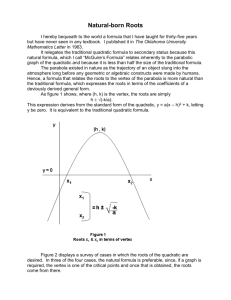
4- -c I) £
advertisement

4-
Il
IkZ
+
II
H
-c
£
Ii
I)
It
‘
•
c1
zff
C)D
CD
CD
tc
LJ
F1
N
Ii
-j
-J
+
03
JJ
Il
—
jJ
;2.
-c
II
+1
0•
—
Fj
jN
I,
II
—
‘I
+
11
k
+
NJ
I’
0
t
N
I’
r”J
LJ
I!
•1-
j’
+
I’
L
/
,1
VI
c.q
0°
I
-
C
p
—
—
N
1
I-
Al
fl
L.
0
-c
—
—
,-rj
N
J
I
—
HI
d.t i
-
G
VI
-J
c
c)
c
5c
‘I
—
3I-
VI
c-’1
c’i
-JI
I
L
-
jJ
T
-C
C-
H
oo
cc
(N
‘I
Al
r
t
1
f•—
f,J1
LCO
-‘
-
u-I
I
Li
-1II
i./It’I,i Al N
LCD
-J
C
L
-r
H
•
‘I
0
-d
0
-d
-d
I
-
‘k’
14-
Lc
Izf
‘I
+
(I
;7__
-
r
r’j
(1(11
-c
(j
7__
II
IIc’I
TI
5j
•—‘
_—‘
II
I
V)
‘-I
/7
[C
‘I
r-j
-
ii
II
-I
,l
-ç
-
(%.J
ov
IJ
c
‘a
-r-’)
4
-
rj
r-’L
C
C
r12
C
Ct
C
—
—
—
C
Oct
o Ct
hO
CC
C
4-
1’
Li
LL
‘1)
-
4
V
c’)
1
--
L!’!2
I—
L
L%J
h
J”T L--4I—
(1t
/LYLS ;,L
i-0
F
II
ZN
.
4-
-.1
—
ii
“
C
A(
‘‘i
I’
mi
D_rj
L
0
L
I.
-
Li
r)
c
—
—
I!
—V
J)
I>’
V
-
D
c.
I
Q
O)J
I
_Q_OQj
I
L
‘I
°
1
1
L
I
.t.
-
c-I
—
—
1
D
b
20. Graph and state the domain, range. x-intercept. and y-intercept of
f(x)
a’ +
1
0
—
I
—2.
—
i2...
x-int(s)=
,:
-
y-int=
,.
R=
2)2 + 3. Make sure to explain each step of the
21. Use graph transformations to graph f(x)
transformation in words. Also state the domain, range, x-intercepts(s). —intercept, and vertex.
—
J?’ C) cA
S\- cc‘J€ ( S
L:
cI
o\Jer rc—
--(r.-z
.
i.
-(-N
x-int(s)
Ci-2 \
D
R_______
vertex
r-2
(a
22. Find the quotient:
—
2
12x
+
9x—2
13x
1
—
\L.r)(—L3
3
-\nc r(—
(2r--
0
ç
a
,
-3(O--2-”
-9
-
y-int
2.
-=o
_S(cr
2ry*-O
4 2—2
Er2_j-Dri-\3N
7
S
W
23. What is the equation of the linear polynomial that passes through the points (2. 4) and (5, 10)?
S\oç 4
b
Lz
bo
24.
(a) Complete the square: Write f(x)
=
32
+ 6x
CoeFc--i-
tP\
>ç:
a
r
VJ’ 4
\k)
O.
(b) What is the vertex of
using
+
R.
-\ec’.
‘rve-m
rev
r-
e
where a,
2
-
“ 1-
se .s
c
-j-krt
(c) Find the roots
3)2
ACAW2
çk’
c- r
e. c -f-
-‘-ie
1y-e
I
‘NOy
oe4-cie’1i.
f(s)?
the form from (a).
\
=
—
-±l\i/\
-4_s
\rL{)
3
For #25-26 determine how many roots the quadratic polynomials have. Solve for these roots using the
quadratic formula (if there are any)
25. 2x2
—
6x + 10
_H9LD
L(ey- rLkC’.
L2LGJ
1+-.
rirt&’eS.
CtC
3
(2
5 in the form a(x +
cj
3o&i-or ec,&dc
,
—
ioot)
8
tjj
j
4-’
(v)
(,.
Z
+
+
c-1
ci
0
1’
‘I
-
3-
ci
±
r1
I’
r-J
-I-I
II
I’
-‘-Ic
L
+
0
iD
I
C-;-°
,—,
II
I
,t
c
—
--
I
t
.—I
I-,--1t
:
9
+1-
U)%)
‘c
P
.-
3A
CU
—
c)
U)
+
-()
U)
II
)
-
-
C
-‘1
C
4-1
Li
0
C
-c
I—.
fa3U)
+
C
U.
‘-C
-C
C
ci
‘1
0
11
co
)
i
r
-
0
I’
‘I
cxl
YJo
Ic
-2
civr
tu
MetPuó
fk yTThci
(f+
2 x 2(Hint: x
1 is a root.) (Your answer should be a product
30. Completely factor f(x) 3x 4x
of a constant and maybe some linear and quadratic polynomials that have leading coefficients equal to
1, and such that any of the quadratics in the product have no roots).
—
Pcc-roi.s
2;
ô
—
‘))
)2
)
0
OOf
\
Gk
z
3-ic —rt-
—\
()
Dsc’f
2
/
((32
2Z
f
1-’-
(_
-nc 2
=
I
+ZH
) 0
-
)
(-
d.
(
I
31. Completely factor —2 + 6x2 2x (Hint: x = 3 isa root.) (Your answer should be a product of
a constant and maybe soiue linear and ciuadratic polynomials that have leading coefficients equal to 1.
and such that any of the quadratics in the product have no roots).
—
l
CLft’\r
(-(-2 -2
\t\1O’
o
o
-
(c-
—z (
(-
-
(r2
)
cc
-((‘
=%)
j3
(ecxL
&c’eir
10
(QkS