Cleveland State University Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
advertisement

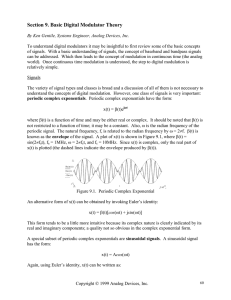
Cleveland State University Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EEC 450: Communications Catalog Description: EEC 450 Communications (3-0-3). Pre-requisites: EEC 313, ESC 310. Baseband pulse and digital signaling; bandpass signaling principles and circuitry; AM, FM and digital modulated systems. Textbook: Digital and Analog Communication Systems, by Leon W. Couch II, 8th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2013. References: 1. An Introduction to Digital Communications, by Jack Kurzweil, Wiley, 2000. 2. A First Course in Digital Communications by Ha Nguyen and Ed Shwedyk, Cambridge University Press, 2009. Coordinator: Dr. Murad Hizlan, Associate Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Course Objectives: This course is designed to: 1. Introduce students to the basic concepts of digital and analog communication systems. 2. Expose students to baseband and bandpass digital communication systems and circuitry. 3. Solidify understanding of concepts through introduction of analog and advanced digital modulation schemes. 4. Allow students to make real-world connections by introducing concrete examples. Expected Outcomes: Upon completion of this course, students should be able to: 1. Understand the concepts of digital and analog communications. 2. Understand the theoretical foundations of baseband and bandpass digital communications. 3. Recognize and interpret common digital and analog modulation schemes and circuitry. 4. Design simple digital communication systems. 5. Exhibit increased awareness and understanding of modern day applications of communications. Fulfills the Following Electrical Engineering Program Objectives and Outcomes: Objectives: 1. Practice electrical engineering in one or more of the following areas: communications computers, controls, power electronics, and power systems. 2. Define and diagnose problems, and provide and implement electrical engineering solutions in an industrial environment. Outcomes: (a)An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering to general electrical engineering and, in particular, to one or more of the following areas: communications, computers, controls, power electronics, and power systems. (c)An ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs. (e)An ability to identify, formulate, and solve electrical engineering problems. (k)An ability to use the techniques, skills, and modem engineering tools necessary for electrical engineering practice. Contribution of Course to Meeting the Professional Component: Math & Basic Science: 0 credits; Engineering Topics: 3 credits; General Education: 0 credits Prerequisites by Topic: 1. Fourier series and transforms 2. Linear system response 3. Probability Topics: 1. Overview of topics 2. Pulse amplitude modulation 3. Pulse code modulation 4. Digital signaling 5. Line codes and spectra 6. Intersymbol interference 7. Delta modulation 8. Time division multiplexing 9. Representation of bandpass signals 10.Bandpass filtering, sampling and distortion 11.Communications circuitry 12.Phase-locked loops 13.Transmitters 14.Amplitude modulation 15.Phase and frequency modulation 16.Binary modulated bandpass signaling 17.Multilevel modulated bandpass signaling 18.MSK, GMSK and OFDM Tests and quizzes Total: 3 1 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 3 2 1 2 3 4 2 2 2 5 45 Computer Usage: Students are expected to use a communication link design and simulation package (SystemView) to design and simulate various communication systems. Design Projects: Students are expected to design and simulate a digital communication system using a software package suitable for this purpose. Non-Design Projects: Students are expected to analyze and simulate an existing communication system design using a software package suitable for this purpose. This project also serves as an introduction to the use of the software package. Prepared by: Dr. Murad Hizlan Date: September 2013