Document 11270481
advertisement
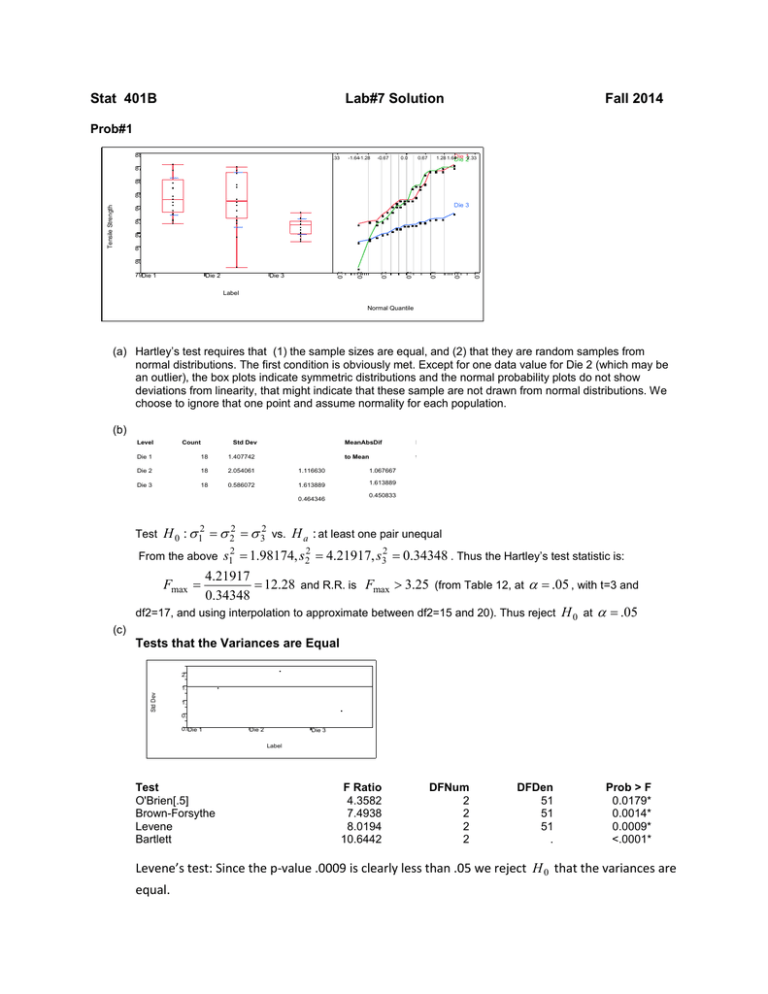
Stat 401B Lab#7 Solution Fall 2014 Prob#1 88 -1.64-1.28 .33 -0.67 0.67 0.0 Die 1.28 1.64 Die 1 22.33 87 86 Tensile Strength 85 Die 3 84 83 82 81 0.9 0.9 0.8 0.5 Die 3 0.2 Die 2 0.0 79Die 1 0.0 80 Label Normal Quantile (a) Hartley’s test requires that (1) the sample sizes are equal, and (2) that they are random samples from normal distributions. The first condition is obviously met. Except for one data value for Die 2 (which may be an outlier), the box plots indicate symmetric distributions and the normal probability plots do not show deviations from linearity, that might indicate that these sample are not drawn from normal distributions. We choose to ignore that one point and assume normality for each population. (b) Level Std Dev Count MeanAbsDif M to Mean t Die 1 18 1.407742 Die 2 18 2.054061 1.116630 1.067667 Die 3 18 0.586072 1.613889 1.613889 0.464346 Test 0.450833 H 0 : σ 12 = σ 22 = σ 32 vs. H a : at least one pair unequal = 1.98174, s22 = 4.21917, s32 = 0.34348 . Thus the Hartley’s test statistic is: 4.21917 Fmax = = 12.28 and R.R. is Fmax > 3.25 (from Table 12, at α = .05 , with t=3 and 0.34348 df2=17, and using interpolation to approximate between df2=15 and 20). Thus reject H 0 at α = .05 2 From the above s1 (c) Tests that the Variances are Equal 2.0 Std Dev 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0Die 1 Die 2 Die 3 Label Test O'Brien[.5] Brown-Forsythe Levene Bartlett F Ratio 4.3582 7.4938 8.0194 10.6442 DFNum 2 2 2 2 DFDen 51 51 51 . Prob > F 0.0179* 0.0014* 0.0009* <.0001* Levene’s test: Since the p-value .0009 is clearly less than .05 we reject H 0 that the variances are equal. Problem 2 (a) See JMP output. (b) 564 16446 ( (c) ) 1785 536 12 54 (e) 2 72 5 51814 ( 1456 2 72 (d) 164 13 ) 4631 12 54 2 72 13 6 (f) See Excel table. (g) See Excel table. (h) See Excel table. ( (i) ) 4631 ( ) 3956 ( ) 675 85 85% of the variability in gas consumption is explained by the linear regression model. (j) 37 51 (k) 26 (l) 95 (2 16, 3 27) , (m) 1 46 , Reject the null hypothesis at of gas consumption. 5 There is sufficient evidence that temperature difference is a predictor (n) Anova Table Source Regression Error Total Df 1 18 19 Sum of Squares 3956 675 4631 1 5 , Reject the null hypothesis at 5 Mean Square 3956 37 F 105 (o) 12 54 2 72 25 8 54 1 95 , (p) 95 , 1 ( ) ( (77 17, 83 95) ) (67 26, 93 87) (q) See JMP output and additional table. (r) The plot of residuals against predicted values suggests some concern for the assumption of homogeneity of variance, since there is a megaphone shape pattern. The normal probability plot supports the assumption of normality of errors, since the plotted points lie near a straight line. (s) : 8 : 8 (77 17, 83 95) 95 80 is contained in the interval so we fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is insufficient evidence that the manufacturers contention is wrong. JMP Output for Problem 2 Simple Linear Regression of Gas_KWh on Temp_Diff Linear Fit Gas_KWh = 12.642442 + 2.7168076*Temp_Diff Summary of Fit RSquare RSquare Adj Root Mean Square Error Mean of Response Observations (or Sum Wgts) 0.854202 0.846102 6.124408 89.27 20 Analysis of Variance Source Model Error C. Total DF 1 18 19 Sum of Squares 3955.5713 675.1507 4630.7220 Mean Square 3955.57 37.51 F Ratio 105.4584 Prob > F <.0001* Parameter Estimates Term Intercept Temp_Diff Estimate 12.642442 2.7168076 Residual by Predicted Plot Std Error 7.586442 0.264556 t Ratio 1.67 10.27 Prob>|t| 0.1129 <.0001* Lower 95% -3.296081 2.1609951 Upper 95% 28.580965 3.2726201 Actual by Predicted Plot Residual by Row Plot Residual Normal Quantile Plot Excel Table for Problem 2 x 20.1 21.1 21.9 22.6 23.4 24.2 24.9 25.1 26 27.2 28.8 29.2 30.6 y 65.3 66.5 67.8 73.2 75.3 81.1 82.2 85.7 90.9 87.4 94.9 93.9 87.1 yhat 67.25027 69.96708 72.14053 74.04229 76.21574 78.38919 80.29095 80.83431 83.27944 86.53961 90.8865 91.97322 95.77675 30.8 32.6 32.4 34.8 35.9 36 36.5 84.2 106.6 111.3 100.9 101.9 110.1 119.1 96.32012 101.2104 100.667 107.1873 110.1758 110.4475 111.8059 ybar= 89.27 y-yhat -1.95027476 -3.46708236 -4.34052844 -0.84229376 -0.91573984 2.71081408 1.90904876 4.86568724 7.6205604 0.86039128 4.01349912 1.92677608 -8.67675456 12.12011608 5.38963024 10.63299176 -6.28734648 -8.27583484 -0.3475156 7.2940806 SSTot= SSE= SSReg= 4630.722 675.1506631 3955.571351 SSReg+SSE= 4630.722014 y-ybar -23.97 -22.77 -21.47 -16.07 -13.97 -8.17 -7.07 -3.57 1.63 -1.87 5.63 4.63 -2.17 yhatybar -22.0197 -19.3029 -17.1295 -15.2277 -13.0543 -10.8808 -8.97905 -8.43569 -5.99056 -2.73039 1.616501 2.703224 6.506755 -5.07 17.33 22.03 11.63 12.63 20.83 29.83 7.050116 11.94037 11.39701 17.91735 20.90583 21.17752 22.53592 Additional Table for Problem 2 Temp_Diff Gas_KWh Predicted Residual 20.1 21.1 21.9 22.6 23.4 24.2 24.9 25.1 26.0 27.2 28.8 29.2 30.6 30.8 32.6 32.4 34.8 35.9 36.0 36.5 25.0 65.3 66.5 67.8 73.2 75.3 81.1 82.2 85.7 90.9 87.4 94.9 93.9 87.1 84.2 106.6 111.3 100.9 101.9 110.1 119.1 . 67.25 69.97 72.14 74.04 76.22 78.39 80.29 80.83 83.28 86.54 90.89 91.97 95.78 96.32 101.21 100.67 107.19 110.18 110.45 111.81 80.56 -1.9503 -3.4671 -4.3405 -0.8423 -0.9157 2.7108 1.9090 4.8657 7.6206 0.8604 4.0135 1.9268 -8.6768 -12.120 5.3896 10.6330 -6.2873 -8.2758 -0.3475 7.2941 . Lower 95% Mean 61.91 65.08 67.61 69.80 72.29 74.75 76.88 77.48 80.15 83.61 87.99 89.04 92.61 93.10 97.44 96.96 102.5 105.0 105.2 106.4 77.18 Upper 95% Mean 72.60 74.85 76.67 78.28 80.14 82.03 83.70 84.19 86.41 89.47 93.78 94.90 98.95 99.54 105.0 104.4 111.8 115.3 115.6 117.2 83.95 Lower 95% Indiv 53.32 56.20 58.50 60.49 62.76 65.02 66.98 67.54 70.04 73.34 77.70 78.78 82.53 83.06 87.80 87.28 93.50 96.31 96.57 97.84 67.26 Upper 95% Indiv 81.18 83.73 85.78 87.59 89.67 91.76 93.60 94.13 96.52 99.74 104.1 105.2 109.0 109.6 114.6 114.1 120.9 124.0 124.3 125.8 93.87