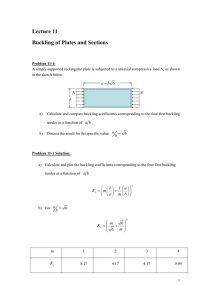
N M R uclear
advertisement
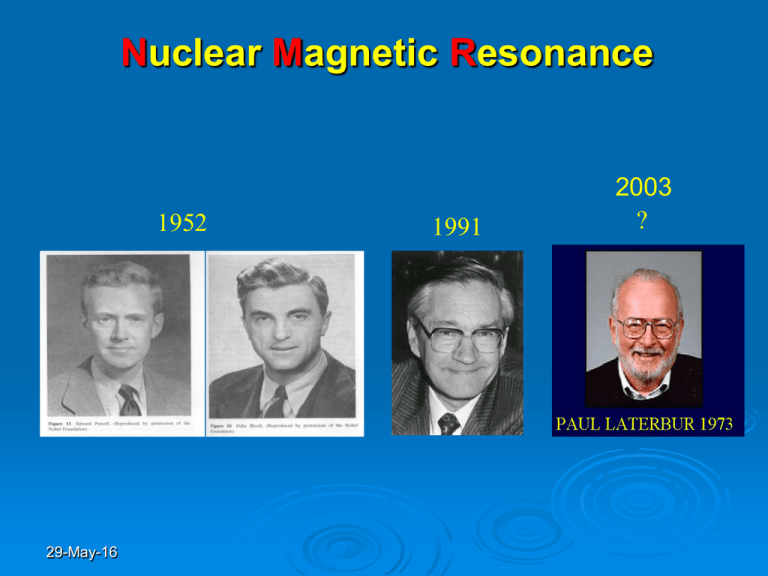
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance 1952 29-May-16 1991 2003 ? Instrumental - principles Prøveholder Radiosender/ mottager Datamaskin 29-May-16 Magnet Applications of MR 29-May-16 Objective To Derive and to Discuss the Bloch Equation Free precession Diffusion Relaxation gradient M u v M M0 2 MxBeff i j k D M (r g )k t T2 T2 T1 M ui vj M z k Beff B1i 0 j ( 0 ) / g 0 z k 29-May-16 Characteristics of a nucleus Magnetic dipole moment (m) and angular momentum (P) µ m = P Exercise 1.1: Derive the above equation (qualitatively) 29-May-16 Magnetic moment in a magnetic field motional characteristics dμ μ B dt Exercise 1.2: Derive the above equation and discuss its solution 29-May-16 Solution Larmor Equation - the basic NMR equation = -B m 29-May-16 Conclusion •THE LARMOR EQUATION ( = B) IS DERIVED FROM A CLASSICAL MECHANICAL APPROACH THE SPIN MOTION IS WITHIN THE MHz-RANGE (Radio-frequencies) 29-May-16 SPIN QUANTUM NUMBER I FOR SOME NUCLEI 29-May-16 MOTION OF m IN A ROTATING FRAME OF REFERENCE MY m V U t MX y x d d dt dt x fixed rot ; rotation frequency of the reference frame relative to the static frame dμ dt 29-May-16 μ B eff ; B eff B 0 ω / Exersize 1.4. Find the solution of the above equation in the rotating frame, (Note 0= -B0) U cos(-0)t V sin(0)t 0; rotational frequency of M in the static frame 29-May-16 How can we observe an MR-signal? z y y x 29-May-16 x Mxy = 0 !!!!! LINEAR POLARIZED FIELD (B1) Rf-irradiation e it eit 2 2 cos(t ) 2 29-May-16 Application of an rf-pulse along the u-direction (Why and what effect ?) dM Beff dt Bo - / M B1 29-May-16 M Beff Beff B1i ( 0 ) / k Excersize 1.5: What effect will B1have on the magnetization when on resonance ? Discuss dU (0 )V dt dV (0 )U B1M z dt dM z B1V dt 29-May-16