Lab #9: Geometric Optics
advertisement

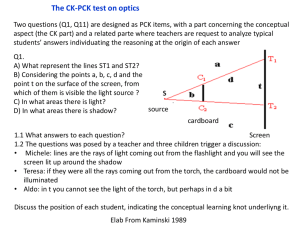
Lab #9: Geometric Optics Theory: • What is geometric optics? • Define and sketch law of reflection. • Define and sketch law of refraction. • What is Brewster’s angle? Experiment: The light rays are produced by a laser beam. Rays are traced by using a straight pin. 1. REFLECTION 1. Trace two rays from an object onto the planar mirror surface. 2. Construct incident and reflected rays using a pin for both rays going through the same object. 3. Verify that θi= θr for both rays. 4. Verify that do=di (object distance=image distance) 2. REFRACTION 1. Trace incident and transmitted rays using straight pin. 2. Move the Plexiglas and construct the refracted ray. 3. Calculate nR using top pair of angles. Call it n1 4. Calculate nR using bottom pair of angles. Call it n2 sin θ i nR = sin θ R δn R δ sin θ i δ sin θ R = + nR sin θ i sin θ R δ sin θ i = cos θ i ⋅ δθ i ⋅ π 180 3. BREWSTER’S ANGLE (do as a class) 1. Calculate nr for each θB n R = tan θ B δn R = 1 π ⋅ δθ B ⋅ 2 180 cos θ B Analysis: • Calculate the weighted average index of refraction n of Plexiglas and its uncertainty using the 4 values of nR • Compare the average nR with the known value of 1.5.