GY 402: Sedimentary Petrology UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA Lecture 10:
advertisement

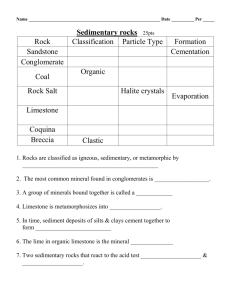
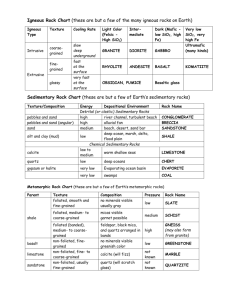
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 402: Sedimentary Petrology Lecture 10: Petrology of Mature Siliciclastic Sed. Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today’s Agenda 1. Recap major types of sediment & sedimentary rock 2. Recap important grain parameters 3. Cement versus matrix 4. Mature sediment/sedimentary rocks Petrography Game Plan Tuesday Lecture: petrographic parameters Online Lecture (student recap): environments of deposition Tues/Thurs. Labs: representative samples (thin-sections and hand specimens) Major Sedimentary Rock Types* * Examined in GY 402 Major Sedimentary Rock Types Siliciclastic Major Sedimentary Rock Types Siliciclastic Volcaniclastic Major Sedimentary Rock Types Siliciclastic Volcaniclastic Carbonates (evaporites/chemical, non-skeletal, skeletal) Siliciclastic Sedimentary Rocks Mature versus immature varieties… … are best distinguished via QFR ternary plots Siliciclastic Sedimentary Rocks Q Q = quartz F = feldspars R = lithic fragments (includes chert) F R Source: Blatt, H., Middleton, G and Murray, R., 1980: Origin of Sedimentary Rocks. Prentice Hill, 782 p. Siliciclastic Sedimentary Rocks Q “Mature” rocks (mineralogically stable) Enriched in quartz and clay minerals F R Source: Blatt, H., Middleton, G and Murray, R., 1980: Origin of Sedimentary Rocks. Prentice Hill, 782 p. Siliciclastic Sedimentary Rocks Q “Immature” rocks (mineralogically unstable) Enriched in feldspars and unstable rock fragments F R Source: Blatt, H., Middleton, G and Murray, R., 1980: Origin of Sedimentary Rocks. Prentice Hill, 782 p. Important Parameters Grain rounding Important Parameters Grain rounding Immature Mature Increasing transport distance Important Parameters Grain sorting Important Parameters Grain sorting Low energy High energy increasing energy of deposition Important Parameters Grain size Important Parameters Grain size High energy Low energy Decreasing energy of deposition Mature Siliciclastic Petrography PPL 250 m XN 250 m Mature Siliciclastic Petrography Quartz-rich (quartz arenites) XN 250 m Mature Siliciclastic Petrography Quartz-rich (quartz arenites) Generally well rounded grains XN 250 m Mature Siliciclastic Petrography Quartz-rich (quartz arenites) Generally well rounded grains Poorly sorted to well sorted XN 250 m Mature Siliciclastic Petrography Quartz-rich (quartz arenites) Generally well rounded grains Poorly sorted to well sorted Gravel to clay sized grains XN 250 m Mature Siliciclastic Petrography An important question…. XN 250 m Mature Siliciclastic Petrography An important question…. ...What holds the rock together? XN 250 m Matrix versus Cement Matrix versus Cement Matrix: fine-grained* material deposited simultaneously with larger particles. Generally appears as darker-coloured detritus between grains * This is a relative term. Matrix is material that is finer than the dominant particle size comprising the sand/gravel sediment fraction. Matrix versus Cement Matrix: fine-grained* material deposited simultaneously with larger particles. Generally appears as darker-coloured detritus between grains Cement: a chemical precipitate between grains formed from pore-water long after deposition. Matrix versus Cement Matrix Heterogeneous Chemically impure Drapes over grains Predates cements Generally dark in color XN PPL 100 µm Matrix versus Cement Cement Homogeneous Chemically pure Lines pores Specific fabrics (acicular, drusy, overgrowths etc.) Multiphased Zoned 50 µm PPL Hematite cement Quartz cement Matrix versus Cement Matrix Cement Heterogeneous Homogeneous Chemically impure Chemically pure Drapes over grains* Lines pores* Predates cements Specific fabrics Generally dark in color* Multiphased Zoned * Can be confusing Hand specimens Mature siliciclastic sandstones (quartz arenite) Liesengang banding, clay and iron oxide cement Quartz and chalcedony cement 4 cm Limonite cement Thin-section Photomicrographs ppl xn 750 m monocrystalline quartz Thin-section Photomicrographs ppl xn cement 750 m polycrystalline quartz Thin-section Photomicrographs xn xn 1250 m cement Chert sedimentary rock fragment Thin-section Photomicrographs Weakly cemented (friable) ppl xn porosity quartz 500 m Thin-section Photomicrographs Strongly cemented ppl xn quartz 250 m Thin-section Photomicrographs Glauconite cement ppl xn glauconite 250 m Thin-section Photomicrographs Chalcedony cement ppl xn chalcedony 500 m Thin-section Photomicrographs Chalcedony cement ppl xn chalcedony 500 m Thin-section Photomicrographs Quartz (overgrowth) cement ppl xn Quartz overgrowth cement 125 m Upcoming Stuff Homework 1) Write 3 redo due today 2) Work on your group grain size project due Friday Feb 26th This Week’s Lab Open (grain size or thin-section petrography review) Next Week: 1) Online paper Activity 4 and Midterm exam 2) Midterm exam issued Tuesday due Tuesday February 23rd 3) Thin-section analysis in labs 4) Embedded writing assignments begin in labs (they are redo-able; the rest of the labs are NOT) GY 402: Sedimentary Petrology Lecture 11: Mature Siliciclastic Sedimentary Rocks Instructor: Dr. Doug Haywick dhaywick@southalabama.edu This is a free open access lecture, but not for commercial purposed. For personal use only.