach to schools Review frequency of D&A testing Opportunity for health / safety by design (eg cab ergonomics) Develop and Validate H&W assessment for Railway staff esp. ‘high risk’ workers Rehabilitation plans reduce absence costs Improved equipment / reduced emissions Data processing system / shared databases Risks are proactively addressed Best practice knowledge transfer Facilities & Infrastructure Standards & Regulation Link reward (or salary sacrifice) to health & wellbeing Send signal through franchise programme for H&W Railway conferences allow crossfertilisation and promotion of best practice All trained on health at work as the norm Development of cross industry training modules & Education for target groups Organisational roles take a holistic approach to health rather than functional Industry productivity is enhanced to improve successful outcomes for all. Deliver Employee engagement by operationalising four enablers described by Mcleod and Clarke Behaviour & Culture change activities. Diet & Nutrition advice (engage food services) Logistics of remote working Research and specialist advice to formulate the basics / strategy Communication leads to access to information for all Industry educational and competence requirements are mapped Specific Interventions Success is measured and reviewed before wider industry roll-out. Better awareness of H&W initiatives across dispersed workforce Hazard specific working groups tackle difficult health hazards Knowledge Make business case link with Health performance through improved cost benefit analyses and tools All stakeholders (incl. individuals taking ownership) understand roles in making positive changes. Employee health and wellbeing issues also impact passengers CP7+ Clinical leadership provides direction for development of industry’s health capabilities Companies publish improved health data indicating the progress of the rail industry Improved occupational health reports Embrace diversity of workforce Other Vision Action based upon sound evidence Intended use of data outputs is understood during the planning stage for collection. Awareness of & training for stress issues 2025 Guidance is developed to assist railway physicians Health and wellbeing monitoring technology Health data collection supports reasoned decisions to drive change. Employee engagement Long term Leadership creates conditions for change Translate proven health activities from other industries into rail Health professionals improve health decisions within organisations Improved understanding of OH issues in rail by OH practitioners Reporting and metrics Behavioural change 2020 Clinical effectiveness is managed within industry Need for data that is more leading / cross-discipline Education & Training 2019 CP6 Collaborative industry approach to common issues Informing policy / standards development for OH Companies reevaluate health policies Clinical leadership Medium term CP5 NSARE accreditation to include occupational health? Increasing mechanisation to eliminate hazardous tasks New technology (eg otoacoustic emission testing) Voluntary standards result in the scope of health activities being fully covered Supply chain standards ensure health is integrated into design Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Supply chain provides tools to reduce harm Regional OH provider centres based at railway premises Smart cards enable the health of employees to be tracked through their working life Rail based health standards are reviewed and improved for better outcomes There is an increase in health skills purchased by the organisation Incentives and penalties? H&W as a contract criterion 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Rank 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Responses Timescale Short 1 2 Board Level champions provide continued purpose, direction and decision making for industry Development of cross industry training modules & Education for target groups medium 2 5 H&W best practice guides created Short 1 2 Deliver Employee engagement by operationalising four enablers described Med-Long 1 by Mcleod and Clarke Make business case link with Health performance through improved cost Medium 2 2 benefit analyses and tools Collaborative industry approach to common issues Medium 2 All stakeholders (incl. individauls taking ownership) understand roles in medium 1 1 making changes. Need forpositive data that is more leading / cross-discipline Short 1 1 Competency frameholders for health and wellbeing line managers Medium 1 1 Opportunity for health / safety by design (eg cab ergonomics) Medium 1 Send signal through franchise programme for H&W Medium 1 2 Behaviour & Culture change activities. Medium 1 Industry educational and competence requirements are mapped Short 2 Action based upon sound evidence medium long 1 All trained on health at work as the norm Better awareness of H&W initiatives across dispersed workforce Medium Trade Union support Short Companies re-evaluate health policies Short Increase employee say in what is happening Medium 1 Health and wellbeing monitoring technology Med-Long 1 1 Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 19 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 2 1 2 1 1 2 1 4 1 1 4 2 1 2 1 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 4 1 3 5 2 Supply Chain Rail / External Body Health Specialist FOC TOC The number in the colour-coded columns shows the priority voting of specific stakeholder groups Infra-structure 4.2 Responses 1 1 2 3 3 3 2 3 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 Total 10 9 9 7 7 6 6 6 6 5 5 4 4 4 4 3 3 3 3 3 4.2 Responses (cont) Rank 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Responses Embrace diversity of workforce Implement all 10 recommendations in briefing Intended use of data outputs is understood during the planning stage for collection. Organisational roles take a holistic approach to health rather than functional Improved understanding of OH issues in rail by OH practitioners Develop and Validate H&W assessment for Railway staff esp. ‘high risk’ workers publish improved health data indicating the progress of the rail Companies industry policy / standards development for OH Informing Health data collection supports reasoned decisions to drive change. Risks are proactively addressed Leadership creates conditions for change Health professionals improve health decisions within organisations Rehabilitation plans reduce absence costs Employee health and wellbeing issues also impact passengers Awareness of & training for stress issues Communication leads to access to information for all Translate proven health activities from other industries into rail Success is measured and reviewed before wider industry roll-out. Industry productivity is enhanced to improve successful outcomes for all. Job roles altered to become more engaging Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 20 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Timescale Short Med-Long Medium Medium Short 1 Medium 1 Medium Short Short Medium Medium Medium Medium Short Medium 1 Medium Medium Medium long Medium 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Total 3 3 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 4.2 Responses (cont) Rank 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Responses Clinical leadership provides direction for development of industry’s health capabilities More effective communication between OH service providers and line managers Clinical effectiveness is managed within industry Hazard specific working groups tackle difficult health hazards Guidance is developed to assist railway physicians Improved occupational health reports Better cooperation between medical professionals eg OHS and GPs Logistics of remote working Link reward (or salary sacrifice) to health & wellbeing Diet & Nutrition advice (engage food services) Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 21 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Timescale Medium Short Short Medium Medium Short Short Medium Med-Long medium 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Total 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 This table shows the identified linkages between Responses and priority Drivers, Stakeholder perspectives and H&W Challenges. The right hand column indicates total number of linkages. Rank 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Ageing workforce / longer working life Need to raise Health higher up Corporate Agenda Social attitudes driving changes in work / life balance Overcoming entrenched rail culture that health risk ‘not an issue' Design with roles and people in mind (RTS) Equipment supplied with health issues Regulation on health risks, ageing disorders & equality Better OH Contracts Rising Obesity Evaluation of role of fit notes Technology advances & automation Need for reliable, timely, consistent & transparent data Poor health management limits ability to work Management of individual health risks Lack of individual resilience and adaptability Fatigue / shift patterns Stress, Anxiety and Depression Access for all to quality OH services Musculoskeletal disorders Engagement Deficit Stress (Trauma management following suicides) Future occupational cancer burden – shift work, DEEE Presenteeism Absenteeism 4.3 Responses Linkages Responses 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 6for industry 2 Board Level champions provide continued purpose, direction and decision making Development of cross industry training modules & Education for target groups 1 1 1 1 H&W best practice guides created 1 1 Deliver Employee engagement by operationalising four enablers described by Mcleod and Clarke Make business case link with Health performance through improved cost benefit analyses and tools Collaborative industry approach to common issues 3 1 1 1 All stakeholders (incl. individauls taking ownership) understand roles in 1 1 making changes. Need forpositive data that is more leading / cross-discipline Competency frameholders for health and wellbeing line managers Opportunity for health / safety by design (eg cab ergonomics) Send signal through franchise programme for H&W Behaviour & Culture change activities. 2 Industry educational and competence requirements are mapped 2 1 Action based upon sound evidence 1 1 1 1 All trained on health at work as the norm Better awareness of H&W initiatives across dispersed workforce 1 1 Trade Union support 1 1 Companies re-evaluate health policies 1 Increase employee say in what is happening 2 1 1 1 1 Health and wellbeing monitoring technology Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 22 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 8 9 10 11 12 A 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 B C D E F G H I J K L 3 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 3 3 1 1 1 1 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk TOTAL 16 17 10 0 0 13 7 0 0 0 0 6 7 10 0 1 10 9 2 1 1 22 0 Rank 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Enablers Occupational Health and Wellbeing expertise Research and specialist advice to formulate the basics / strategy Railway conferences allow cross-fertilisation and promotion of best practice Incentives and penalties? - H&W as a contract criterion Best practice knowledge transfer Resources (Numbers of professionals) Data processing system / shared databases Voluntary standards improve organisational management of health to agreed levels Rail based health standards are reviewed and improved for better outcomes Improved equipment / reduced emissions Guidance enables better contracts developed with OH providers Supply chain standards ensure health is integrated into design Smart cards enable the health of employees to be tracked through their working life Increasing mechanisation to eliminate hazardous tasks Supply chain provides tools to reduce harm Regional OH provider centres based at railway premises Voluntary standards result in the scope of health activities being fully covered There is an increase in health skills purchased by the organisation New technology (eg otoacoustic emission testing) NSARE accreditation to include occupational health? Review frequency of D&A testing Regulator's forum Education outreach to schools Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 23 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Timescale short short 1 Short long short long short medium Medium Medium short Medium long Medium Medium long Medium Medium Medium long short Medium 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 1 1 3 2 1 Supply Chain Rail / External Body Health Specialist FOC TOC The number in the colour-coded columns shows the priority voting of specific stakeholder groups Infra-structure 4.4 Enablers 1 Total 4 4 3 2 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 This table shows the identified linkages between Enablers and priority Drivers, Stakeholder perspectives and H&W Challenges. The right hand column indicates total number of linkages. Rank 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Ageing workforce / longer working life Need to raise Health higher up Corporate Agenda Social attitudes driving changes in work / life balance Overcoming entrenched rail culture that health risk ‘not an issue' Design with roles and people in mind (RTS) Equipment supplied with health issues Regulation on health risks, ageing disorders & equality Better OH Contracts Rising Obesity Evaluation of role of fit notes Technology advances & automation Need for reliable, timely, consistent & transparent data Poor health management limits ability to work Management of individual health risks Lack of individual resilience and adaptability Fatigue / shift patterns Stress, Anxiety and Depression Access for all to quality OH services Musculoskeletal disorders Engagement Deficit Stress (Trauma management following suicides) Future occupational cancer burden – shift work, DEEE Presenteeism Absenteeism 4.5 Enabler Linkages Enablers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 A B C D E F G H I J K L TOTAL Occupational Health and Wellbeing expertise 0 Research and specialist advice to formulate the basics / strategy 2 1 3 1 1 4 2 1 1 16 Railway conferences allow cross-fertilisation and promotion of best practice 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 24 Incentives and penalties? - H&W as a contract criterion 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 7 Best practice knowledge transfer 1 1 2 Resources (Numbers of professionals) 0 Data processing system / shared databases 0 Voluntary standards improve organisational management of health to agreed 0 levels Rail based health standards are reviewed and improved for better outcomes 0 Improved equipment / reduced emissions 0 Guidance enables better contracts developed with OH providers 0 Supply chain standards ensure health is integrated into design 0 Smart cards enable the health of employees to be tracked through their 0 working life Increasing mechanisation to eliminate hazardous tasks 0 Supply chain provides tools to reduce harm 0 Regional OH provider centres based at railway premises 0 Voluntary standards result in the scope of health activities being fully covered 0 There is an increase in health skills purchased by the organisation 0 New technology (eg otoacoustic emission testing) 0 NSARE accreditation to include occupational health? 0 Review frequency of D&A testing 1 1 1 3 Regulator's forum 0 Education outreach to schools 0 Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 24 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 4.6 Linkages Key Rank 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Rank A B C D E F G H I J K L Driver / Perspective Ageing workforce / longer working life Need to raise Health higher up Corporate Agenda Social attitudes driving changes in work / life balance Overcoming entrenched rail culture that health risk ‘not an issue' Design with roles and people in mind (RTS) Equipment supplied with health issues managed (e.g. built with ergonomics in mind) Regulation on health risks, ageing disorders & equality Better OH Contracts Rising Obesity Evaluation of role of fit notes Technology advances & automation Need for reliable, timely, consistent & transparent data Challenges Poor health management limits ability to work Management of individual health risks Lack of individual resilience and adaptability Fatigue / shift patterns Stress, Anxiety and Depression Access for all to quality OH services Musculoskeletal disorders Engagement Deficit Stress (Trauma management following suicides) Future occupational cancer burden – shift work, DEEE Presenteeism Absenteeism Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 25 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Workshop 18 11 11 9 8 4 8 4 7 4 6 4 Workshop 16 14 10 9 9 8 8 7 7 6 6 5 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk % 6% 4% 4% 3% 3% 1% 3% 1% 3% 1% 2% 1% % 9% 8% 6% 5% 5% 5% 5% 4% 4% 3% 3% 3% 5. Detailed exploration of H&W Challenges (explored in breakout groups) Team 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Responses Team Team Team Team Team Comments 1 2 3 4 5 Development of cross industry training modules Board Level champion for this agenda Industry best practice guides created Engagement-4 enablers as described by McLeod and Clarke Develop and Validate H&W assessment for Railway staff Create accurate and usable ergonomic design specs Send signal through franchise programme for H&W VR NL JP JT inc "Training courses & Education for target groups" and "Competency frameholders for health and wellbeing line managers" SW OK GC CM inc "Make business case link with Health performance" MT SM DE JG PA KA BJ PW SM GL DH SC DB MG SA TR See over for outputs from breakout group exploration of Priority Responses & Enablers. Key: Black text: Red text: Copyright Institute for Manufacturing original team input carousel group comments indicates agreement indicates disagreement Page 26 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Team: 1 Cross-industry training for line managers Timescale to Full Implementation GND 2015 Required Develop training material and performance assessment criteria for line Response / Action managers DfT Include in ITTs ORR RM3 model TOCs FOCs Work together to develop standards and support implementation Network Rail The Industry Needs to… Have completed research; help development workshops of produced cross-industry training standards and materials Workforce & TU Others RSSB, OCC health providers Legal compliance; moral responsibility; reducing absenteeism - lost time - financial losses; positive health and safety culture impact; engagement Addresses Key Drivers & Stakeholder increase; significance of risks not fully identified/understood; poor customer service Needs ...because: We want to create an environment where people are safe and enjoy working and meet out legal obligations Addresses Key Health & Wellbeing Challenges / Opportunities By educating managers and providing them with the tools to manage their people effectively Benefit in delivering Rail Workforce H&W Benefit in Efficient & Productive Railway Likelihood of adoption and success Costs to implement (1=High / 5=Low) Knowledge gap; not knowing how to deal with issues; breaking down stigmas; lack of 'softer' skills; opportunity to make wellbeing and OCC health MGT part of 'business as usual' - culture change; educate/develop; share good practice; better partnership working with OCC health specialists Enable managers to successfully identify and manage OCC health risks on both individual and company level 5 Consistency in standards/health management across industries Management that then medicalised Reduced absenteeism This will deliver the following benefits for the Rail workforce and the industry as a whole… Increase productivity Reduce absenteeism Improve quality of life at work and home 5 High - due to legal requirement and impact on business management/financials 4 ...with the following costs and likelihood of success Negligible costs compared to short and long-term benefits R&D, facilitations, release, materials 3 Other Key Enablers Sound underpinning data and related issues Corporate, union, management, regulatory support Potential barriers & how to overcome them Lack of resource - sharing resource, RSSB support Parent company mandates; Lack of MGR willingness to develop Future proofing Enablers, barriers and mitigating actions include… Board level committee industry-wide adoption culture change Knowledge Gaps & Next Steps in validation / evaluation: R&D, peer reviews Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 27 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Team: 1 Milestones 2014 Short R&D including workshops 2016 End of 2015 materials available 2017 Roll-out delivery TOCs FOCs 2019 Embed in industry wide culture 2018 review effectiveness RM3 RM3 Release MGRs for training Participate in workshops ROGS update Assist in review and update Network Rail RSSB 2020 Consider inclusion in ITT DfT ORR Medium Produce materials Data collation Lead review and update Suppliers InfraCos Workforce & TU Participate Others Participate (OCC health) Consultation Participation of MGRs Participate in review and update Participate in review and update Other Key Enablers eg Knowledge; People & Skills; Facilities & Infrastructure; Standards & Regulation; Partnerships & Collaboration External Stakeholders Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 28 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Long 2025 Team: 2 Board level champions and business case Timescale to Full Implementation Required All director's role and all should lead Response / Action IOD checklist Adopting an approach that health is considered in all decisions would facilitate discussion at board level Determine how/who will be champion Should they leave a healthy lifestyle themselves The Industry Needs to… Each member needs to have a board level champion (clearly identified) for H&W How do we get the CEO/board member aware they need a champion DfT ORR TOCs FOCs Network Rail Workforce & TU Others Supply chain Business case for H&W Addresses Key Drivers & Stakeholder -Money -Ethics/reputation -Good for our TU members -Long term sustainability onwards) Needs For sustainability, avoid flash in the pan and tokenism Focus on using board level coaches. Get them to influence CEOs to benefits Addresses Key Health & Wellbeing Challenges / Opportunities The elements in each organisation which feed in to above Both short term 'fixes' and long term delivery are importance. Key word is 'both' Benefit in delivering Rail Workforce H&W Part of critical enabler of everything else (does not deliver in own right) Benefit in Efficient & Productive Railway Likelihood of adoption and success Costs to implement (1=High / 5=Low) -Works for short and medium and long term (CP4, 5, 6 and ...because: It makes good sense (business case is clear) Addresses organisation specific elements in both short and long term This will deliver the following benefits for the Rail workforce and the industry as a whole… Critical enabler of everything else so makes it all happen 5 Board member therefore it all happens 5 2 Many board pressures/so much else is happening Needs to be on one page of A4 (business case) e.g. increases profit/EBIT/ROI PTC No 'killer slide' at present One business case used multiple times ...with the following costs and likelihood of success Low cost but needs agreed killer slide to out through board stuff Cheap (very cheap) 5 Other Key Enablers Good data on cost of poor H&W to the business i.e. obvious and 'hidden' costs e.g. absence through poor management etc Good model from the H&W outcomes to business bottom line Potential barriers & how to overcome them Industry culture either 'ignore' or 'if you don't like it get lost' Enablers, barriers and mitigating actions include… Needs more research to get costs/outcomes defined/agreed and must challenge and change industry culture Knowledge Gaps & Next Steps in validation / evaluation: Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 29 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Team: 2 Milestones DfT ORR TOCs FOCs Network Rail RSSB 2014 Short 2016 Identify champions Agreed business case(s) 2017 Medium Developed strategic plans to improve H&W Adapt/send right signals in franchise model Adapt/send right signals by active supportive rewards Identify champion 2019 Review of actual business benefits of improved H&W Do not penalise economic success Use industry model to build your business case Identify champion Use industry model to build your business case Develop adaptable business case methodology Build model linking H&W outcomes to business performance Individual co plans and strategies Individual co plans and strategies Plan do review Plan do review Suppliers InfraCos Workforce & TU Work with employers to support the activity because it is good for business hence good for TU members Others Other Key Enablers eg Knowledge; People & Skills; Facilities & Infrastructure; Standards & Regulation; Partnerships & Collaboration Political will to support in reality not just soundbite (No distraction from HS2) Start process at RSSB board Guidance helps to define: 1) How do we identify a champion 2) How to influence then 3) Define their role External Stakeholders Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 30 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 2020 Long 2025 Team: 3 Industry best practices guide Timescale to Full Implementation The Industry Needs to… Survey: QHRC; HSE; NICE Link: SEQOHS Link up ARIOPS MD team Required Collaboration and sharing of best practice from all rail areas of business DfT Response / Action regarding health and wellbeing ORR I think there is already plenty of guidance TOCs FOCs Network Rail Workforce & TU Others ARIOPS/ ORR/ RSSB/ BENCHMARK Uniform approach to addressing health and wellbeing in rail Addresses Key Drivers & Stakeholder Needs ...because: Clear guidance and consistency = improved engagement, productivity, attendance, work/life Addresses Key Health & Wellbeing Challenges / Opportunities Health conditions but also policies and procedures impact on health Benefit in delivering Rail Workforce H&W Benefit in Efficient & Productive Railway Likelihood of adoption and success Costs to implement (1=High / 5=Low) Obesity, MSD, fatigue/shift working, stress, resilience, bullying/harassment, ageing workforce, proactive policies - common sense If this is a collaborative approach - resources/evidence based to support all 5 Right time railway = happy customers - increased revenue, trust in service, engaged workforce Need to evaluate quality of BP recommending - techniques available at literature reviews This will deliver the following benefits for the Rail workforce and the industry as a whole… Evidence based resource Increase revenue Better engagement 5 If communicated well with ALL stakeholders, develop 'host' site group with forum access - acceptable to all (e.g. ORR) 5 ...with the following costs and likelihood of success Stakeholder commit Initial costs high but long term benefit will support business case Initial costs high to develop - however ongoing costs will be moderate 2 Other Key Enablers Motivation and passion, benchmarking other industries and organisations, facilitated Potential barriers & how to overcome them Disagreement - what is good practice - right people Risk adverse - technology vs. standards Enablers, barriers and mitigating actions include… Benchmarking 'Risk averse'… Power plays Knowledge Gaps & Next Steps in validation / evaluation: Forum FAQ - identify issues and knowledge gaps Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 31 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Team: 3 2014 Milestones Select project manager and committee DfT ORR Short 2016 2017 Collate data and info Medium Bench mark Determine best practice 2019 Web based tools/forum Fund Facilitate TOCs FOCs Network Rail RSSB Facilitate Suppliers InfraCos Workforce & TU Others ARIOPS Other Key Enablers eg Knowledge; People & Skills; Facilities & Infrastructure; Standards & Regulation; Partnerships & Collaboration External Stakeholders Share best practice and develop Move on to industry standards Possible hosts of meter are NSE/ORR Other professionals HSE, FOM, SOM, AOHNP Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 32 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 2020 Long On-going review 2025 Team: 4 Engagement Timescale to Full Implementation Required Industry needs better engagement on health issues Response / Action Action - in line with the 4 enablers: Narrative, Engage managers, Employee voice, Integrity DfT HLOS could include collaborative working requirement ORR Encourage engagement - enforce if necessary TOCs FOCs Do it Network Rail Do it Workforce & TU Do it Others OCC health profession facilitate and encourage join up 4 (attitudes) and 2 ( high in corporate agenda) Addresses Key Drivers & Stakeholder Needs Addresses Key Health & Wellbeing Challenges / Opportunities Benefit in delivering Rail Workforce H&W Benefit in Efficient & Productive Railway Likelihood of adoption and success Costs to implement (1=High / 5=Low) The Industry Needs to… Have a strategy for encouragement that encourages manager/employee engagement and makes it work right consistently over time ...because: Engagement will drive health up the corporate agenda and promote change in attitudes to health and you get better management of individual health risks and minimise engagement deficit H (engagement deficit) and B (management of health risks) This will deliver the following benefits for the Rail workforce and the industry as a whole… Greater clarity gives us better management leads to getting right things done right first time and workforce healthy 4 3 ...with the following costs and likelihood of success Costs minimal - it is time commitment for existing people 3 Net cost - example: full time health and safety reps 5 Other Key Enablers Absolutely vital key enabler is CEO level champions (like Higgins) who does it and promotes it Potential barriers & how to overcome them Middle management 'inversion' layer. 'Die hard'/political TU person Enablers, barriers and mitigating actions include… Knowledge Gaps & Next Steps in validation / evaluation: Mutual understanding of running a 'just culture'. Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 33 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Team: 4 Milestones 2014 Short 2016 Engagement needs analysis by each company driven by board/CEO champion 2017 Define engagement strategy/narrative Where are we? Medium Where do we want to get to? 2019 Sustain DfT ORR State ORR want industry to do this TOCs FOCs Plan and do the engagement Network Rail Plan and do the engagement Check it's happening Middle management: Consistent messages Training Middle management: Consistent messages Training Testing, validation and adjustment Testing, validation and adjustment RSSB Suppliers InfraCos Workforce & TU Others Other Key Enablers eg Knowledge; People & Skills; Facilities & Infrastructure; Standards & Regulation; Partnerships & Collaboration Managers having the time Training/briefing in how to have proper health conversations External Stakeholders Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 34 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 2020 Long 2025 Team: 5 Develop and validate H&W assessment for railway staff Timescale to Full Implementation 6 months to pilot; 5 years to full roll-out Required Tailored self report questionnaire (format flexible) for specific rail job Response / Action families to inform and evaluate health strategy Can this build into H&W assessment work done by RSSB? There is mileage in this. Potential quick win DfT Franchising ORR Sponsor? Regulate TOCs FOCs Network Rail Contractual provision Workforce & TU Evidence based Others RSSB specialists Obesity; ageing workforce; SAM; MSDs; Mental health; Litigation; Standards for franchising; league table for KPIs; lower insurance premiums (PL, Addresses Key Drivers & Stakeholder EL); level playing field Needs Addresses Key Health & Wellbeing Challenges / Opportunities Benefit in delivering Rail Workforce H&W Benefit in Efficient & Productive Railway Likelihood of adoption and success Costs to implement (1=High / 5=Low) ...because: To improve health and reduce cost. Currently £220m (absence top 5 conditions) As above. Nothing similar currently exists Need for anonymisation 5 4 Targeted interventions Industry specific Validates benefits delivered to employees Makes business case This will deliver the following benefits for the Rail workforce and the industry as a whole… Inform effective programmes and priorities for key risk areas to be addressed in the work place putting rail at forefront of H&W movement Reduced healthcare costs, ROI Reduced absence Improved engagement and productivity, metrics 80% ...with the following costs and likelihood of success £50k investment, 80% uptake 4 £50k to develop questionnaire 5 Other Key Enablers Potential barriers & how to overcome them The Industry Needs to… Develop a H&W assessment for specific rail job families covering all aspects of work that impact on wellbeing Enablers, barriers and mitigating actions include… Early adopters drag others along MD scepticism - funding RSSB? Cost Lack of ownership Knowledge Gaps & Next Steps in validation / evaluation: Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 35 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Team: 5 2014 Milestones Study outline Short 2016 2017 Medium Publish pilot results 2019 Wide adoption DfT ORR Sell proposition Rolloct to TOCs/FOCs/IC Complete pilot TOCs FOCs Network Rail RSSB Potential sponsor Identify pilot IC/TOC/FOC Evaluate and review Suppliers Complete pilot InfraCos Workforce & TU Others Other Key Enablers eg Knowledge; People & Skills; Facilities & Infrastructure; Standards & Regulation; Rolloct to IC Consult unions and OH Identify job families Design questionnaire 2 year review cycle Partnerships & Collaboration External Stakeholders Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 36 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 2020 Long 2025 Team: 6 Create accurate and usable design specs - ergonomics Required Research (incl. what's been done) Response / Action Implement research outputs across all industry Timescale to Full Implementation 5 years DfT Provide guidance and info ORR Satisfy legal obs. TOCs FOCs Implement specs Network Rail Implement specs Workforce & TU Healthier, TU demonstrate success Others RSSB - specify The Industry Needs to… Set standards by unearthing what exists and researching what doesn't Ageing workforce (1) ; Obesity (7); Workforce diversity; MSDs; Psychosocial; technological advances; ergonomics Addresses Key Drivers & Stakeholder 1,6,7 Psychosocial aspects becoming more important Needs ...because: It's a major source of ill-health and further issues developing solutions for future can be found Addresses Key Health & Wellbeing Challenges / Opportunities Broad application across industry to enable better wellbeing Benefit in delivering Rail Workforce H&W Benefit in Efficient & Productive Railway Likelihood of adoption and success Costs to implement (1=High / 5=Low) Covers most A-L to greater or lesser extent Wide range of application and benefit across all sectors This will deliver the following benefits for the Rail workforce and the industry as a whole... 5 Creates 'objective' info for managers 4 On basis of business case and setting of standard ...with the following costs and likelihood of success 4 Principles often exist. Research costs relatively low 5 Other Key Enablers HSE, university and academic researchers. International knowledge sharing Potential barriers & how to overcome them Lack of awareness and training (understanding) Enablers, barriers and mitigating actions include… Who will fund? RSSB? Knowledge Gaps & Next Steps in validation / evaluation: Lack of specific data. People of influence unaware of it Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 37 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Team: 6 Milestones 2014 Short 2016 Plan 2017 Medium 2019 Standard 2020 Long Review DfT ORR Integrate TOCs FOCs Apply STD Network Rail RSSB Suppliers Discover existing research Consultation Standard Validate Apply learning Integrate into specs Reserved to fill in blanks Apply STD Validate Validate application of standard Integrate into specs InfraCos Feedback Feedback Gather user feedback Apply STD Workforce & TU Others Other Key Enablers eg Knowledge; People & Skills; Facilities & Infrastructure; Standards & Regulation; Partnerships & Collaboration External Stakeholders BS1/HS1 working group on EU cab ergo standard OH specialists Awareness Training competence Unions Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 38 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 2025 Team: 7 Franchise programme Timescale to Full Implementation 2018 Required Send signal through franchise Response / Action Programme for health and welfare DfT Include in franchise programme ORR Engage with DfT and use knowledge, expertise, policies and data collection TOCs FOCs DfT to engage with and understand issues Network Rail DfT to engage with ek Workforce & TU DfT to engage with ek Others ROSCOLS; supplies; NSARE The Industry Needs to… DfT signed important Overcoming franchise system and short termism 1,2,4,5,8,11,12 Addresses Key Drivers & Stakeholder Needs ...because: HECP to embed H&W into TOC planning Addresses Key Health & Wellbeing Challenges / Opportunities to improve OH, absence and productivity Benefit in delivering Rail Workforce H&W Benefit in Efficient & Productive Railway Likelihood of adoption and success Costs to implement (1=High / 5=Low) Investment long term to reduce absence due to ill health delivering healthy, more productive workforce. Aging workforce Mobile workforce A-L This will deliver the following benefits for the Rail workforce and the industry as a whole... 4 4 Success depends on implementation - effective monitoring and enforcement ...with the following costs and likelihood of success 4 Low as % of long term franchise bid 5 Other Key Enablers I.D best practice, data, skills, better info business benefits Potential barriers & how to overcome them Enforcement - life cycle of franchise. Lack of political support - industry push Enablers, barriers and mitigating actions include... Knowledge Gaps & Next Steps in validation / evaluation: Need CBA evidence. Build industry support. ID best practice, rail and elsewhere Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 39 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Team: 7 Milestones DfT ORR TOCs FOCs Network Rail RSSB Suppliers InfraCos Workforce & TU 2014 East coast ITT Short 2016 TPE 2017 Medium Franchise Franchise Involve industry Review and Review and Monitor, Monitor, Review and in developing engage with report and engage with report and engage with spec industry enforce industry enforce industry Advise DfT on best practice, policies, bus case Advise DfT on best practice, policies, bus case Advise DfT on best practice, policies, bus case Franchise specific Advise DfT on best issues practice, policies, bus case Advise DfT on best practice, policies, bus case Advise DfT on best practice, policies, bus case TU - Agree principle Advise DfT on best and provide input practice, policies, bus case Monitor, report and enforce 2019 Franchise Review and engage with industry Monitor, report and enforce Knowledge; People & Skills; Facilities & Infrastructure; Standards & Regulation; Review and engage with industry Training KPI and develop Partnerships & Collaboration External Stakeholders Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 40 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 Long Franchise Others ROSCOS MINISTERS Other Key Enablers eg 2020 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Monitor, report and enforce 2025 Appendices A. B. C. D. E. Participants Workshop Feedback Responses & Enablers – Detailed Comments Workshop Process Participant Perspectives Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 41 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Appendix A: Workshop Participants Name Bridget Juniper Caroline Meek Dame Carol Black Dave Bennett David Hitchcock Diane Eversfield Gary Cooper Geoff Ledger Jay Thompson Jennie Pitt John Gillespie Keith Atkinson Mark Gaynor Megan Taylor Natasha Lelyveld Owen Keyes-Evans Paul Appleton Paul Whitehead Richard Sharp Sharon Allaway Stephen Watson Steve Coe Susan Murray Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Company Work and Well-Being Ltd Network Rail Expert Adviser on Health and Work to the Department of Health ASLEF Ergonomics Design Safety Consultancy Training Research TFL National Taskforce Bombardier Transportation UK Ltd Greater Anglia East coast ORR ORR DFT Southern Greater Anglia Consultant Occupational Physician ORR Balfour Beatty Rail Ltd Murphy Group Marum Healthcare Arthur D. Little UK - Cambridge TSSA UNITE Page 42 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Appendix B.1: Feedback Joining instructions and preworkshop information Opening remarks and introduction to the workshop Facilitation of the workshop Piccies Structure / process of the workshop Opportunity to participate and contribute Make-up of workshop participants Catering Venue Time keeping Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 43 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 5. Excellent 4. Very Good 3. Good 2. Satisfactory 1. Poor 97% Excellent, Very Good or Good 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Appendix B.2: Feedback I enjoyed the workshop I found the workshop stimulating I feel I have contributed to the workshop I found my participation worthwhile The workshop provides useful insights 5. Strongly Agree 4. Agree 3. No comment 2. Disagree 1. Strongly Disagree 98% Strongly Agree or Agree Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 44 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Appendix C. Responses & Enablers – Detailed Comments Rank Responses 1 2 3 4 5 Board Level champions provide continued purpose, direction and decision making for industry Development of cross industry training modules & Education for target groups H&W best practice guides created Deliver Employee engagement by operationalising four enablers described by Mcleod and Clarke Make business case link with Health performance through improved cost benefit analyses and tools Comments Decide whether industry approach is voluntary or mandatory to health and wellbeing; Board level champion for this agenda; Need to raise health higher up agenda; Directors and senion management buy in - need their engagement to make it work; Compete in the jobs market by emphasisng that we're companies the properly manage people's health - we become employer of choice Education/health interventions to be delivered in a different/engaging format; Education program developers; Development of crossIndustry OH Training Modules for Line Managers Establish clear stress management protocol in across industry; Focus on what OH services do (and the expertise required for that) and less on the mechanisms/arrangements by which they do them The four enablers for engagement as described by Mcleod and Clarke operationalise them; Articulate the industry and company business cost for improved health wellbeing; Make business case to link health with performance (to convince C-suite) 6 Collaborative industry approach to common issues Better collaboration between providers; Achieve partnership of trust between all players; OH and GPs working in collaboration; TUs management regulators to have a forum to promulgate best practice; "Health" implications must be a standard question all management raise when considering changes. Collaborate cross functionally (e.g. TOCs, TU, OCC health) to share data and best practice 7 All stakeholders (incl. individauls taking ownership) understand roles in making positive changes. Ensure all workers are involved in procurement of equipment; 8 9 10 11 12 13 Need for data that is more leading / cross-discipline Competency frameholders for health and wellbeing line managers Opportunity for health / safety by design (eg cab ergonomics) Send signal through franchise programme for H&W Behaviour & Culture change activities. Industry educational and competence requirements are mapped 14 Action based upon sound evidence 15 All trained on health at work as the norm Better awareness of H&W initiatives across dispersed workforce 16 Creat cross discipline data sets Create accurate and useable ergonomics design specifications and data Send signals through franchise programme that health and wellbeing matters; Extend no blame culture; A "just" management culture (rather than a default culture); Management and Tus must adopt a commitment to "evidence based" approach to health issues; Develop and validate health and wellbeing assessment specifically for railway staff to inform priority actions Train line managers in people skills; Do practical things that help e.g. job design, clothing design, workplace design 17 Trade Union support 18 Companies re-evaluate health policies TUs must step back from wielding "health and safety" for non-health-and-safety puposes and management must accept health issues properly raised; Create award programme to encourage appropriate change; safety manage health Ensure that equality considerations are embedded in all policies and actions reflect equality act and affect action taker 19 Increase employee say in what is happening Ensure all workers are involved in procurement of equipment; Recommendation of the needs of the business against that of the individual 20 Health and wellbeing monitoring technology Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 45 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Appendix C. Responses & Enablers – Detailed Comments Rank Responses 21 Embrace diversity of workforce 22 Implement all 10 recommendations in briefing Intended use of data outputs is understood during 23 the planning stage for collection. Organisational roles take a holistic approach to 24 health rather than functional Improved understanding of OH issues in rail by OH 25 practitioners 26 Develop and Validate H&W assessment for Railway staff esp. ‘high risk’ workers 35 Companies publish improved health data indicating the progress of the rail industry Informing policy / standards development for OH Health data collection supports reasoned decisions to drive change. Risks are proactively addressed Leadership creates conditions for change Health professionals improve health decisions within organisations Rehabilitation plans reduce absence costs Employee health and wellbeing issues also impact passengers Awareness of & training for stress issues 36 Communication leads to access to information for all 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 37 38 39 Comments Embrace the diversity of the workforce - treat people as individuals Better collaboration between providers of H&W - good practice sharing ideas and intentions Risk assessments carried out on shift working with involvement of workers; Develop machanism for line manager to assess workforce 'fitness for work' when planning work; Leaders introduce employee health risk management measures into business task management tools; Pro-active health surveillance for exposed worker groups; Medicals for all regardless of role; Establish guidelines for recording of health data to consider trends and inform "FOWS" Translate proven health activities from other industries into rail Success is measured and reviewed before wider industry roll-out. Industry productivity is enhanced to improve successful outcomes for all. Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 46 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Appendix C. Responses & Enablers – Detailed Comments Rank Responses Comments 40 Job roles altered to become more engaging Clinical leadership provides direction for 41 development of industry’s health capabilities More effective communication between OH service 42 Good communication within diverse organisations i.e. internet, intranet, written, visual providers and line managers 43 Clinical effectiveness is managed within industry Hazard specific working groups tackle difficult health 44 Work/life balance (shift management) hazards 45 Guidance is developed to assist railway physicians Create cross-discipline (e.g. OH and FLEET) datasets to enable empirical thinking and understanding; Assess effectiveness of interventions 46 Improved occupational health reports to determine impact and success Better cooperation between medical professionals Poor GP and OCC health judgements. Too much detail of what can't be done rather than what can. Guidance issued; Shift work that ensures 47 eg OHS and GPs that BSG assessments are carried ut on shift patterns with involvement of the workers. 48 Logistics of remote working 49 Link reward (or salary sacrifice) to health & wellbeing 50 Diet & Nutrition advice (engage food services) Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 47 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Appendix C. Responses & Enablers – Detailed Comments Rank Enablers 1 Occupational Health and Wellbeing expertise 5 6 Research and specialist advice to formulate the basics / strategy Railway conferences allow cross-fertilisation and promotion of best practice Incentives and penalties? - H&W as a contract criterion Best practice knowledge transfer Resources (Numbers of professionals) 7 Data processing system / shared databases 2 3 4 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Voluntary standards improve organisational management of health to agreed levels Rail based health standards are reviewed and improved for better outcomes Comments Clearer understanding of OCC and health risks in rail; OH aspects to fall into two categories: physical and mental. Within management this needs to be holistically owned. R&D project; Make good H&W the easy option remove damaging optional drivers; Research and write taking healthy decisions (like taking safety decisions); Implement all ten rec's in briefing Embed H&W in all decisions relating to job, task and equipment design Ensure that policies are developed collaboratively to help prevent harassment and bullying Standardised language Improved equipment / reduced emissions Guidance enables better contracts developed with OH providers Supply chain standards ensure health is integrated into design Smart cards enable the health of employees to be tracked through their working life Increasing mechanisation to eliminate hazardous tasks Supply chain provides tools to reduce harm Regional OH provider centres based at railway premises Voluntary standards result in the scope of health activities being fully covered There is an increase in health skills purchased by the organisation New technology (eg otoacoustic emission testing) NSARE accreditation to include occupational health? Review frequency of D&A testing Regulator's forum Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 48 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Appendix C. Vision – Detailed Comments / Additions Vision component Additional comments Better workforce health and physical, social and psychological wellbeing Leadership and collaboration to drive long term health improvement A culture which demonstrates that health at work is everybody's responsibility A culture which demonstrates (etc) led by management . Getting managers and senior directors to engage in wellbeing and see as being as important as safety Change: A culture which demonstrates that health at work is manager's responsibility, work ing with individuals Nationalisation will help joined up work on OH. Not employers job to enforce health and wellbeing for individuals. Prevent bullying. Legal compliance and moving towards broader industry bestin-class An inclusive and sustainable workforce Effective management of health and wellbeing in order to give our work forces choices i.e. they can decide when to retire as opposed to having that decision imposed on them due to work related mental or physical problems. Shift work (including gender issues) Professionalised health and wellbeing provision in Rail Highlight/Stress/Sell The need for trained competent line manager. Training for all in dealing with mental health. Government OCC health service a good idea but should not displace good OCC. Health provision already in place. Train line managers. Join up activities on H&S and wellbeing. A more efficient and productive railway for the benefit of everyone Articulate better business benefit for health and wellbeing Working for the rail industry is a long, productive and attractive career Environmental wellbeing e.g. mess facilities Look after all workers including older workers An engaged and committed supply chain working together Involve workers in procurement process e.g. when buying vehicles and equipment (NB seating) Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 49 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Appendix D. Workshop Process Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 50 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Workshop agenda Morning 9:15 Registration & Coffee 9:45 Introduction, agenda and process 10:00 Participants share perspectives – Vision; Key Challenges & Actions needed 11:00 Prioritise Vision elements; Drivers and Challenges 11:15 Break 11:30 Identify leading Actions Needed 12:30 Lunch Afternoon 13:15 Identify breakout groups for Afternoon Session 13:30 Characterise priority Actions for Impact / Effectiveness 14:15 Develop Action Plan 15:00 Break 15:15 Present Elevator Pitch & Carousel Review 16:15 Review 16:30 Close Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Background and Aims of Workshop • Purpose of the roadmap: We are looking for a roadmap to bring about commitment and understanding for a series of well-planned, effective and prioritised tasks that a diverse range of stakeholders believe will improve health and wellbeing management within the railway and therefore the health and wellbeing of the Rail Workforce and the efficiency of the sector. • Commitment: Individual managers, companies aware and prepared, Managing Directors engaged, customer willing to act or request RSSB to act • Understanding: What tasks, costs, impacts? The organisations role? Role for RSSB/ industry? • Well planned: Timed well, those participating are able to act, coordinates with and benefits the customer, yearly costs align with industry’s capacity to meet them, meets new control period timeframe, customer has time to implement • Effective tasks: tasks are needed, cost effective, generate company action, generate industry action • Prioritised: By industry or organisational level of importance?, By sector? By Cost? By Stage? • Improve: industry level? Organisational /customer level? Both? At low cost? At high cost with high return? Evolutionary? Planned? Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Workshop Definitions Occupationa Contemporary thinking and government policy on workforce health recognise that health has three fundamental elements. • The effect of work on health (eg airborne contaminants, asbestos, musculoskeletal disorders, mental health) l Health • Fitness for work (eg safety critical tasks, drugs and alcohol testing, health assessments) • General wellbeing (eg obesity, smoking, sickness absence management, rehabilitation) Industry consensus, including the Industry Safety Meeting (ISM), now supports rail employers actively embracing these three elements. Wellbeing The three components of employee wellbeing, taken from Wellbeing, Productivity and Happiness at Work (Ivan Robertson and Cary Cooper, 2011), are said to be: 1. Psychological wellbeing – for example, the ability to handle the stresses of everyday life and maintain a positive attitude and sense of purpose 2. Physical wellbeing – for example, the amount of exercise, sleeping habits, alcohol 3. Social wellbeing – for example, a positive and supportive social network Engagement Employee engagement is a measure of how motivated an employee is to give their best to their job. It shows how well motivated, energised and inspired they are to ‘go the extra mile’. Engagement is uniformly measured via staff surveys and typically asks questions about pride in their company, would they recommend as a great place to work, belief in company vision and goals, a willingness to go beyond their job requirements and whether they are considering leaving at the present time. Companies with high levels of employee engagement experience greater profitability, reduced absence and greater levels of employee wellbeing, amongst many other benefits. See http://www.engageforsuccess.org/ for more information. “This is about how we create the conditions in which employees offer more of their capability and potential.” – David Macleod – author of UK Govt’s ‘Engage For Success’ report. Employee engagement should not be confused with how we communicate and interact with our people. Presenteeis m The term presenteeism is often interpreted in different ways. Robertson and Cooper (2011) suggest three attributes to the term: 1. Attending work when unwell 2. Putting in long hours but not working all of the time (often known as ‘face time’) 3. Working at a reduced level because of distractions (for example, going online) Additional attribute added: People who have a health risk factor that inhibits their ability to do their job (for example, obesity and manual work). Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Roadmapping- Linking future to present What? Why? Time Trends & D1 Drivers D2 M1 Markets M2 we now? & Capabilities T1 M4 O2 we want we get O3 O2 O1 T1 Where do M2 O1 Opportunities M3 How can Where are Technologies How? D2 T2 there? O4 T4 C3 to go? C6 T5 Funding Enablers Infrastructure Staff / skills Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Past 2014 CP4 Trends & Drivers Short 2016 2017 CP5 Medium 2019 2020 Long CP6 2025 Vision CP7+ Social Templates Technological Environmental Trends & Drivers What is shaping the future context and environment for H&W Economic Stakeholder Perspectives On-board WorkTrackside force Station & Other TOCs & FOCs Stakeholder Perspectives What are the needs of the different stakeholder groups Network Rail Suppliers InfraCos Other inc Health Professionals Health & Wellbeing Challenges Work-related Non work-related H&W Challenges: Current and Future Challenges (and Opportunities to improve) H&W Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other Responses Stakeholder Actions (eg for TOCs & FOCs; Network Rail; ORR, RSSB, ISLG & Contractors & Suppliers, OH, Tus; Workforce & Others Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Responses that could be put in place to deliver improved H&W outcomes and performance ...and associated Actions by Rail Stakeholders Other Other Enablers Knowledge People & Skills Facilities & Infrastructure Enablers and other resources also necessary for success Standards & Regulation Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Supply Chain Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk VISION Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR 2-Step Workshop process Step 1: Scan (‘Landscape’) - Large group activity - Broad scope - Share and capture perspectives - Link, focus and prioritise Step 2: Probe (‘Landmark’) - Small group activity - Focused scope - Share and capture expertise - Organise, plan and action Google Earth Copyright Institute for Manufacturing UK Robotics & Autonomous Systems Roadmap January 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Team: Response / Action: Cross-Industry Required Response / Action Industry needs consistent standards for data gathering, applied uniformly across the sector. Timescale to Full Implementation: 2016 Data Collection (Underpins much other work) DfT ORR Include in franchising model Define standards TOCs FOCs Network Rail Workforce & TU Others Involvement in ensuring data is useful for all stakeholders to actually drive improved H&W outcomes Addresses Key Drivers & Stakeholder Needs Wellbeing Challenges / Enables evidence-based investment in H&W by capturing benefits Opportunities Benefit in delivering Rail Workforce H&W Impact onWorkforce Needs and H&W This will enable effective communication of H&W activity 1 2 3 4 This will deliver the following benefits for the Rail workforce and the industry as a whole... Will enable cross-industry collaboration and synergies Better focussed intervention and meauserement of outcomes Will require widespread changes in numerous areas ...with the following costs and likelihood of success Significant start-up costs should soon be eroded through reduced duplication Significant initial costs will soon be recovered through more effective allocation of resources and reduced duplication 5 Benefit in delivering Efficient & Productive 1 2 3 4 ...and support appropriate intervention Will enable resources and action to be prioritised towards appropriate interventions Challenges Railway Impact on other Establish onsistent standards for data gathering, applied uniformly across the sector. ...because: Addresses need for transparancy and openness. Resolves under-reporting Addresses Key Health & The Industry Needs to... 5 Stakeholder Needs Likelihood of adoption and success across all stakeholder groups 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 Costs to implement (1=High / 5=Low ) Other Key Enablers Identify best practice in other / adjacent industries and non-UK Rail Enablers, barriers and mitigating actions Identify best practice in other / adjacent industries and non-UK Rail include... Potential barriers - and how to overcome them Compatibility of systems??? Knowledge Gaps & Next Steps in validation / evaluation: Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Are there any systems implications? Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Team: 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long Milestones Milestone 1 DfT Milestone 2 Map current practice and ORR Define full systems specification Define Draft systems specification TOCs FOCs Review Pilot Network Rail Pilot RSSB Pilot Suppliers InfraCos Workforce & TU Others Other Key Enablers eg Knowledge; People & Skills; Facilities & Infrastructure; Standards & Regulation; Partnerships & Collaboration External Stakeholders Benchmark adjacent industries Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Update systems & infrastructure Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Roll-out awareness & training Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 2025 Appendix E. Participant pre-work Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 59 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk ENABLERS RESPONSES H&W CHALLENGES & ACTIONS & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION Name: Simon Millward (ECML) 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: 1. 2. 3. Forward thinking and introduce opportunities for individuals to educate themselves which in turn influence lifestyle choices which impact themselves and their immediate families. Monitor trends to ensure OH and other health related services are current and appropriate Examine the environmental factors to develop ways that minimise the impact of these on individuals Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR •Collate difficulties experienced since the introduction of ‘fit notes’ Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Suppliers InfraCos Network Rail Health Professionals Other •Diet and nutrition advice •Staff food and food services being encouraged to form part of a balanced diet •Really manage OH/EAP providers to ensure you’re getting value for money. •Review working environments establish how much investment might be needed •Develop further industry standards taking into account ‘fit notes’ etc •Investment in working environment •Start to investigate how to get H&W into schools, colleges and the home •Salary sacrifice options to encourage participation •Work with local gyms/pools for open days/ trial periods – accessible prIcing •Cross TOC sports day/events? Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other •Work with schools and colleges to develop strong links to the industry needing balanced and healthy workforce (H, W, D&A policies) •Provide feedback to influence political agenda to ensure ‘fit notes/GPs’ link to OH industry specialists to ensure they don’t impose risk to the industry •Check uniforms are provide adequate •Review progress for management of OH/EAP to establish industry success to progress through all TOCs •Review industry standards •Develop a year long calendar so that we generate/encourage activities Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Knowledge People & Skills Copyright for Manufacturing Facilities & Institute Infrastructure •Education, Develop an industry calendar to have a UK roll out on key initiatives enabling charities and other organisations to join in •Roll out education road shows core sites •Establish how to engage with small locations (<35 FTEs) •Cross TOC working group to further develop •Central library for cross TOC collaboration Health & Wellbeing Roadmap •Working group to develop this area •Review Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk ENABLERS RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION Name: Paul Appleton 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: Excellence in the management of health Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR Cost of occ health – see ORR NR Determination chapter 11 - Occ health efficiency in determination. Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Suppliers InfraCos Network Rail Health Professionals Other •Healthy staff Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other •24/7 railway – shift work – fatigue management. •Move beyond simple counting of hours for shift work. Consult with staff on what works and what doesn’t. Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Other •Industry recognises that it has a problem •Workforce education Knowledge People & Skills Facilities & Infrastructure Standards & Regulation Supply Chain •Educate management in occ health issues so they can recognise problems, measure them and design controls. Copyright Institute for Manufacturing •Aging population •Loss of skilled staff due to health issues •Extension of retirement age – older people in the work force. •Takes on leadership rather than being driven •Collect occ health data rather than ignore issue. Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk ENABLERS RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION David Bennett, ASLEF 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: Accept all ten issues recommendations , and work towards implementation on an agreed timescale Accept ORR OH strategy, and work towards implementation on an agreed timescale Mainstream gender occupational safety and health good practice (GOSH) Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR • Embed gender occupational safety and health good practice (GOSH) •Review progress on embedding GOSH •Re-nationalise the railway! •Elect a Government with renationalisation as policy Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Suppliers InfraCos Network Rail •All - Set up Fatigue Risk management groups •Use recognised trade union health and safety reps – view as an asset not a “burden on business” •Review progress •HS reps consulted in good time, views given consideration, and allowed to develop skills •Fatigue risk management embedded •HS reps input valued and training not seen as a burden but as an asset Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other •All 3 of work related, non work related and lifestyle considered, but priority given to occupational risk – not just look at lifestyle of the individual - “blame the worker” “resilience” •Use ORR OH policy to assist •Review progress – would expect OH costs to be falling as health improves •ORR to monitor progress of policy •OH management embedded Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Other •Clinical – agree with recommendation on issue 5 OH market •Review progress •Healthier workforce, less stress, less absence, less injuries, with progress being measured by using good data, engaging workforce and using agreed collective bargaining machinery •Metrics –agree recommendation issue 1 on data •Review progress •Review if collective bargaining is being bypassed •Employee engagement should not be used to bypass collective bargaining • GOSH “mainstreamed” •Ensure funding for expanded nationalised industry •Behaviour changes and “nudging” must include managers and directors, not just imposed on the workforce. Knowledge People & Skills Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Facilities & Infrastructure •Agree recommendation issue 6 on training Health & Wellbeing Roadmap •Review progress •Occupational hygienists, ergonomists other health Dominic Oughton and do251@cam.ac.uk NABLERS RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION Name: Jennie PItt 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: To work collaboratively across the industry to become ‘employers of choice’ ,creating a healthy and engaged workforce that will better serve our passengers Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR •Significant organisational change as a result of the Intercity Express Project •Technological advances resulting in automation of tasks (Medium to Long term) •Change in franchise – job insecurity •Economic Uncertainty (Medium to Long term) Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Suppliers InfraCos Network Rail Health Professionals •Training for managers in managing absence/ health & wellbeing of employees •Introduction of ‘truly’ randomised D&A screening •OH Suppliers - understand the TOC/industry vision for H&W Work in Partnership together •Review job design in line with technological changes Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other •Challenge - Exposed worker groups Opportunity- Consider how Health Surveillance can be established •Challenge - Psychosocial impact of work Opportunity - Improved people management /health management training for managers •Use management information to inform Health & Wellbeing Strategy Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Other •Mental Health First Aid training for managers •Review terms and conditions •Aging workforce – ongoing review/changes to pension provisions (Medium to Long term) •Establish joint forum across the industry to include OH suppliers, HR & Safety professionals •Use management information to inform Health & Wellbeing roadshows •Link reward to health & wellbeing e.g. Discounted gym membership, cycle to work scheme etc. Knowledge People & Skills Facilities & Infrastructure Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Standards & Regulation •Share initiatives •Improved reporting/management information Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk TRENDS & VISION DRIVERS Name: Sharon Allaway 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: The need for an industry culture that acknowledges the need to consider health in every business decision made Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR •Introduction of government Health and Work Service (late 2014). •Introduction of Train Driver Licencing Regs for new entrants (2014) •Introduction of Train Driver Licencing Regs for existing drivers (2018) •Anticipation that morbidity will be compressed into final few days / hours of life thus reducing likelihood of severe illness during working life ENABLERS RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES •Pre-employment screening to be tailored for job-specific hazards Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other •Creation of a guidance / a schematic outlining how individual employers can integrate their health and wellbeing offerings to deliver a specific goal eg. increased productivity or Employer of Choice that will allow a staged approach to this work •Adopt the Workability Index as a tool to be used by OH for helping predict length of employees’ working lives •Develop H&W services that employees can access to help themselves stay healthy Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Other •Leaders to take the long view and embed wellbeing and resilience into everyday working life •Leaders to introduce employee health risk management measures (leading and lagging) into business risk management tools •OH to focus more intently on cultivating a culture of preventive healthcare in anticipation of working with conditions that have ill-defined symptoms eg stress, chronic fatigue, multiple chemical sensitivity, diffuse pain syndrome, psycho neuro immunology •Investigate the links between actions managers take and the reduction in stress Knowledge People & Skills Facilities & Infrastructure Standards & Regulation Supply Chain Copyright Institute for Manufacturing •Create Knowledge Officer role(s) to help achieve the integration of health and wellbeing with other business practices Health & Wellbeing Roadmap and undertake knowledge •Develop •OH to gear themselves up to help employees change their lifestyles •Create an Award Programme for the railway industry cf. Everett Coop Award (- to bring about critical attitudinal and behavioural changes in the American health care system, so that providers and consumers employ its vast resources with increasing knowledge and understanding.) •Achieve a partnership of trust between employers and employees in relation to health and wellbeing rather than one of blame as typified by managing for attendance •Celebrate award of first prize for Award Programme Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Name: Diane Eversfield 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 ABLERS RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: The culture and policies in the UK Rail industry, from CEO to worker in Client Organisations and all parts the supply chain, fully embrace the attainment of a healthier workplace. Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR Better understanding required of the cost to business of both absence and presenteeism. What is the deleterious impact on productivity and wellbeing of person being stuck in an unsuitable job with very low job satisfaction Will there be any impact of the forthcoming government driven changes to OH provision Learn / enquire about organisational culture in relation to health. What are the specific health needs of the employees Changes in public health strategy and moves to mo local policy setting and provision A strategy for culture change – to a culture that recognises the importance of employee health to industry performance, a culture where there is no stigma attached to having mental health problems A long term strategy for health improvement Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Ensuring employees have access to fast good quality psychological support Ensuring employees at risk of trauma have fast access to specialist counselling Ensuring employees have access to health improvement opportunities Closer cooperation between NHS, private & in-house OH providers and specialist organisations and charities Develop a cross organisational group to steer, support and influence health improvement work Make better use of technology and provide good q training to improve staff knowledge – some basic computer skills training may be required Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other Better understand the impact of shift working on health and wellbeing Improve employee engagement with assessment and treatment processes Achieve much more timely and useful GP & Specialist reports Improve staff canteens (menus and food labelling) Remove from the workplace vending machines plying unhealthy drinks and snacks Explore the use and impact of life coaches, perso trainers, health coaches within the industry Explore the opportunity of workplace health activat across the industry Utilisation of in house health statistics to drive hea promotion – ie anonomised sickness absence reas and health data from periodic medicals ie BP,weigh and identify priorites Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Other Work on getting buy in from the highest levels – not just words but actions Good – informative communications with employees on health and health related matters and services/support available to them – various ways to communicate and identify fun resources Undertake more structured research to better understand the impact of interventions on health and wellbeing and absence from work Think about interventions/ support/ strategies that focus on specific organisational needs Work in partnership with employees, don’t do it all for them, give them the opportunities, involve them in the planning OH Nurse degree training is currently Public Health based rather then Occupational Health focussed – change to include more OH/health and wellbeing content. Training for employees and managers – how well does the industry support the Look at the skill set for recruitment of people mana – are people skills a high enough priority? Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Knowledge Include time in working day to allow People & Skills employees attendRoadmap health fairs/training Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Health &to Wellbeing Facilities & ENABLERS RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION Name: Mark Davies (Carillion) 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: “Treating Health Like Safety”. Our strap lines always say … Safety First, we need it to be “Health and Safety” First Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR • Transient Workforce • Direct Employment • Inclusion (Ageing Workforce) (Ageing Workforce) (Ageing Workforce) Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Suppliers InfraCos Network Rail Health Professionals Other • Make Health simpler • Motivated Workforce • Increased Productivity Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other • Awareness and Education • Positive Intervention by Management and Individual • Industry Changed Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Other • Make Health simpler • Management Ownership • Healthy Behaviour by All Knowledge People & Skills Facilities & Infrastructure Standards & Regulation Supply Chain • Best Practice Now • Industry Expectation and Minimum Standards • Health and Fitness Measure for Railway Workers Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk ENABLERS RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION Name: Dr Owen KEYES-EVANS 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: Commitment by all stakeholders to an ongoing process based on organisational learning and continued improvement Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR •Higher profile of diet and exercise •Current interest in outsourcing •Plurality/ silos within the industry and within organisations •Evaluation of intervention/ control measures Knowledge People & Skills Facilities & Infrastructure Standards & Regulation Supply Chain Copyright Institute for Manufacturing •?Greater proportion of immigrant workers •Other demographic financial pressures •Ongoing safety control measures •Image/ PR •Mental health and musculoskeletal problems •Smoking and substance misuse •Confusion/ misperceptions about the employment relationship, processes Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Other •24-hour, “mobile” (but also more sedentary) society •Ageing workforce •Workforce to stay aware of their own responsibilities Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Suppliers InfraCos Network Rail Health Professionals Other Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other •Increased public expectations and demands •Maximising productivity •Lack of suitable data/ use of data •Variety of “assessment tools” available •Reduced occupational disease and incidents •Confusion/ misperceptions about health, medicine •Clarify ongoing resourcing and coordination of this initiative •Repeated review and adjustment of portfolio of actions •Identify target groups •Benchmarking •Refer to published guidance and best practice •Cross-organisational working on links •Refresher training •Ongoing communications strategy •?Tax incentives •Liason with healthcare service providers Health & Wellbeing Roadmap •Use of internet and social media •Earlier treatment of mental health and musculoskeletal problems •Support by lenders, insurers, pension schemes etc •Top management commitment to Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk ongoing support ENABLERS RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION Name: Geoff Ledger 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR •Peer and social pressure is contrary to improving health – fast and processed food, use of cars, etc. •Increasingly sedentary lifestyle at home and at work •Increased retirement age and chronic conditions •The changing pace of technology may restrict the adoption of such by older people Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Suppliers InfraCos Network Rail Health Professionals Other Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Other Knowledge People & Skills Facilities & Infrastructure Standards & Regulation Supply Chain Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk ENABLERS RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION Name: Richard Sharp 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR •Aging Workforce Reduction in absenteeism through occ health issues •Climate change Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Suppliers InfraCos Network Rail Health Professionals Other •Clearer understanding of problem •Plan for improvement •Consistent approach throughout industry Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other •24/7 lifestyle •Diet and fitness improvement •Low cost access Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Other •Joint education plan •Industry leadership group Knowledge People & Skills Facilities & Infrastructure Standards & Regulation Supply Chain •Learning from others •Sharing best practice Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION Name: Natasha Lelyveld 2014 Short 2016 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: Improving the overall health and wellbeing of the workplace, particularly obesity and general health & fitness, to achieve reduced absenteeism Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Suppliers InfraCos Network Rail •c. 1 in 4 people in UK are obese •Current health impairing ability of some to perform role Work-related Non work-related •Increased workloads, longer hours, and increased financial pressures are causing higher stress levels Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other •Busy lives, taking on too much, not leaving time for healthy eating and exercise Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Knowledge People & Skills Facilities & Infrastructure Copyright& Institute for Manufacturing Standards Regulation •50% obese by 2030 •Increased reliance on technology means less active lifestyles • Spotting the warning signs of potential issues and offering support as early as possible •Stricter adherence to MFA procedure •Challenging stigma and discrimination •Assistance in managing a shift-work lifestyle to enable better sleep, eating habits and exercise •Partnership working with OH professionals •Better access to gyms and other fitness opportunities (industry-wide deals?) •Healthy,fit and active workforce •Industry-wide health & wellbeing standard •H&W education currently limited and sporadic Behavioural change Other ABLERS 2017 •Adopting existing initiatives e.g. Global Corporate Challenge Health & Wellbeing Roadmap •H&W awareness training for individuals •Training for managers •Healthy eating culture throughout the industry •Industry sharing of best practice •Cross-industry sharing of best practice •Rail industry-led wellbeing initiatives Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk ENABLERS RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION Name: DAVID HITCHCOCK 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: ERGONOMICS & HUMAN FACTORS…the core requirement being to facilitate to improved understanding and communications between designers and ergonomists. Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Suppliers InfraCos Network Rail Health Professionals Other The role of ergonomics and human factors in future systems. Ergonomics specifications of cab design for future provision – providing details rather than vague guidelines without stifling creativity. Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other MAT development to incorporate more specific task tools in place of the general ART. Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Other Driver training to incorporate MSD controls (e.g. exercises) Knowledge People & Skills Facilities & Infrastructure Standards & Regulation Supply Chain How to improve the perception of occupational health to all stakeholders within the industry. Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Using mock-ups and representative participants in station design and upgrades. Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk ENABLERS RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION Name: David Litchfield 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long 2025 The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: A Healthier Workforce safely delivering a more productive & Sustainable Railway Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Suppliers InfraCos Network Rail Health Professionals Other • Automation of repetitive tasks • Strain of ill health on NHS • Riddor Under reporting •ISLG O/H manifesto Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other • Sleep disorders • stress Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Other • Leadership (shared pro-active approach) Knowledge People & Skills Facilities & Infrastructure Standards & Regulation Supply Chain • shared best practice Copyright Institute for Manufacturing • effective engaged communication • A reliable supply chain • HS2 • transient workforce •Work / life balance (reduced travel) • improved & coordinated data collection • smart card technology (recording) Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk ENABLERS RESPONSES & ACTIONS H&W CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES STAKEHOLDER NEEDS TRENDS & DRIVERS VISION Name:John Gillespie 2014 Short 2016 2017 Medium 2019 2020 Long The Industry Vision for Health and Wellbeing in UK Rail should include: Consistent proactive management of the activities that can give risk to ill health, such as noise, vibtation, asbestos, other substances hazardouc to health. Social Technological Environmental Economic Political & Legal inc DfT/ORR Pace of life. Work-force: - On-board - Trackside - Station, Depots & Back-Office - Other environments TOCs & FOCs Suppliers InfraCos Network Rail Health Professionals Other •Productivity. Work-related Non work-related Lifestyle Opportunity & Access Other •Develop competent managers working in a good system who deal with health like they deal with money and other management tasks. •We can develop this system by “pinching with pride” from other industries on what works. Industry leadership Clinical leadership Evidence based action Reporting and metrics Employee engagement Education & Training Behavioural change Other Leadership at all levels is essential. Knowledge People & Skills Facilities & Infrastructure Standards & Regulation Supply Chain •Training for 1st and 2nd line managers •Access to “hand holding” assistance for them (this is a legal requirement in the Management Regulatiions). Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Pace of technological change. •Leave some thinking they don’t need to deal with people. This leaves some feeling they’re behind the curve. But most essential of all is 1st and 2nd line managers: their world must include the ability, time and confidence to deal with health risks. Health & Wellbeing Roadmap Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk 2025 Additional participant comments at start of workshop Susan Murray Need to ensure opportunities for prevention is not missed Consultation and engagement at all aspects of Occupational Health including procurement of services Sickness absence management process – positive policies, not to be feared Bridget Juniper Data - Work occupational health currently does misses needs of the workforce and can be misdirected as people do not have the right data Steve Coe Concerned of the comments ‘putting emphasis on individuals to look after themselves’. Companies need to be responsible Technological change Issue about diversity and realising every person is different and has individual needs Line management is crucial Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 74 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk Additional participant comments at start of workshop Owen Keyes-Evans Occ health can be interpreted in different ways Can be hidden and misperceived Clarity of roles and responsibilities needed H&S legislation – employer has a role Terminology, roles and responsibilities John Gillespie Media – this is a wider issues. Failure of system and management Press need to recognise a business’ responsibility and not one individual at the top. Dame Carol Black Improve Health & Wellbeing of workers. Need to link to H&S with the work of occ health professionals and promotion of health H&W and H&S should not be separated Train manager to understand ‘softer skills’ – Should make a KPI Management has a critical role Copyright Institute for Manufacturing Page 75 Rail Health & Wellbeing Workshop 2 7 Nov DRAFT 1.0 Nov 2013 Dominic Oughton do251@cam.ac.uk