Document 11270485
advertisement

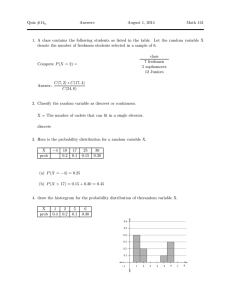
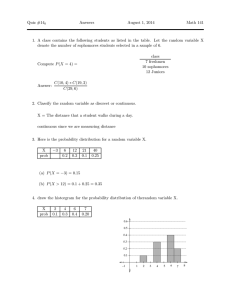
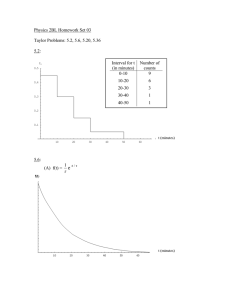
Stat401B Lab#9 Problem #1 Spring 2014 Analysis of Variance Source Model Error C. Total DF 2 9 11 Sum of Squares 883.3333 220.3333 1103.6667 Mean Square 441.667 24.481 F Ratio 18.0408 Prob > F 0.0007* Lack Of Fit Source Lack Of Fit Pure Error Total Error DF 6 3 9 Sum of Squares 211.58333 8.75000 220.33333 Mean Square 35.2639 2.9167 F Ratio 12.0905 Prob > F 0.0330* Max RSq 0.9921 Parameter Estimates Term Intercept Temp Conc Estimate -51.5 0.4533333 0.8666667 Std Error 19.94553 0.080798 0.403992 t Ratio -2.58 5.61 2.15 Prob>|t| 0.0296* 0.0003* 0.0605 Residual by Temp Residual Percent Residual by Predicted Plot Residual Percent Residual by Conc Normal Plot of Stud. Res. Fit of the Full Model Summary of Fit RSquare RSquare Adj Root Mean Square Error Mean of Response Observations (or Sum Wgts) 0.971912 0.948505 2.27303 67.83333 12 Analysis of Variance Source Model Error C. Total DF Sum of Squares 5 1072.6667 6 31.0000 11 1103.6667 Mean Square 214.533 5.167 F Ratio 41.5226 Prob > F 0.0001* Lack Of Fit Source Lack Of Fit Pure Error Total Error DF Sum of Squares 3 22.250000 3 8.750000 6 31.000000 Mean Square 7.41667 2.91667 F Ratio 2.5429 Prob > F 0.2318 Max RSq Parameter Estimates Term Intercept Temp Conc (Temp-225)*(Temp-225) (Conc-20)*(Temp-225) (Temp-225)*(Temp-225)*(Conc-20) Residual by Predicted Plot Estimate -48.66667 0.4533333 0.9 -0.0112 -0.026 -0.00008 Std Error 10.58038 0.037118 0.321455 0.0021 0.009092 0.00063 t Ratio -4.60 12.21 2.80 -5.33 -2.86 -0.13 Prob>|t| 0.0037* <.0001* 0.0312* 0.0018* 0.0288* 0.9031 Fit of the Reduced Model Summary of Fit RSquare RSquare Adj Root Mean Square Error Mean of Response Observations (or Sum Wgts) 0.933555 0.908638 3.02765 67.83333 12 Analysis of Variance Source Model Error C. Total DF Sum of Squares 3 1030.3333 8 73.3333 11 1103.6667 Mean Square 343.444 9.167 F Ratio 37.4667 Prob > F <.0001* Lack Of Fit Source Lack Of Fit Pure Error Total Error DF Sum of Squares 5 64.583333 3 8.750000 8 73.333333 Mean Square 12.9167 2.9167 F Ratio 4.4286 Prob > F 0.1252 Max RSq Parameter Estimates Term Intercept Temp Conc (Temp-225)*(Temp-225) Percent Residual Residual by Predicted Plot Estimate -48 0.4533333 0.8666667 -0.0112 Std Error 12.2361 0.049441 0.247207 0.002797 t Ratio -3.92 9.17 3.51 -4.00 Prob>|t| 0.0044* <.0001* 0.0080* 0.0039* Problem#2 (a) 80 Tensile Strength 75 70 65 60 2 1 4 3 Mix Source Mix Error C. Total Test DF Sum of Squares 3 448.15000 16 154.40000 19 602.55000 H 0 : µ= µ= µ= µ4 1 2 3 Mean Square 149.383 9.650 H a : at least at α = .05 . vs. reject the null hypothesis F Ratio 15.4801 one inequality. Since p-value<.05, (b) The sample means are : LSD= y1 = 62.2 , y2 = 65.4 , y3 = 70.4 , y4 = 74.6 2.12 × 9.65 × 2 / 5 = 4.165 mix 1 2 62.2 65.4 ------------ 3 70.4 4 74.6 From JMP: LSMeans Differences Student's t α=0.050 t=2.11991 Level 4 A 3 B 2 C 1 C Least Sq Mean 74.600000 70.400000 65.400000 62.200000 Levels not connected by same letter are significantly different. (c) W= mix 4.05 × 9.65 × 1/ 5 = 5.626 1 2 3 4 62.2 65.4 70.4 74.6 ---------------------------------- Prob > F <.0001* From JMP: LSMeans Differences Tukey HSD α= 0.050 Q= 2.86102 <<<<<<<Note :This Q value is different from the value from the table. i.e. 4.05/ 2 =2.864 Level 4 A 3 A B 2 B C 1 C Least Sq Mean 74.600000 70.400000 65.400000 62.200000 Levels not connected by same letter are significantly different. (d) H 0 :1/ 2( µ1 + µ2 ) − 1/ 2( µ3 + µ4 ) = 0 Hypothesis Contrast : = 1 1 −1 −1 1 Estimate: 62.2 + 65.4 − 70.4 − 74.6 = −17.4 ˆ 1 = Standard Error= = V (ˆ 1 ) 12 + 12 + 12 + 12 9.65 = 5 = 9.65 4 / 5 2.78 Thus the t-statistic is: tc = −17.4 = −6.26 and the percentile from the t-table is t.025,16 = 2.12 2.78 Thus R.R. is | t |> 2.12 ; Thus the null hypothesis is rejected at α = .05 since 6.26 is in the rejection region. From JMP output: t-statistic = -6.26 p-value = <.0001 Reject null hypothesis at α = .05 Hand computations for the other three comparisons are not shown here but those computations are similar to above and are summarized below. Contrast A B C D Est s.e. t p-value i) 1 1 -1 -1 -17.4 2.78 -6.26 <.0001 ii) 1 -1 1 -1 -7.4 2.78 -2.66 .017 iii) 1 -1 0 0 -3.2 1.96 -1.63 .1229 iv) 0 0 1 -1 -4.2 1.96 -2.14 .0483 The results from JMP are shown below: Contrast Test Detail 1 2 3 4 Estimate Std Error t Ratio Prob>|t| SS 0.5 0.5 -0.5 -0.5 -8.7 1.3892 -6.262 1.1e-5 378.45 0.5 -0.5 0.5 -0.5 -3.7 1.3892 -2.663 0.017 68.45 1 -1 0 0 -3.2 1.9647 -1.629 0.1229 25.6 0 0 1 -1 -4.2 1.9647 -2.138 0.0483 44.1 Summary Statement The data show that there is a significant difference between the average tensile strength of asphalt for the two aggregate types and two compaction methods, respectively. The average strength appear to be higher for the kneading compaction method compared to the static compaction method . and higher for the basalt aggregate type compared to the silicious aggregate type. However, there is no significant difference in average strength between the two compaction methods when used with silicious aggregate type, where as there is a significant difference between them when used with basalt aggregate type.