Capital Structure Strategies for the Generations
advertisement
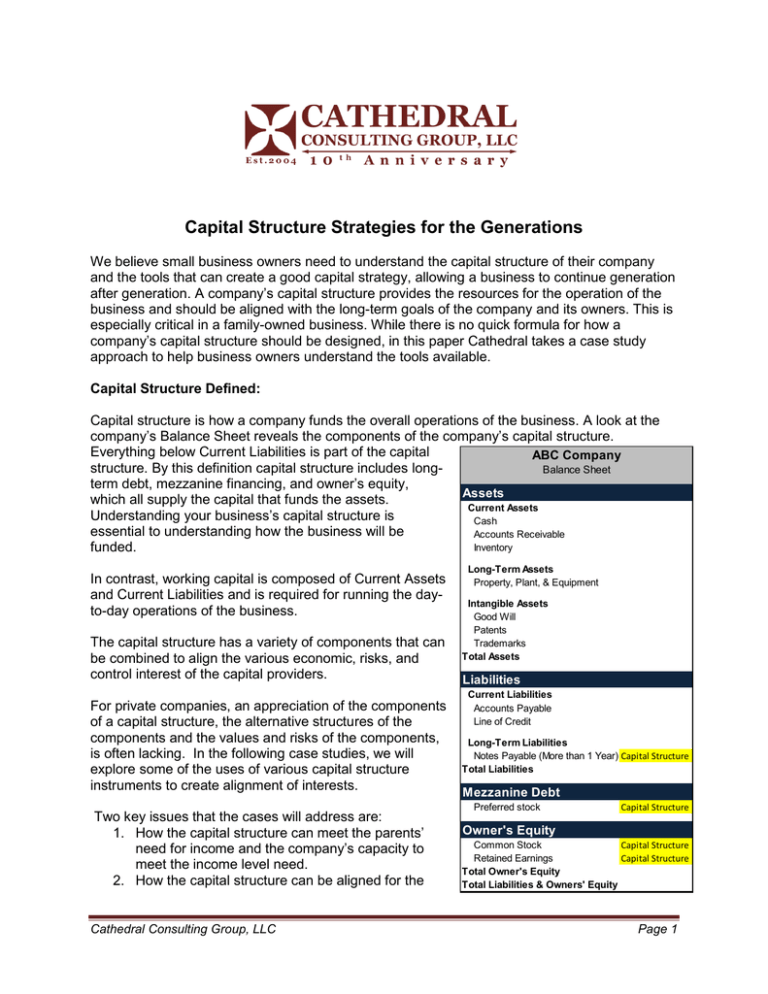
Capital Structure Strategies for the Generations We believe small business owners need to understand the capital structure of their company and the tools that can create a good capital strategy, allowing a business to continue generation after generation. A company’s capital structure provides the resources for the operation of the business and should be aligned with the long-term goals of the company and its owners. This is especially critical in a family-owned business. While there is no quick formula for how a company’s capital structure should be designed, in this paper Cathedral takes a case study approach to help business owners understand the tools available. Capital Structure Defined: Capital structure is how a company funds the overall operations of the business. A look at the company’s Balance Sheet reveals the components of the company’s capital structure. Everything below Current Liabilities is part of the capital ABC Company structure. By this definition capital structure includes longBalance Sheet term debt, mezzanine financing, and owner’s equity, Assets which all supply the capital that funds the assets. Current Assets Understanding your business’s capital structure is Cash essential to understanding how the business will be Accounts Receivable Inventory funded. In contrast, working capital is composed of Current Assets and Current Liabilities and is required for running the dayto-day operations of the business. The capital structure has a variety of components that can be combined to align the various economic, risks, and control interest of the capital providers. For private companies, an appreciation of the components of a capital structure, the alternative structures of the components and the values and risks of the components, is often lacking. In the following case studies, we will explore some of the uses of various capital structure instruments to create alignment of interests. Two key issues that the cases will address are: 1. How the capital structure can meet the parents’ need for income and the company’s capacity to meet the income level need. 2. How the capital structure can be aligned for the Cathedral Consulting Group, LLC Long-Term Assets Property, Plant, & Equipment Intangible Assets Good Will Patents Trademarks Total Assets Liabilities Current Liabilities Accounts Payable Line of Credit Long-Term Liabilities Notes Payable (More than 1 Year) Capital Structure Total Liabilities Mezzanine Debt Preferred stock Capital Structure Owner's Equity Common Stock Capital Structure Retained Earnings Capital Structure Total Owner's Equity Total Liabilities & Owners' Equity Page 1 child who works in the business versus aligned for the siblings that are not in the business. The tools available for creating alignment are in the table below. The type of entity and its tax status offer the ability to use these tools. C Corp S Corp LLC Tools: Pension X -X X Retirement Payout Obligations: Unfunded Deferred Compensation X X X Guaranteed Retirement Payments X Debt X X X Preferred Stock X N/A Preference Interest X Common Stock/Member Equity X X X Voting X X X Non-Voting X X X Gifting Shares/Interest (Current Tax Rules permit up to $5 million) X X X Note: S Corp’s are lighter on pension plan options. Also, while the current tax rules as of September 2012 permit up to $5M in gifting, these could reset to $1M in 2013. The discussion of a specific tool, its limits and uses, is beyond the scope of this Topic of the Month. The cases give an example of some of the elements. Case Studies to Illustrate Strategies: We will use the following fact pattern for the three case studies. The only change with each case will be whether the company is a Corporation taxed as a C Corp, a S Corp, or is a Limited Liability Company. ABC Company is wholly-owned by its founder. The business represents the majority of the net worth of the founder. The founder has a family that includes a wife and three children. The family is close. One child works in the business and the other two children do not have a real interest in the business. It is also anticipated that the spouse will survive the founder. The founder needs income from the business for the rest of his and his wife’s life. The founder has some worry about control. The founder and his wife wish to divide their estate evenly between their children. The child in the business desires some control. Case Study 1: Company ABC is a Corporation taxed as a C Corp. Key factor: A C Corp creates double taxation, but has some qualified retirement benefits. Strategy: 1. Establish a pension and retirement obligations. This is a tax efficient way to align the parent’s economic needs for income. But retirement plans burden the company and should be viewed as a part of the capital structure. The reason to use the pension and retirement obligation strategy is: a. Avoiding double taxation. Cathedral Consulting Group, LLC Page 2 b. Reduce the value of the company allowing for shares to be transferred to the children. The 2012 tax rules allow for up to a $5 million transfer as a gift without tax. 2. If the parents think the pension is not enough to meet their income needs, giving supplemental income through a preferred stock, that the parents would hold, could be used, since a C Corp allows for preferred stock. 3. The son in the business may want control and premium economic interest but the parents want each child to participate equally. (See below for the use of voting/nonvoting stock) 4. The balance of common stock would then be given equally to the three children. Observations: 1. The pension is deferred income for the parents. Qualified plans remove the fund from the company minimizing future risks. 2. Giving each of the three children 1/3 of the company does not align the effort of operating the company with ownership, which can lead to future stress in the family and the company. 3. Preferred stock addresses the economic concerns of the parents but dividends from preferred stock are double taxed in contrast to the interest on the debt which is single taxed. 4. Parents often struggle with giving up control. A pension and preferred stock without voting rights addresses economic need, but not control transfer issues. Case Study 2: Company ABC is a Corporation taxed as a S Corp. Key factor: S Corp avoids double taxation, but can have both inside-outside basis concerns and limits pension options. Strategy: 1. Use of a pension strategy in an S Corp can be more limited than in a C Corp, requiring more preferred stock or debt to meet the parent’s income needs and cash requirements. A non funded compensation plan could be used as well. 2. Parents in this case want to keep control but pass the value of the company on to their children. To solve the control issue the strategy will be to utilize voting and non-voting common stock. Common Stock will be converted into: a. Voting common stock representing 10%. b. Non-voting common stock representing 90%. Relative to the dividend participation: 51% held by the parents and 49% held by the child who is in the business. Non-voting common stock will be split equally between the three representing 90%. 3. If needed instead of preferred stock, use debt because a S Corp allows only one class of stock. Observations: 1. Parents have an income strategy and retain control of the company. 2. The child in the business has a sense of control, yet the children are treated approximately equally relative to the economic participation in the company. 3. Efficiency of payout to parents can be about the same, or better than with a C Corp. Cathedral Consulting Group, LLC Page 3 Case Study 3: Company ABC is a Limited Liability Company (LLC). Key factor: A LLC allows great flexibility in designing interests to meet the needs of the parents and the children. Qualified pensions are more limited, but the use of guaranteed payment structures creates similar and clearer deferred compensation arrangements. Strategy: 1. Parents upon retirement will receive a guaranteed payment. 2. The son participating in the business can be given a voting interest with parents retaining a voting interest as in case study 2. 3. Each of the three children will receive a membership interest of 1/3 of the results afer the guaranteed payment. Observations: 1. An LLC provides unlimited flexibility of the terms between the parent and the children. 2. Parent’s payout guaranteed payment is a direct profit interest that creates a single tax. 3. The child in the business can receive a management vote while having the same net economic interest as all the siblings. Actions: 1. Look at the organizational tax status to see whether it is optimized. 2. Review the capital structure and its alignment with long-term economic interest, management activities, and ownership needs. Philip Clements is CEO of Cathedral Consulting Group, LLC and a Managing Director in the New York Office. Elizabeth Christenson is a former Associate in the New York Office. For more information, please visit Cathedral Consulting Group LLC online at www.cathedralconsulting.com or contact us at info@cathedralconsulting.com. Cathedral Consulting Group, LLC Page 4