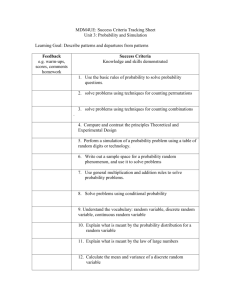
Applied Statistics Midterm II Review 1. Chapter 3: Discrete Random Variables

Applied Statistics Midterm II Review
1. Chapter 3: Discrete Random Variables
(a) Binomial RV: bin ( n, p ) i. Know the experiment which defines the binomial RV ii. Know what the parameters of a binomial RV stand for iii. Note: You will be given the binomial pmf, and the formulas for expected value and variance on the exam.
(b) Negative Binomial RV: nb ( r, p ) i. Know the experiment which defines the negative binomial RV ii. Know what the parameters of a negative binomial RV stand for iii. Note: you will be given negative binomial pmf and the formulas for the expected value and variance on the exam
(c) Hypergeometric RV: hyp ( N, M, n ) i. Know the experiment which defines the hypergeometric RV ii. Know what the parameters of a hypergeometric RV stand for iii. Note: you will be given hypergeometric pmf and the formulas for the expected value and variance on the exam.
(d) Note: You will not be questioned about the Poisson RV on the exam
(Although you should still know what it is).
2. Chapter 4: Continuous RVs
(a) Definition of a pdf
(b) Given a pdf of a continuous RV, know how to compute probabilities corresponding to that RV.
(c) Know the definition of a uniform RV on (a,b), i.e. you should know it’s pdf.
(d) Definition of the CDF of a continuous RV.
(e) Know how to get the CDF from the pdf and the pdf from the CDF
(f) Be able to compute the p th percentile of a continues RV (by the definition of the p th percentile on page 147 of the text.)
(g) Compute the expected value and variance of a continuous RV.
(h) The Normal Distribution/ Normal Random Variables i. Note: the pdf of the normal random variable will be given on the exam
ii. Know what the parameters of the normal RV stand for.
iii. Use the technique of standardization to compute normal probabilities with the help of the standard normal table. (the table will be given on the exam.) iv. Know the definition of critical values/ percentiles of a distribution, and be able to compute them for a normal RV using the standard normal tables.
v. Understand and be able to use normal probabilities to estimate binomial probabilities (when n is large).
(i) Probability Plots i. Know why probability plots are useful ( at least the reason we talked about in class/ what is presented in the text book).
ii. Be able to look at a probability plot and tell if the sample data follows a specified distribution.
3. Chapter 5: Jointly Distributed RVs
(a) Know the definitions of the joint pmf and joint pdf of jointly distributed discrete and continuous RVs respectively.
(b) Be able to compute probabilities corresponding to jointly distributed
RVs. (you may have to practice your integration for this).
(c) Know how to compute the marginal pmfs/pdfs of jointly distributed random variables.