Class Notes Chapter 2: Research Methods
advertisement

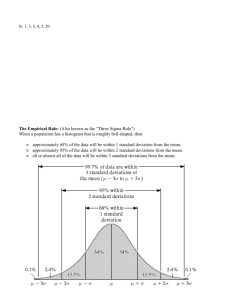
Chapter 2: Research Methods Psychology: From Inquiry to Understanding 1/e C. Brown Unit 2 Scott O. Lilienfeld Steven Jay Lynn Laura Namy Nancy J. Woolf Class Notes • Remember taking notes is like sending a text message to yourself. • Do not expect to write down every word. • The members of each study group should help th i “t their “team mates” t ” fill in i the th gaps. • You learn best by having to fill in the missing information after the class period is over, but before the day is over. • __________________________________ • __________________________________ This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or part, of any images; any rental, lease, or lending of the program. The Importance of Research Methods • Protecting ourselves from inaccurate impressions: • The _____________________ Saga Psychosurgery: A Sad History • Following WWII thousands of returning veterans sought assistance ____________________. Some veterans may have been suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder. • Prior to the development of ________________ a lobotomy was “thought” to be a reasonable treatment. • Lobotomies were most prevalent in the ____________ States: nearly ________ WWII veterans received lobotomies. Psychosurgery • The first controlled lobotomy was performed by the Portuguese physician António Moniz in 1936. • Moniz won the Nobel Prize for medicine in 1949 for this work. • The procedure was brought to the United States by Drs. Walter Freeman and James W. Watts. Notable Cases: Rosemary Kennedy Rosemary Kennedy, sister of ______________________, was given a lobotomy at age 23 to “control” her moodiness and growing interest in men. She was reduced d d tto an iinfantile f til mentality. t lit The nature of Rosemary's condition was concealed for years by her father, and was presented to the public as the result of mental retardation. Her sister, Eunice Kennedy Shriver, founded the ___________________ in her honor in 1968. 1 Notable Cases: Howard Dully • Howard Dully received a lobotomy at 12, to control his "youthful defiance". • He had no memory of the procedure, and did not discover the story of his l b t lobotomy until til h he was iin hi his 50’s. • He noted, "I've always felt different -- wondered if something's missing from my soul”. • He is shown holding an icepick like instrument similar to the one used for his lobotomy. The Psychosurgery Saga • Illustrates the _______________________ in the absence of ethical guidelines, and research methods. • Lobotomies were adopted for use on human j following g the report p of only y one case subjects study conducted on one chimpanzee. • No controlled experiments were ever conducted. • _________________: surgeons perceived “improvements” in the behavior of their patients that supported their belief in the benefits to be derived from the procedure, and downplayed outcomes that didn’t. Modern Ethical Guidelines • HUMAN RESEARCH – Institutional Review Board (IRB) – ___________________ – Justification of ____________ – _______________ of subjects afterward • Animal Research – Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) – About 8% of psychological research uses animals Psychosurgery Today • In 1977, the U.S. Congress created a National Committee for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research to investigate allegations that lobotomy techniques produced unethical after effects. • It concluded that psychosurgery could have positive effects in some cases. • Today about 10-15 lobotomies are conducted in the US each year. Textbook Assignment Ch2-1 • The figure to the left is from our textbook. • What phenomenon is being depicted here? • Ans:____________ Ans: • Were the results supporting this procedure more scientific than those supporting prefrontal lobotomies? Ans:______ • Email your response to your SI. The Need for Unbiased Observations • It is clear that behavioral scientists need to develop rigorous methods to insure that their conclusions are derived from ______ and __________ scientific observations, observations and are not “contaminated” by errors in human judgment. • The following exercise illustrates how psychologists conduct experiments. Copyright © Allyn & Bacon 2008 2 The Research Process In Class Experiment • In Chapter 3 we will learn that the two sides of the brain are not symmetrical regarding their function. This finding is called _______________. • In the following exercise we will “test” the idea that the two sides of the human face are unequal regarding the expression of human emotion. • Research scientists would test this idea by posing two alternative hypothesizes. Studies are designed to collect data to determine if the Null Hypothesis yp is statistically y unlikely. y • Hypothesis: the two side of the face differ in their capacity to express (or conceal) emotion. • Null Hypothesis: the two sides are equally expressive. Research Designs • In this experiment a computer has been used to split the human face into two images. • One image is composed of the left-side and a mirror image of the left half of the face. • The second image is composed of the right-side and the mirror image of the right half of the face. Class Results • The results from our class suggest that the two sides of the human face are equally expressive. – T/F • Vote for the most expressive side! Class Results • The results from our class “rejected” the null hypothesis (the two side are equally expressive). Confounding Variable • A variable__________________________ – T/F 3 Our Class Experiment Has A Confound In Its Design • Results from a large sample of students suggest that the left-side of the face is emotionally most expressive. This side of the face is controlled by the right brain. possibility y that the right g • The confound is the p brain is also more sensitive to the detection of emotion, and it receives images from the left visual field. • Thus, we are uncertain if the left side of the face is more expressive emotionally, or if images in the left visual field are perceived as being more emotionally expressive. Answer • • • • • • • • __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ How to Influence +/- Thoughts • Give the exam on a computer and present “bogus” feedback during an exam via computerized testing. • Deceive the subjects into thinking they are performing very well or very poorly. – E.g. “Correct! Not many students select the right answer the first time they are tested on this concept.” How could you change the location of the pictures in the slides to correct for this potential confound? • Confer with the members of your study group to propose a solution to the confound. • You have 60 seconds to meet. • There are at least two ways to resolve the confound. Anatomy of an Experiment • Some students score well on exams while others score poorly. • Differences between exam scores may not always be due to the student’s student s ability level. level • Positive and negative thoughts that arise during the exam may reduce or heighten anxiety, and differences in anxiety may alter test performance. Hypothetical Experiment • In the hypothetical experiment that follows the investigator attempts to “improve” performance during the exam by giving “positive” positive feedback to the students students. After a response is submitted, the student is always told that they were correct. • A control group_____________________ 4 Question Population of Students Random Sample A Random Sample B Experimental Group Independent Variable (positive feedback) Outcome (test scores) Dependent Variable Control Group (no feedback) Outcome (test scores) Answer • • • • • • • • __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ Research Designs Experiments • Experimental Group – ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ • Control Group – ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ • It would be easier for the investigator to assign all the female students to the Experimental Group, and all the male students to the Control Group. Group Would this be a good idea? Justify your answer. • Confer with the members of your study group and develop your response. • You have 60 seconds to meet. Research Designs Experiments • Independent Variable – __________________________________ __________________________________ – The proposed cause of change in the dependent variable. • Dependent Variable – __________________________________ __________________________________ – Proposed to be affected by the independent variable. Experimentation • Random Assignment –assigning participants _____________________________ _____________________________ –minimizes _____________________ between those assigned to the different groups 5 Data Analysis Question • The Dependent variable is the variable that is being altered, changed or manipulated by the investigator. – T/F Researchers rely on statistics to analyze the results they collect. Statistics is a branch of mathematics that is used for analyzing research data. Central Tendency Summary Statistics • Measures of _____________________ – Mean – Mode – Median - ________________ score ________________ score ________________ score • Measures of Variability – Range – Average Deviation – Standard Deviation Subject 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Sum • Mode – the most ________________ score in a distribution • Mean – the arithmetic ___________ of a distribution – obtained by adding the scores and then dividing by the number of scores • Median – the ___________ score in a distribution – half the scores are _____ it and half are _____ it Dispersion Summary Statistics Score 100 96 126 130 104 110 98 100 108 100 102 1174 Central Tendency • Range Mean = 1174/11 = 106.7 Mode = 100 Median = 102 – _______________________________________ _______________________________________ • Standard Deviation – _______________________________________ _______________________________________ 96 98 100 100 100 102 104 108 110 126 130 6 Subject Class Notes Summary Statistics 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Sum Mean Score /X – M/ /X – M/2 6.7 10.7 19.3 23.3 27 2.7 3.3 8.7 6.7 1.3 6.7 4.7 96.1 8.7 44.89 114.49 372.49 542.89 7 29 7.29 10.89 75.69 44.89 1.69 44.89 22.09 1282.19 116.56+ 100 96 126 130 104 110 98 100 108 100 102 1174 106.7 • The average deviation is an intuitively sensible way to characterize dispersion around the mean. • The values generated by the average and standard deviation are different numbers, but they tend to be similar to each other. • The average deviation is of no value in statistical tests, and it is rarely ever calculated. • Standard deviations are a very useful value to calculate. Historical Figure Summary Statistics • Sir Francis Galton, 1812-1911 (Charles Darwin’s half cousin). Measures of Variability • Founder of ____________. • Discovered that psychological traits were _________ distributed. • Proposed that a distribution be described by only two numbers: the ______ and ________________. • Invented the concept of ___________ and the formula for its computation. Range 96 – 130 Average Deviation Σ/X – M/ N Standard Deviation Σ/X – M/2 N Distributions Statistical Reasoning** • Skewed Distributions • The Normal Curve • Rectangular A Skewed Distribution 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 90 475 710 70 Mode Median One Family Mean Income per family in thousands of dollars 7 Measures of Variation** Standard Deviation Units and the Normal Distribution** Range: The difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution. Standard Deviation: A computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean. h d th Revised 2006 PSB Rectangular Distribution Question • Which value is the mode in a rectangular distribution? – A. Every value within the range of scores in the distribution has the same frequency frequency…they they are all the mode. – B. The median value. Low Scores High Standard Deviation Units and the Normal Distribution** 34% of the scores fall between the mean and 1 SD below or above the mean Class Notes • For the purpose of this class round 34.13% to 34%. • Round 13.59% to 14%. • SD = Standard Deviation • __________________________________ • __________________________________ • __________________________________ 8 Standard Deviation Units and the Normal Distribution** Question • What is the approximate percentage of scores that fall between the mean and 1 SD above the mean? 14% of the scores fall between 1 and 2 SD either above or below the mean Question • What is the approximate percentage of scores that fall between 1 SD below the mean and 2 SD below the mean? Question • For his first two college assignments Sam earned a score of 26 in his psychology class and a 32 in biology. In which of these classes did Sam perform best relative to his classmates? – 1. Psychology – 2. Biology – 3. I need to know the mean and SD for the scores in each class to answer this question. Question • Given: Psy: M = 20, SD = 3 Bio: M = 30, SD = 4 In terms of percentile ranks, which score is better, better a value of 26 in psychology or a grade of 32 in biology? 1. Psychology 2. Biology Class Notes • M = mean • You are expected to know how to evaluate scores using percentile rankings. Ask questions now if this is unclear! • __________________________________ • __________________________________ • __________________________________ • __________________________________ 9 Correlation** Correlation • Sometimes ___________ cannot be conducted. • The correlation coefficient is a measure of how strongly two variables are “____________”. • A high association ___________ imply causation. • Correlation Coefficient – a statistical measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus how well either factor predicts the other Indicates direction of relationship (positive or negative) Correlation coefficient r = +.37 Indicates strength of relationship (0.00 to 1.00) Examples of a Scatterplot Correlation • Scatterplot – a ___________________, each of which p the values of _____ variables represents – the ______ of the points suggests the direction of the relationship – the _________ of scatter suggests the _______ of the correlation • little scatter indicates ____ correlation – also called a scattergram or scatter diagram Copyright © Allyn & Bacon 2008 Correlation** Perfect positive correlation (+1.00) No relationship (0.00) Correlation Perfect negative correlation (-1.00) Scatterplots, showing patterns of correlations • A correlation is an x y plot of how strongly two variables are associated. • In a positive correlation (positive slope) as x values ________ yy-values x-values values also tend to _________. • In a negative correlation (negative slope) as x-values __________, y-values tend to _________. 10 Textbook Assignment Ch2-2 Free Transportation • In addition to experiments and studies using correlation, two other methods are sometimes used in psychological research. What are they? • _______________designs involve watching g behavior in real-world settings. • _______________ designs can provide existence proofs, but are largely anecdotal. • Of the two designs noted above, ________________has high external validity, but low internal validity. • Email your response to your SI. • At the University of South Alabama a free public transportation system (Jag Tran) was launched just prior to the onset of the rise in the cost of gasoline. • It took a while for students to begin to ride the Jag Tran. • The association between the number of students riding the Jag Tran and the cost of gasoline is shown in the next slide. Correlation and Causation Correlation and Causation Jag Tran and the Cost of Gas • Is it fair to argue that the increase in the number of Jag Tran riders has caused the increase in the cost of gasoline? • A strong correlation or association does not prove ___________!! 700 Riders per We eek 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 Dollars per Gallon The Advantage of Experiments • Experiments permit researchers to establish cause and effect relationships between dependent and independent variables. • Other types of research design may provide greater ________ validity. Question • All psychological research is conducted in laboratory settings. – T/F 11 THE RULES Cooperative Group Challenge • • • • • • Q1 1. _____- harm resulting from the mere expectation of harm Placebo effect Nocebo effect Double blind design Experimenter expectancy effect Demand characteristics Hawthorne effect Q2 2. _____- neither researchers nor subjects know who is in the experimental or control group Q3 3. _____- phenomenon in which participants’ knowledge that they’re being studied can affect their behavior 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Q4 • 4. _____- improvement resulting from the subject’s expectation of improvement 12 Q5 • 5. _____- cues that participants pick up from a study that allow them to generate guesses regarding the researcher’s hypothesis Q6 • 6. _____- improvement resulting from the investigator’s expectation of improvement 13