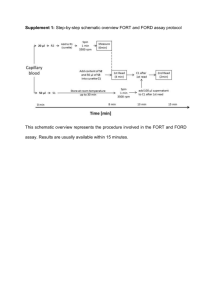
STUDENT WORKBOOK Consume Tutorial
advertisement

Consume Tutorial STUDENT WORKBOOK Land Management Tool Training Package Fire and Environmental Applications Team USFS - PNW Research Station Pacific Wildland Fire Sciences Laboratory 400 North 34th Street, Suite 201 Seattle, Washington 98103 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION ........................................................................................i Instructions for Installing Consume 3.0 Software .................................. iii Consume 3.0 Tutorial .............................................................................. vi Welcome to the Consume 3.0 Tutorial .....................................................1 Part 1: Introduction to Consume 3.0........................................................2 What is Consume? .................................................................................. 3 Consume 3.0 Features............................................................................. 4 Hierarchical Organization ......................................................................... 5 Bailey's Ecoregion Divisions...................................................................... 6 Potential Applications .............................................................................. 7 Part 2: Installing Consume 3.0 ................................................................8 Downloading Consume 3.0....................................................................... 9 Installing Consume 3.0.......................................................................... 10 Part 3: Using Consume 3.0.....................................................................11 Consume Welcome Screen ..................................................................... 12 Instructions for Beginning Users ............................................................. 13 Getting Help...................................................................................... 14 Quick Keys........................................................................................ 15 Main Window ....................................................................................... 16 Viewing Projects in the Navigation Tree................................................. 17 Resizing the Navigation Tree Window.................................................... 18 Status Bar ........................................................................................ 19 Using Sample Data............................................................................. 20 Moving, Copying and Deleting Items in the Navigation Tree ..................... 21 Creating Items in the Navigation Tree................................................... 22 Importing and Exporting Projects ......................................................... 23 Project Screen...................................................................................... 24 Unit Screen.......................................................................................... 25 Fuelbed Screen .................................................................................... 26 Fuelbed Screen: General fuelbed information ......................................... 27 Fuelbed Screen: Environmental variables page....................................... 28 Fuelbed Screen: Fuel characteristics page ............................................. 29 Loading Calculator buttons .................................................................. 30 FCCS Wizard ..................................................................................... 31 FCCS Wizard: Loading a standard FCCS fuelbed ..................................... 32 FCCS Wizard: Importing custom fuelbeds .............................................. 34 Pile Group Wizard ................................................................................. 36 Entering Data....................................................................................... 37 Weather Zone Screen............................................................................ 38 Consumption and Emissions Summary Screen .......................................... 39 Reports Screen..................................................................................... 40 Creating Reports................................................................................ 41 Creating Graphs ................................................................................ 42 Report and Graph Types ..................................................................... 43 Viewing Reports................................................................................. 56 Scenario Testing................................................................................... 57 Piled Scenarios .................................................................................. 58 Non-Piled Scenarios ........................................................................... 59 Scenario Tool Summary Report ............................................................ 60 Scenario Tool Fuel Consumption Graphs................................................ 61 Scenario Tool Emissions Graphs ........................................................... 62 Using Consume in Batch Mode ................................................................ 63 Part 4: Case Studies...............................................................................64 Southern Case Study ............................................................................ 65 Step 1: Creating a Project .................................................................. 66 Step 2: Entering Unit Data .................................................................. 67 Step 3: Importing Fuelbed Data ........................................................... 68 Step 4: Entering Fuelbed Data ............................................................. 69 Step 5: Reviewing and Editing Fuel Characteristics ................................. 70 Step 6: Calculating Consumption and Emissions ..................................... 72 Step 7: Comparing Fuelbeds................................................................ 74 Step 8: Comparing Consumption and Emissions ..................................... 75 Western Case Study.............................................................................. 76 Step 1: Creating a Project .................................................................. 77 Step 2: Entering Unit Data .................................................................. 78 Step 3: Importing Fuelbed Data ........................................................... 79 Step 4: Entering Fuelbed Data ............................................................. 81 Step 5: Reviewing and Editing Fuel Characteristics ................................. 82 Step 6: Pile Wizard............................................................................. 83 Step 7: Calculating Consumption and Emissions ..................................... 85 Step 8: Comparing Fuelbeds................................................................ 87 Step 9: Comparing Consumption and Emissions ..................................... 89 Step 10: Generating Reports ............................................................... 90 i INTRODUCTION Fire is a natural process in many ecosystems, and managers are increasingly expected to use fire as a landscape-level fuel treatment to improve ecosystem health and reduce the likelihood of catastrophic fires. Fuel consumption is a key variable in the modeling of fire effects. It is one of the most critical factors in understanding when and how fire should be applied to meet site and landscape objectives, and assessing wildland fire consequences. Although a tremendous amount of research has been accomplished thus far in the development of fuel consumption models in the United States, until recently, little effort was directed to non-forested fuel types such as chaparral, sage, and palmetto/galberry shrublands in the West and South, pinyon juniper savannas in the Southwest, boreal forest types in Alaska, and hardwood forests in the East and South. In addition, relatively little work has been devoted to characterize long-duration fuel consumption from the burning of large, rotten logs, stumps or deep concentrations of organic matter such as duff or moss, which are often prevalent in forested areas where natural fire has been eliminated for the past 80 to 100 years. Fire is becoming an important landscapelevel fuel treatment tool. In order for managers to develop improved wildland fire plans that meet specific land management objectives, research is required to better characterize both the fuel loading and fuel consumed during wildland fire in forested and nonforested fuel types throughout the United States. Fuel Consumption Research Between 1994 and 2003, FERA inventoried and burned 106 sites in the United States including marsh grass, tallgrass prairie, sagebrush shrublands, chaparral, palmettogalberry shrublands, Ponderosa pine/mixed conifer forests, black and white spruce/hardwood forests, longleaf pine forests, southeastern sand hill scrub, and southeastern hardwood and pine forests. Data from all burns were compiled and analyzed, and fuel consumption models were constructed for the following fuelbed types: black and white spruce/hardwoods, longleaf and loblolly pine, ponderosa pine, nonwoody vegetation (including marshgrass and tall grass prairie), and sagebrush. ii Overview of Consume 3.0 Consume v 3.0, released in the fall of 2005, reflects our improved understanding of fuel consumption and emissions in wildland fire throughout major fuel types in the United States. Consume v 3.0 is a decision-making tool, designed to assist resource managers in planning for prescribed fire, wildland fire for use, and wildfire. Consume predicts fuel consumption, pollutant emissions, and heat release based on a number of factors including fuel loadings, fuel moisture and other site characteristics. Using these predictions, resource managers can determine when and where to conduct a prescribed burn or plan for a wildland fire to achieve desired objectives, while reducing the impact on other resources. For more information, contact: Roger Ottmar, Research Forester Fire and Environmental Applications Team USFS - PNW Research Station Pacific Wildland Fire Sciences Laboratory 400 North 34th Street, Suite 201 Seattle, Washington 98103 iii Instructions for Installing Consume 3.0 Software System Requirements You can install Consume on a personal computer with the following system: • 30 MB of available disk space. • Microsoft Windows® 2000 or XP operating systems. • Optional requirement: Consume links to Microsoft Excel for viewing 1000-hr fuel moisture graphs. If you do not have Excel on your computer, Consume will run but will not support this graphics feature. Administrative Privileges If you do not already have administrative privileges on your computer, you must obtain them before installing Consume 3.0. To check if you have administrative privileges, click on the clock at the bottom right of your desktop. If you are allowed to change the date and time on your computer, you already have administrative privileges. If you do not, please contact your system administrator for assistance. Downloading and Installing Consume 3.0 Consume 3.0 has a flexible design and can be run in Microsoft® Windows or in a simple batch mode for use in other operating systems. The Consume calculator engine was written in Java to allow it to be used in batch mode. The Java implementation for the Windows interface was done using Microsoft® J#.Net. J# requires an extra run-time environment, called the Visual J#.NET Redistributable 1.1. In order to run Consume in Microsoft Windows®, it is necessary to have both Microsoft Framework .NET v 1.1 (or .Net v 2.0) and Visual J#.NET installed on your computer. Most computers will already have the Microsoft Framework .NET v1.1 (or .NET v 2.0), but Visual J#.NET will need to be installed on most computers. The best way to check if you have the necessary Microsoft Windows updates is to try installing Consume 3.0. You will receive detailed error messages if you need to install Microsoft Framework.NET version 1.1 and/or Visual J# .NET. To download and install the necessary updates, you may either follow the on-screen instructions provided by Microsoft® or the instructions provided later in this installation guide. To Download and Install Consume 3.0: 1) Go to the Consume website: http://www.fs.fed.us/pnw/fera/products/consume.html 2) Under the Consume 3.0 software download, double-click Setup.msi. iv 3) From the File Download dialog box, click Save to Disk. Depending on your internet connection speed, the file download may take a few minutes. 4) Once the download is complete, double-click on the file Setup.msi to launch the installation process. 5) Follow the on-screen instructions to install Consume 3.0. You will receive detailed error messages if you need to install Microsoft Framework.NET version 1.1 and/or Visual J# .NET. To download and install the necessary updates, you may either follow the on-screen instructions provided by Microsoft® or the following sections of this User’s Guide. Installing Microsoft® Framework .NET version 1.1 Redistributable Package: Most Microsoft® Windows 2000 and XP operating systems should have a working version of Microsoft.NET. Newer computers will have a working version of .NET v 2.0. If your computer does not have Microsoft.NET (v.1.1 or 2.0), follow these installation instructions: 1) Connect to the internet (a high speed connection is recommended). 2) Go to: http://www.microsoft.com/downloads 3) Under “Popular Downloads,” click on .NET Framework Version 1.1 Redistributable Package. If you cannot locate the link under Popular Downloads, type “.NET Framework Version 1.1” under “Search” and then click on .NET Framework Version 1.1 Redistributable Package in the search results. 4) Click Download. 5) In the File Download dialog box, click Save to Disk. 6) Once the download is complete, double-click on the file dotnetfx.exe to launch the installation process. 7) Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation. If your operating system already has Microsoft Framework .NET v1.1 or v 2.0 installed, you will get an error message during this installation process. Cancel this installation and proceed to Installing Microsoft® J#.Net Redistributable Package version 1.1. Installing Visual J#.NET Redistributable Package 1.1: Most Microsoft® Windows 2000 and XP operating systems will not have Visual J#.NET. If your computer does not have Visual J#.Net v 1.1, follow these installation instructions: 1) Connect to the internet (a high speed connection is recommended). v 2) Go to: http://msdn.microsoft.com/vjsharp/downloads/howtoget/def ault.aspx 3) .Click Download Microsoft® Visual J#.NET Redistributable Package 1.1. 4) Click the Download button. 5) In the File Download dialog box, click Save to Disk. 6) Once the download is complete, double-click on the file vjredist.exe to launch the installation process. 7) Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation. If your operating system already has Microsoft Visual J#.NET 1.1, you will get an error message during the installation process. Cancel this installation and proceed to the Consume 3.0 download and installation. For further information about the Consume 3.0 download, contact: Susan Prichard, Research Scientist and Consume Manager (509) 996-2408 sprich@u.washington.edu vi Consume 3.0 Tutorial The following pages follow the online tutorial which can be downloaded and/or viewed at: http://www.fs.fed.us/pnw/fera/products/software_tutorials.html The student workbook includes everything in the tutorials and provides space at the bottom of each page for your notes. 1 Welcome to the Consume 3.0 Tutorial To start the tutorial, click on a topic in the tutorial index. You can view the entire tutorial page by page by clicking the ► button at the top right of each screen or look up specific topics by clicking them in the index. If you click on a hyperlink within a tutorial page, please use the back button in your browser or click on the topic in the tutorial index to return to that tutorial page. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 2 Part 1: Introduction to Consume 3.0 • What is Consume? • Features • Hierarchical Organization • Bailey's Ecoregion Divisions • Potential applications Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 3 What is Consume? • Consume is a software program that models the amount of fuel consumption and emissions of a prescribed or wildland fire. • Consume 3.0 accommodates a wide range of fuel characteristics, including those defined by the user. • Version 3.0 builds on Consume 2.1 with more flexibility, updated equations, and a direct link to the Fuel Characteristic Classification System (FCCS). Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 4 Consume 3.0 Features • Requires Windows operating systems (2000 or XP) to run the full version. • A batch mode version can be run via command line on any operating system. • Uses region-specific equations (boreal, southern, western) to calculate fuel consumption. • Provides the FCCS Wizard to import customized fuelbeds directly into Consume. • Allows users to edit or create fuelbeds directly in Consume and create a library of customized fuelbeds. • Imports daily weather observation files from the Weather Information Management System (WIMS). • Creates printable and exportable reports. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 5 Hierarchical Organization To reflect actual management strategies, Consume is organized hierarchically into projects containing one or more burn units. Burn units are further divided into multiple fuelbeds. The majority of fuel and environmental information is managed at the fuelbed level. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 6 Bailey's Ecoregion Divisions Fuelbeds are organized geographically into Bailey’s ecoregion divisions including: tundra, subarctic, warm continental, hot continental, subtropical, prairie, marine, Mediterranean, tropical/subtropical steppe desert, tropical/subtropical desert, temperate steppe, temperate desert, savanna, and rainforest. Consume uses ecoregion divisions to determine which of three regional equation sets (boreal, southern or western) are used for natural fuel consumption calculations. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 7 Potential Applications 1. Consume is a decision-making tool for wildland fire planning. 2. Consume can help achieve burn objectives while minimizing impact of fire on air quality and other resources. 3. The regional equations in Consume model our current understanding of wildland fuel consumption and emissions and can be used in hypothesis testing for future consumption and emissions research. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 8 Part 2: Installing Consume 3.0 • Downloading Consume 3.0 • Installing Consume 3.0 Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 9 Downloading Consume 3.0 To download Consume 3.0: 1. Go to the Consume website: http://www.fs.fed.us/pnw/fera/products/consume.html 2. Under the Consume 3.0 software download, double-click Setup.msi. 3. From the File Download dialog box, click Save to Disk. Depending on your internet connection speed, the file download may take a few minutes. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 10 Installing Consume 3.0 Tip: If you do not already have administrative privileges on your computer, you must obtain them before installing Consume 3.0. To install Consume 3.0: 1. Double-click on the file Setup.msi that you downloaded from the Consume 3.0 website. 2. Follow the on-screen instructions to install Consume 3.0. You will receive detailed error messages if you need to install Microsoft Framework.NET version 1.1 and/or Visual J# .NET. To download and install the necessary updates, you may either follow the on-screen instructions provided by Microsoft® or the installation instructions provided on the Consume website (File name: Consume 3.0 Download and Installation Instructions.pdf): http://www.fs.fed.us/pnw/fera/products/consume.html. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 11 Part 3: Using Consume 3.0 • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Consume Welcome Screen Instructions for Beginning Users o Getting Help o Quick Keys Main Window o Viewing Projects in the Navigation Tree o Resizing the Navigation Tree Window o Status Bar o Using Sample Data o Moving, Copying and Deleting Items in the Navigation Tree o Creating Items in the Navigation Tree o Importing and Exporting Projects Project Screen Unit Screen Fuelbed Screen o General fuelbed information o Environmental variables page o Fuel characteristics page o Calculators FCCS Wizard o Loading standard FCCS fuelbeds o Importing custom FCCS fuelbeds Pile Group Wizard Entering Input Data Weather Zone Screen Consumption and Emissions Summary Screen Reports Screen o Creating Reports o Creating Graphs o Report and Graph Types o Viewing Reports Scenario Testing o Piled Scenarios o Non-Piled Scenarios o Scenario Tool Summary Report o Scenario Tool Consumption Report o Scenario Tool Emissions Graphs Using Consume in Batch Mode Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 12 Consume Welcome Screen When you first open Consume, the Welcome Screen appears and displays examples of fuel consumption trials throughout the United States. Click Next to proceed to the program. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 13 Instructions for Beginning Users This screen provides basic instructions for using the program. • If you do not need these instructions when you open Consume, you can check the box next to “Click here if you do not want to see these instructions again.” • Click Continue to Consume to proceed to the program. Tip: You can always reinstate this screen by selecting Show Entry Screen in Administration Information Screen (Tools menu > Options > Administrative Information). The screen will appear the next time you launch Consume. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 14 Getting Help You can get help from many places in Consume by pressing F1 on your keyboard. Consume displays a Help screen with specific information about that part of the application. More general help can be obtained from the help menu. To use the help menu: 1. Open the Help menu. 2. Select Index for a list of specific help topics. 3. Select About for the version of Consume and support contacts. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 15 Quick Keys Type the following keys or key strokes to activate quick keys: File menu: ALT-F New item: ALT-F N Exit: ALT-F X New item: CTRL-N Save: Edit menu: ALT-E CTRL-S Cancel changes/undo: CTRL-Z Cut: CTRL-X Copy: CTRL-C Paste: CTRL-V Tools menu: ALT-T Context-sensitive help: F1 Help menu: ALT-H Loading calculators: F2 Tip: To view key stroke commands in menus, press the ALT key. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 16 Main Window The main window is the entry point for all Consume activities. To enter into Project, Unit and Fuelbed screens, use the navigation tree at the left side of the main window. Projects are organized into four categories: • • • • Planned activity: projects that have not been implemented. Active projects: projects that are currently undergoing burn treatments. Completed projects: projects that have recently completed all burn treatments. Archived projects: projects that have completed all burn treatments and are now part of a project archive. Click on a project category to view existing projects or create a new project. All weather zones are stored in the weather zone folder. Note: Weather zone data are only required if you wish to predict the Adjust 1000-hr (Adj-Th) fuel moisture content for activity fuels. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 17 Viewing Projects in the Navigation Tree To view existing projects, click on a project category name or the + sign to the left of a project name to expand the tree. Click on a project, unit or fuelbed to view its corresponding input screen. Tip: If you select a project, unit, fuelbed or weather zone in the navigation tree, the input screen appears to the right and the selected item is highlighted in blue. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 18 Resizing the Navigation Tree Window To resize the width of the navigation tree, position your mouse cursor on the border between the navigation window and main screen. Expand the window to the right when the resizing cursor appears. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 19 Status Bar The Status Bar is located on the bottom left of the main screen. The bar tells you which screen is active. In this example, the fuelbed screen for Longleaf-FCCS185 is open (scroll down to view). The corresponding Unit and Project Names are also listed in the Status Bar. Projects, units and fuelbeds that are missing information are marked as invalid in the status bar (bottom left of the main screen) and appear with red icons in the navigation tree. When you save your work, Consume will notify you of any validation issues and allow you to save your inputs. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 20 Using Sample Data Consume includes some sample projects and weather zones. Before you use Consume to create your own projects and weather zones, you can use these data to try out Consume and see how it works. For example, you can use the examples to view and modify existing data and create reports. When you are ready to start using Consume to enter your own data, you can delete the sample projects and weather zones by selecting them in the navigation tree and pressing the DELETE key on your keyboard or selecting Delete from the File menu. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 21 Moving, Copying and Deleting Items in the Navigation Tree Navigation tree items can be moved by clicking on items then dragging and dropping them to a new destination, or by copy, cut and paste commands. Items may be deleted by clicking on them individually and selecting Delete from the File menu or pressing delete on your keyboard. Tip: Many commands (cut, copy, paste, delete) that are available in Consume menus can be done using your keyboard. See the Quick Key page for a full listing of options. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 22 Creating Items in the Navigation Tree To insert a new project, click on a project category in the navigation tree, select New from the File menu, and enter a project name. A blank unit and fuelbed will be inserted within the project. Each project can contain multiple units and fuelbeds. • • To create a new unit in a project, click on a project in the navigation tree, select New from the File menu, and enter a unit name. To create a new fuelbed, click on a unit, select New from the File menu and enter a fuelbed name. • Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 23 Importing and Exporting Projects Consume allows you to export projects to a file that may be stored as a backup or transferred to other computers. To export a Project: 1. Click on a project (or an associated unit or fuelbed) to export in the navigation tree. 2. Select Export from the File menu. Consume opens a save dialog box and prompts you for a file location. 3. Select a file location to save the exported project and then click OK. 4. Consume writes the project files to the specified folder and opens the following message: The export was successful. Project files have been created at: pathname\EXP_projectname 5. The exported project resides in a folder that contains multiple files. The Consume Export File (.cef) depends on the multiple .xml source files in the shared folder. To avoid corrupting the exported project, do not move or delete individual files from this folder. Tip: If you share exported projects to other Consume users or wish to move exported projects to another location, copy the entire project folder. The Consume Export File (.cef) depends on the multiple .xml source files in the shared folder. To avoid corrupting the exported project, do not move or delete individual files from this folder. To import a Project: 1. Select Import from the File menu. 2. Select Import Projects. 3. Browse to the project location and double click on the project folder 4. Select the Consume Export File with the extension .cef. 5. Click OK. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 24 Project Screen The project screen records basic information on your project including the project name, organization ID, organization name, start date, end date, project status (planned, active, completed or archived) and total project size (acres). Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 25 Unit Screen The unit screen records basic information about your burn unit including the unit name, permit number, burn date, treatment type (prescribed burn, wildland fire use or wildfire), total unit size (acres) and number of fuelbeds in the unit. Tip: Consume will alert you if your burn date doesn’t fall within your project start and end dates and will automatically reset the project end date to accommodate your burn date. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 26 Fuelbed Screen The fuelbed screen is divided into three main sections: • General fuelbed information • Environmental variables page • Fuel characteristics page Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 27 Fuelbed Screen: General fuelbed information The upper third of the fuelbed screen is visible at all times and contains general fuelbed information including fuelbed type, fuelbed description and fuelbed location data using Bailey’s ecoregion division, vegetation form and cover type. The FCCS wizard is accessible by clicking the red button to the left of Classification. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 28 Fuelbed Screen: Environmental variables page The environmental variables page records environmental data necessary to perform consumption and emissions calculations. • The General Environmental Variables section records inputs required for all calculations. • The Activity Fuelbed Environmental Variables section records input required only for activity fuel calculations. (Scroll down to view example). Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 29 Fuelbed Screen: Fuel characteristics page The fuel characteristics page records fuel loadings and dimensional data in separate tabs for the canopy, shrub, nonwoody vegetation, woody fuels, litter-lichen-moss, and ground fuels strata. Click on stratum tabs to view and enter stratum data. (The Canopy stratum is displayed in this example). Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 30 Loading Calculator buttons Consume offers loading calculators if you wish to enter your own data but do not have loading values for all strata. Loading calculators are available for trees, snags, ladder fuels, shrubs and stumps. The calculators use the same equations as in FCCS but with defaults in place of speciesspecific variables such as crown bulk density and wood particle densities. Because default values are used, results can vary substantially from the species-specific loading calculations in FCCS. The use the Loading Calculators: 1. Click on the calculator icon to the right of the input loading variable (overstory trees shown below). 2. Enter input values and Click the Calculate button. Click the Accept button to accept the loading calculation or the Cancel button to cancel changes and return to the fuelbed screen. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 31 FCCS Wizard You can use the FCCS wizard to import fuel characteristics data from the Fuel Characteristics Classification System (FCCS). To enter the FCCS Wizard: 1. Click on the red FCCS wizard button in the top section of the Fuelbed screen. This is an unlabelled red button to the left of “Classification” (circled below). 2. If you are viewing a fuelbed, you may also select FCCS wizard from the Tools menu. This option is available only when the fuelbed screen is open. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 32 FCCS Wizard: Loading a standard FCCS fuelbed If you are loading a standard FCCS fuelbed, you can select a fuelbed from the entire list of FCCS fuelbeds or query the fuelbeds using five selection variables. Standard fuelbeds contain fuel loadings and dimension data that were created for each of the FCCS national fuelbeds and preloaded into Consume. To select a fuelbed by name: 1. When you first launch the FCCS wizard, all available FCCS fuelbeds are listed in the results window under "Fuelbed ID and Description." 2. Select a fuelbed from the results window. 3. Click the Load Values button at the bottom right of the FCCS wizard screen. To query the FCCS fuelbeds (scroll down to view example): 1. Select an ecoregion and/or vegetation form from the drop-down lists. 2. You may then consecutively select a cover type, forest structure class and change agent. Each selection narrows the selection list. Not every selection variable may be necessary to narrow the list to a single fuelbed. 3. Select a fuelbed from the results window under "Fuelbed ID and Description" 4. Click the Load Values button at the bottom right of the FCCS wizard screen. Tip: if you selected an Ecoregion, Vegetation Form and Cover type to query FCCS fuelbeds, Consume will automatically fill these variables under General Fuelbesed Information. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 33 Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 34 FCCS Wizard: Importing custom fuelbeds If you have created custom fuelbeds in FCCS, you can import them into your own library in Consume 3.0. To import a custom FCCS fuelbed into the library of custom fuelbeds: 1. Click the Get Custom FCCS Fuelbed button to import the fuelbed into Consume. Tip: if this is your first time using this feature, Consume will ask you to either browse to location where FCCS is stored on your computer or perform an automated search to located the pathway. 1. Select either an input or intermediate file. Although Consume requires both files, you only need to specify one of them for import: …/fccs/results/consume/projectname_intermediate.xml OR …fccs/results/consume/projectname_input.xml. 2. Click the Open button to import the custom FCCS fuelbed file. To load a custom fuelbed (scroll down to view example): 1. Click on the checkbox next to "Load values from a custom FCCS fuelbed". 2. If you have already compiled a library of custom fuelbeds, you can select a custom fuelbed under Fuelbed ID and Description. 3. Click the Load Values button to populate the fuel characteristics pages of the fuelbed screen. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 35 Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 36 Pile Group Wizard The term “Pile” is used generically in Consume to represent any woody fuel accumulation, created from timber harvesting, other management activities, or though natural processes. Pile groups are entered in the Woody Fuels stratum tab of the Fuel Characteristics page (scroll down to view example). Click Add to launch the Pile Group Wizard. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 37 Entering Data 1. Enter data in the white entry cells. Data cells that are not required for your particular project will be grayed out. To switch between cells, you may use your mouse to click on a different cell or press the Enter or tab key. Shift-tab will jump to the previous cell. 2. The fuelbed and weather zone screens have multiple data entry tabs. To switch between tabs, click on the labeled tabs at the top of the page or press Page Down or Page Up on your keyboard. 3. Once you are finished entering your data on a screen, click the Save button. Consume will validate data entry and display any problems. If no problems were identified, Consume will save the information. Otherwise, Consume will list the problems and will prompt you to save the information as is, cancel your work, or continue editing. Tip: Browse mode vs. Edit mode Browse mode allows you to view information and move from one selection to another. When you change any information on a screen, Consume automatically switches to edit mode. Edit mode is indicated by the presence of the Cancel Changes or Save buttons in place of the Calculate Consumption and Emissions and Reports buttons at the bottom right of the screen. When you are in edit mode, you cannot leave the screen you are editing or use the navigation tree until you save or cancel any changes. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 38 Weather Zone Screen Weather zone data are only required if you wish to predict the Adjust 1000-hr (Adj-Th) fuel moisture content for activity fuels. • The Weather Zone Information page contains initial weather zone data. • The Daily Observations page contains for each day following the initial information. (Scroll to view example). Tip: Daily weather records must run consecutively from the start of the weather zone until the given burn date. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 39 Consumption and Emissions Summary Screen The Consumption and Emissions Summary screen provides a summary of consumption and emissions for any valid project, unit or fuelbed selected in the navigation tree. To view a summary of Consumption, Emissions and Heat Release: 1. Click on a valid project, unit or fuelbed. 2. Click the Consumption and Emissions Summary button at the bottom of the main screen. The screen will automatically display the item you select in the navigation tree. For example, you may wish to view summary information for an entire project and then view individual unit and/or fuelbed information. 3. To exit the Consumption and Emissions Summary screen, click the Return to Editing button at the bottom of main screen. Tip: The Consumption and Emissions Summary button becomes inactive when invalid items in the navigation tree are selected. It is also not available during edit mode. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 40 Reports Screen The Reports screen is accessible whenever you are in browse mode. • To open the Reports screen, click on the Reports button at the bottom right of the main screen. From the Reports screen, you can select one of several reports and graphs types. • To exit the Reports screen, click the Return to Editing button at the bottom of main screen. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 41 Creating Reports To create a report using the Reports Screen: 1. Select a report from the Select Report/Graph pull-down list. 2. Select a project name. 3. Select the elements to be included in your report. 4. Enter any report parameters that apply. (Parameters are grayed out if they are not required.) 5. Enter report measurement units if required. (Measurement units are grayed out if they are not required.) 6. Click the Display Report button. Tip: The Display Report button is inactive until all necessary parameters have been selected. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 42 Creating Graphs To generate a graph using the Reports Screen: 1. Select a graph from the Select Report/Graph pull-down list. 2. Select a valid project and any project items (i.e., units and fuelbeds) you wish to include in your report. Tip: All projects, including those that are invalid, are listed in the project menu. However, Consume can only calculate results for completely validated projects. 3. Enter graph parameters including lowest and highest 1000-hr fuel moisture and the increment to plot. 4. Specify which values to include in your graph (fuelbed strata and total). 5. Enter graph units (lbs or tons if English was selected or kg or Mg if Metric was selected). Click on the corresponding check box if you want results in per unit area. 6. If you have a working copy of Microsoft Excel on your computer, you can view Consumegenerated graph results in Excel by clicking on the Excel button at the bottom right of the Reports screen. If you wish to export the graphics data to be viewed and/or printed in a different program, click the Export to TextFile button. Tip: The Excel and Export to TextFile buttons are inactive until all necessary parameters have been selected. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 43 Report and Graph Types The following reports and graphs are available in Consume: • Input Data Report: displays input data for selected projects, units and fuelbeds. • Weather Zone Report: summarizes weather zone and daily weather observation inputs. • Consumption by 1000-hour Fuel Moisture Report: displays the quantity of fuels consumed at different values of 1000-hour fuel moisture. • Consumption by Combustion Phase Report: displays total fuel consumption and the quantity of fuels consumed in the flaming, smoldering and residual phases of a burn. This report also details consumption data by fuelbed stratum and category. • Emissions by 1000-hour Fuel Moisture Report: displays the quantity of emissions at different values of 1000-hour fuel moisture. • Emissions by Stratum Report: summarizes pollutant emissions for each fuelbed stratum in selected projects, units and fuelbeds. • Emissions by Combustion Phase Report: displays total pollutant emissions and the quantity of emissions of a selected pollutant released in the flaming, smoldering and residual phases of a burn. This report also details emissions data by fuelbed stratum and category. • Heat Release by Combustion Phase Report: displays total heat released and the quantity of heat released in the flaming, smoldering and residual phases of a burn. This report also details heat release data by fuelbed stratum and category. • Consumption by 1000-hr Fuel Moisture Graph - by Stratum: plots consumption of selected fuelbed strata over a specified range of 1000-hr fuel moistures. • Consumption by 1000-hr Fuel Moisture Graph – by Project / Unit / Fuelbed: plots consumption over an input range of 1000-hr fuel moisture and differs between a project, units and fuelbeds. • Emissions by 1000-hr Fuel Moisture Graph – by Pollutant: plots emissions of selected pollutants over a specified range of 1000-hr fuel moistures. • Emissions by 1000-hr Fuel Moisture Graph – by Project / Unit / Fuelbed: plots emissions of a selected pollutant over a range of 1000-hr fuel moistures. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 44 Example: Input Data Report Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 45 Example: Weather Zone Report Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 46 Example: Consumption by 1000-hr FM Report Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 47 Example: Consumption by Combustion Phase Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 48 Example: Emissions by 1000-hr FM Report Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 49 Example: Emissions by Stratum Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 50 Example: Emissions by Combustion Phase Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 51 Example: Heat Release by Combustion Phase Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 52 Example: Consumption by 1000-hr FM Graph by Project Item Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 53 Example: Consumption by 1000-hr FM Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 54 Example: Emissions by 1000-hr FM Graph by Pollutant Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 55 Example: Emissions by 1000-hr FM Graph by Project Item Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 56 Viewing Reports Use the toolbar at the top of the Consumption and Emissions Summary screen or Reports viewing screen to view, save and print reports. The following tools are available in the toolbar: Moves to first page of the report Goes to specified page number. Moves one page back Opens print dialog box Moves one page forward Refreshes report screen Moves to end of report Export to file (.pdf, .xls, .doc, .rtf) Changes report size on screen. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 57 Scenario Testing You can use the Scenario Testing Tool to examine how environmental variables and pile properties affect estimates of consumption and emissions. The Scenario Testing Tool accommodates up to ten scenarios per fuelbed. To open the scenario testing tool: 1. Select a valid fuelbed in the navigation tree. 2. Select Scenario Testing from the Tools menu. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 58 Piled Scenarios To evaluate how pile properties influence pile consumption and emissions: 1. Click on the Add button at the bottom of the page to add a new scenario. 2. Check Piled and specify inputs for the scenario. Your fuelbed must have piles to use this feature of the scenario testing tool. 3. Save the scenario by clicking the Save button at the bottom of the main screen. 4. Click the Add button and repeat the above steps to create up to 9 additional scenarios. Tip: Once you have created multiple scenarios, you can use the slider bar at the bottom left of the page to scroll between scenarios. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 59 Non-Piled Scenarios To evaluate how fuel moisture inputs influence non-piled fuel consumption and emissions: 1. Check Non-Piled and specify fuel moisture inputs for the scenario. 2. Save the scenario by clicking the Save button at the bottom of the main screen. 3. Click the Add button and repeat the above steps to create up to 9 additional scenarios. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 60 Scenario Tool Summary Report To view a summary of consumption and emissions for the current scenario, click on the Summary Report tab. The summary report lists consumption and emissions in tons/acre for your fuelbed under the specified scenario parameters. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 61 Scenario Tool Fuel Consumption Graphs To view a fuel consumption graph: 1. Click on the Fuel Consumption tab. 2. Select a graph type. Depending on your computer’s processing speed, the graph may take a few moments to load. Each graph type compares fuel consumption over all of the scenarios you have created for a particular fuelbed. 3. To print the graph, click on the Printer icon in the tool bar. 4. To export the graph, click on the Export icon in the tool bar. 5. To resize the graph, select a different zoom setting by clicking on the down arrow to the right of the magnifying glass. Note: the Sound and Rotten woody fuel consumption graphs include continuous downed and dead woody fuels only and do not include piles or stumps. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 62 Scenario Tool Emissions Graphs The scenario testing tool offers a variety of emission graphs including: Total emissions, Total emissions by combustion phase, Total emissions by stratum, Woody fuel emissions by combustion phase, LLM emissions by combustion phase, Ground emissions by combustion phase and Pile emissions. To view an emissions graph: 1. Click on the Emissions tab. 2. Select a graph type. Depending on your computer’s processing speed, the graph may take a few moments to load. Each graph type compares emissions over all of the scenarios you have created for a particular fuelbed. 3. To print the graph, click on the Printer icon in the tool bar. 4. To export the graph, click on the Export icon in the tool bar. 5. To resize the graph, select a different zoom setting by clicking on the down arrow to the right of the magnifying glass. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 63 Using Consume in Batch Mode All Consume 3.0 calculations are handled in a Java-based engine that can be run in batch mode on a variety of operating systems. Even if you are running Consume on a MS Windows operating system, some applications may be more efficient to run in batch mode. For example, if you wish calculate consumption and emissions from a large number of fuelbeds associated with a GIS mapping project, it may be most efficient to create a single input file and generate a single comma-delimited output report using the Consume batch mode. To download the Consume batch program: Go to the Consume webpage and follow instructions there to download and run the Consume batch program. Editing the Batch Input File: An Excel workbook is included in the Consume Batch files with several supporting worksheets to help you build a batch input file. You may create your own input file by creating a comma delimited file following the specifications listed in the Consume User's Guide or edit the comma-delimited input file provided on the Consume webpage. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 64 Part 4: Case Studies The following three case studies provide you with regional applications of Consume 3.0. • • • Southern Region: Planning for prescribed fire in Longleaf-Pine-Turkey Oak Western Region: Evaluating fuel conditions and treatment options in central Oregon Boreal Region: under development Each regional case study is designed to demonstrate Consume 3.0 as a tool that can be used in tandem with the Natural Fuels Photo Series, FCCS, and Fire Emissions Production system (FEPS). If you are planning to use Consume 3.0 in conjunction with other FERA products, including the Natural Fuels Photo Series, FCCS, and FEPS, please refer to the tutorial webpage (http://www.fs.fed.us/pnw/fera/products/tutorials/) for a continuation of these case studies. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 65 Southern Case Study You are a fire management officer for a Forest Reserve in south-central Georgia. As part of your burn prescription plan, the forest supervisor has requested an assessment of the fuel characteristics and a fire hazard survey in an area of the district near summer homes and cabins. In addition, you have been asked to estimate fuel consumption and emissions from a prescribed fire. The common fuelbed is a longleaf pine with turkey oak component with some palmetto shrub and wire grass cover. The site has not been burned for 5 years. In the Natural Fuels Photo Series tutorial, we estimated fuel characteristics using the Sandhill photo series (Volume VIa). In the FCCS tutorial, we created a custom fuelbed based on date in the photo series. Use Consume 3.0 to calculate potential fuel consumption and emissions from a prescribed burn planned for February 2007 in this longleaf pine - turkey oak forest type. Georgia Field Site photo Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 66 Step 1: Creating a Project Open Consume 3.0 and create a new project in the Planned Activity category. • • To create a new project, click Planned Activity in the navigation tree and select New Project from the File menu. Consume prompts you for a project name and automatically creates a unit and fuelbed within the project. Use the following screen capture to enter data on the Project screen. • • When you are done entering data on the Project screen, click the Save button. Consume will notify you of validation errors (simply meaning you can't calculate results yet); click OK to continue saving your work. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 67 Step 2: Entering Unit Data Use the following screen capture to enter unit data for the prescribed burn. • • When you are done entering data on the Unit screen, click the Save button. Consume will notify you of validation errors; click OK to continue saving your work. Tip: the planned burn date must fall within the start and end dates we specified in the Project screen. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 68 Step 3: Importing Fuelbed Data The Georgia Field Site fuelbed, created in the FCCS Tutorial's Southern Case Study, has been preloaded into Consume 3.0. To load the fuelbed: 1. Click on the red box above Ecoregion in the upper section of the Fuelbed Screen. 2. Check the box next to "Load values from a custom fuelbed" 3. Select SouthernCaseStudy from the custom fuelbed library under Fuelbed Name. 4. Click the Load Values button. Fuel characteristics will be automatically entered in the Fuel Characteristics page of the Fuelbed screen. Tip: if you just completed the FCCS Southern Case Study and wish to fully import the fuelbed export file into Consume, refer to Importing custom FCCS fuelbeds. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 69 Step 4: Entering Fuelbed Data Although most of the fuel characteristics were automatically loaded using the FCCS wizard, we still need to enter more data on the fuelbed screen before we are ready to make calculations. Use the following screen capture to enter general fuelbed information on the upper fuelbed screen and fuelbed environment data on the Environmental Variables page. Tip: Because this fuelbed has not undergone recent timber harvesting, we checked Natural under Fuelbed Type. The Natural fuel consumption equations used in Consume 3.0 require only the General Environmental Variables in the Environmental Variables page. Those variables required for Activity Fuel consumption equations are grayed out. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 70 Step 5: Reviewing and Editing Fuel Characteristics It is always a good idea to review the Fuel Characteristics page after using the FCCS wizard. There is also one variable, Percent Black, on the shrub stratum page that is not imported from the FCCS and requires an input (the default value is zero). 1. Click on the Fuel Characteristics tab. 2. Review the data entry screens from the Canopy stratum to Ground Fuels stratum. 3. Enter 80% in the Shrub stratum next to Percent Black. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 71 Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 72 Step 6: Calculating Consumption and Emissions Your project should now be valid. If any part of your project is invalid (indicated by red icons in the navigation tree), select Save from the File menu for a list of validation errors. Once you have a completely valid project, click on the Georgia Field Site fuelbed in the navigation tree and then the Consumption and Emissions Summary button to view a summary report of Consumption, Heat Release, and Emissions Results. Tip: Click on the Heat Release or Emissions tabs to switch between report views. Summary of Consumption Results Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 73 Summary of Emissions Results Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 74 Step 7: Comparing Fuelbeds In your smoke management planning, it might be helpful to compare the potential emissions from the Georgia Field Site with a fuelbed after 20 years of fire exclusion. To evaluate the potential difference in emissions between the two scenarios (scroll down to view sample fuelbed screen): 1. Make a copy of the Georgia Field Site fuelbed in Unit 1 (within Project SouthernCaseStudy). To do this, click on Georgia Field Site in the navigation tree and select Copy from the Edit Menu. Click on Unit 1 in the navigation tree as your destination for the copied fuelbed, and select Paste from the Edit Menu. 2. Click on the Copy of Georgia Field Site in the navigation tree to view the corresponding fuelbed screen. Change the Fuelbed Name to FCCS184. 3. Using the FCCS Wizard (Load a standard FCCS Fuelbed Value), select FCCS Fuelbed 184 - Longleaf Pine - Turkey Oak (prescribed fire) from the bottom list and click the Load Values button. 4. On the Fuelbed Screen, enter Ecoregion = 230 Subtropical, Vegetation Form = Mixed Forest, Cover Type = SAF 71 Longleaf Pine - Scrub Oak under Classification (top right of the screen). 5. Save your changes. Consume will notify you of any validation errors. 6. Once you have a valid project, click on the Consumption and Emissions Summary button to view results. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 75 Step 8: Comparing Consumption and Emissions To compare pollutant emissions between the Georgia Field Site and FCCS184 fuelbeds, click on the two fuelbeds in the Navigation Tree (and the Consumption and Emissions Summary button if you have not already done so). Tip: Consumption and Emissions Summary Reports change dynamically with the items you click on the navigation tree. The following screen capture compiles the results for the two fuelbeds (In Consume, they do not appear on the same Emissions summary). As would be expected, emissions are much greater in FCCS 184, which has not had a fire in 20 years. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 76 Western Case Study You are a fire management officer for the USDA Forest Service outside of Bend, Oregon. The lodgepole pine forests in your district have experienced high mortality from ongoing bark beetle outbreaks and a prolonged regional drought. These forests are dominated by lodgepole pine with scattered ponderosa pine, and some sites have high woody fuel loadings associated with recent tree mortality. The district ranger has asked you to evaluate the fuel conditions and fire hazard of these lodgepole pine forests and develop a treatment plan that includes forest thinning and prescribed fire. You have already used the Natural Fuels Photo Series to estimate fuel loadings and other characteristics for this site and the Fuel Characteristic Classification System (FCCS) to evaluate fuel characteristics and calculated fire potentials for this site. Use Consume 3.0 to calculate potential fuel consumption and emissions from a prescribed burn planned for June 2007 in this lodgepole pine forest. Oregon Field Site: Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 77 Step 1: Creating a Project Open Consume 3.0 and create a new project in the Planned Activity category. • • To create a new project, click Planned Activity in the navigation tree and select New Project from the File menu. Consume prompts you for a project name and automatically creates a unit and fuelbed within the project. Use the following screen capture to enter data on the Project screen. • • When you are done entering data on the Project screen, click the Save button. Consume will notify you of validation errors (simply meaning you can't calculate results yet); click OK to continue saving your work. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 78 Step 2: Entering Unit Data Use the following screen capture to enter unit data for the prescribed burn. • • When you are done entering data on the Unit screen, click the Save button. Consume will notify you of validation errors; click OK to continue saving your work. Tip: the planned burn date must fall within the start and end dates we specified in the Project screen. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 79 Step 3: Importing Fuelbed Data The WesternCaseStudy fuelbed, created in the FCCS Tutorial's Western Case Study, has been preloaded into Consume 3.0. To load the fuelbed: 1. Click on the red box above Ecoregion in the upper section of the Fuelbed Screen. 2. In the FCCS Wizard, check the box next to "Load values from a custom fuelbed." Note: if you have not used this feature before, Consume will prompt you to either browse or search for the FCCS file location. 3. Select WesternCaseStudy from the custom fuelbed library under Fuelbed Name. 4. Click the Load Values button. Fuel characteristics will be automatically entered in the Fuel Characteristics page of the Fuelbed screen. Tip: If you just completed the FCCS Southern Case Study and wish to fully import the fuelbed export file into Consume, refer to Importing custom FCCS fuelbeds. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 80 Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 81 Step 4: Entering Fuelbed Data Use the following screen capture to enter general fuelbed information on the upper fuelbed screen and fuelbed environment data on the Environmental Variables page. • We selected Natural under fuelbed type because this fuelbed has not been substantially altered by timber harvesting. • The Natural fuel consumption equations used in Consume 3.0 require only the General Environmental Variables in the Environmental Variables page. Those variables required for Activity Fuel consumption equations are grayed out. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 82 Step 5: Reviewing and Editing Fuel Characteristics It is always a good idea to review the Fuel Characteristics page after importing fuelbed information from the FCCS wizard. Percent Black on the shrub stratum page is not imported from the FCCS and requires an input (the default value is zero). 1. Click on the Fuel Characteristics tab. 2. Review the data entry screens from the Canopy stratum to Ground Fuels stratum. 3. Enter 80% in the Shrub stratum next to Percent Black. 4. Click the Save button to save and validate your fuelbed. Tip: If you have any validation errors, Consume will list them for you. Simply correct the errors and resave the fuelbed. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 83 Step 6: Pile Wizard To calculate pile consumption and emissions, Consume requires many inputs not recorded in the FCCS. If your fuelbed has woody fuel accumulations (i.e., piles, jackpots or windrows) and you wish to include them in Consume calculations, you will need to enter the information using the Consume pile wizard. Tip: The term "pile" in Consume 3.0 is carried over from Consume 1.0 and 2.1 and refers to all woody fuel accumulations, including piles (woody material piled for future burning), windrows (woody material piled into a continuous row), and jackpots (natural accumulations of woody material). The Oregon Field Site fuelbed has jackpots. We will enter the jackpot information into Consume with the required additional data: 1. In the Fuel Characteristics - Woody page, click on the Add button under Pile Groups. (Scroll down to view screen capture). 2. Within the pile wizard, enter the following pile characteristics on the three tabbed data entry pages. 3. Click the Save button to save and validate your entries. Pile Group Name: Jackpots Pile Shape and Dimensions (click for sample screen) Packing Ratio (click for sample screen) Other Details (click for sample screen) Shape: Half-section sphere Packing Ratio: 20% (option 2) Percent Soil by Pile Volume: 0 Width 1: 5 feet Primary Species: lodgepole pine Height 1: 5 feet Percent of Primary Species: 100% Number of piles of this type: 3000 Pile Quality: Clean (0%) Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 84 Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 85 Step 7: Calculating Consumption and Emissions Your project should now be valid. If any part of your project is invalid (indicated by red icons in the navigation tree), select Save from the File menu for a list of validation errors. Once you have a completely valid project, click on the Oregon Field Site fuelbed in the navigation tree and then the Consumption and Emissions Summary button to view a summary report of Consumption, Heat Release, and Emissions Results. Tip: Click on the Heat Release or Emissions tabs to switch between report views. Summary of Consumption Results Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 86 Summary of Consumption Results Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 87 Step 8: Comparing Fuelbeds In the Western Case Study of the FCCS tutorial, we created another custom fuelbed (Oregon Field Site - heavy loading) to compare potential fire hazard between lodgepole pine sites with moderate versus heavy woody fuel loadings. Let's use Consume to compare the difference in consumption and emissions from planned prescribed burning in both fuelbeds. 1. Under the project WesternCaseStudy (and unit Rx 2007), make a copy of the Oregon Field Site fuelbed. To do this, click on Oregon Field Site in the navigation tree and select Copy from the Edit Menu. Click on Rx 2007 in the navigation tree as your destination unit for the copied fuelbed, and select Paste from the Edit Menu. 2. Click on the Copy of Oregon Field Site in the navigation tree to view the corresponding fuelbed screen. Change the Fuelbed Name to OFS - Heavy Loading. 3. If you created the Oregon Field Site - Heavy Loading fuelbed (OregonFieldSiteHeavy.xml) in the FCCS, you can use the FCCS wizard (load values from a custom fuelbed) to import the fuel loadings. Alternatively, you can enter the following woody fuel loadings into Consume directly. To do this: • Click on OFS-Heavy Loading in the navigation tree. • On the Fuelbed Screen, click on the Fuel Characteristics tab on and the Woody tab. • Use the screen capture below to enter new loadings in the Woody screen: 4. Click the Save button. Consume will notify you of any validation errors. 5. Once you have a valid project, click on the Consumption and Emissions Summary button to view results. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 88 Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 89 Step 9: Comparing Consumption and Emissions To compare emissions between prescribed burns in the Oregon Field Site and OFS-Heavy Loading, click on the Consumption and Emissions Summary button, click the Emissions tab, then click on each fuelbed in the navigation tree to compare results. Tip: Consumption and Emissions Summary reports change dynamically with the items you click on the navigation tree. The following screen capture compiles the results for the two fuelbeds (In Consume, they do not appear on the same Emissions summary). As would be expected, emissions are much greater from OFS-Heavy Loading, which 3.5 times the woody fuel loadings as in the Oregon Field Site fuelbed. Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 90 Step 10: Generating Reports Consume offers several reports and graphs that you might use in your burn planning. In this example, you may wish to generate fuel consumption and pollutant emissions reports that summarize outputs for both fuelbeds. To create a Consumption by Combustion Phase report that lists total fuel consumption by fuel stratum and category and by flaming, smoldering, and residual smoldering stages of combustion: 1. Click on the Reports button from any screen (save or cancel changes if you are in edit mode). 2. Use the following screen capture to enter the necessary report parameters: Click Display Report to view the report (Click here for sample report). Notes: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________