O-GlcNAcylation regulates FoxM1 levels via SIRT1 in breast cancer
advertisement

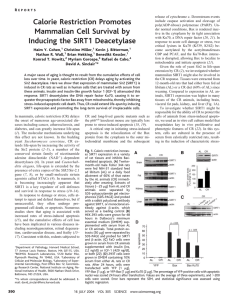
O-GlcNAcylation regulates FoxM1 levels via SIRT1 in breast cancer Jenna M. Marinock1, Christina M. Ferrer1, Mauricio J. Reginato1 1Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA Hypothesis Abstract Cancer cells are known for exhibiting marked increases in glucose uptake. This leads to an altered metabolic state unique to cancer cells known as the Warburg effect in which cancer cells upregulate glycolysis even in the presence of sufficient oxygen. A portion of the glucose obtained will enter the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP), however the role this pathway plays in cancer progression is not well understood. Glucose flux into the HBP pathway leads to an increase in the modification of O-linkedN-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) by the enzyme O-GlcNAc Transferase (OGT). Previously our lab reported that OGT is upregulated in breast cancer cells and inhibiting OGT reduces cancer cell invasion and the oncogenic transcription factor FoxM1. SIRT1, a member of the NAD+dependent deacetylase family of Sirtuin proteins involved in longevity, can function as a tumor suppressor and has been implicated in regulating breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Indeed SIRT1 has been found to be downregulated in many cancers including breast, colon and liver cancer. Recently our lab has shown reducing OGT expression or activity increases levels of SIRT1 and this increase is required for OGT-mediated effect on cellular invasion. Here, we demonstrate that the SIRT1 can regulate FOXM1 levels as MDA-MB-231 and SUM159 breast cancer cells expressing SIRT1 RNAi increase FoxM1 protein levels. Thus, we identify a novel pathway in which SIRT1 regulates FoxM1 and contributes to OGlcNAc regulation of invasion in breast cancer cells. O-GlcNAcylation modulates FoxM1 levels through a SIRT1-dependent mechanism. MDA-MB-231 A) Hexosamine Biosynthetic Pathway (HBP) and OGT Carcinoma RW P N EPT 1 XPC 153 2 3 PC 3M D U L 14 5 Normal O-GlcNAc shControl shSIRT1 A) shControl l o sh r t T n OG Co MDA-MB-157 shControl shSIRT1 l l h o o sh r s r t T t T n n G o o OG O C C B) shSIRT1 l sh ro t T n OG Co SIRT1 SIRT1 OGT OGT FOXM1 FOXM1 Ac-p53 Ac-p53 Actin Actin MDA-MB-231 B) ls h h lsh h o o r Ts ntr GTs nt G o C O O Co MDA-MB-468 A) Results DMSO EX-527 MDA-MB-231 h lsh h EX-527 h o n T s ontr GT s o G C O C OGT CC OGT O ls DMSO o r t SIRT1 OGT OGT FOXM1 FOXM1 Ac-p53 MMP2 Figure 3: OGT regulation of FOXM1 through SIRT1 in other Triple Negative Breast Cancer cell lines Actin MMP9 The reduction of SIRT1 levels using a stably expressed SIRT1 shRNA in MDA-MB468 (A) and MDA-MB-157 cells (B) induces the upregulation of FOXM1 in control and OGT knockdown (KD) as seen previously in MDA-MB-231 mammary adenocarcinoma cells (Figure 1B). Ac-p53 SIRT1 Actin Figure 1: OGT Modulates FOXM1 levels in a SIRT1-dependent manner The reduction of SIRT1 levels using a stably expressed SIRT1 shRNA (A) or using the SIRT1 inhibitor EX-527 (B) induces the upregulation of FOXM1 in control and OGT knockdown (KD) MDA-MB-231 mammary adenocarcinoma cells (A,B). Background B) Cancer cells contain elevated levels of OGT and O-GlcNAc Results A) MDA-MB-231 shControl shFOXM1 l sh trol sh ro 1 t 1 T n n R RT I Co Co SI S B) 3D Culture: MDA-MB-231 Controlsh SIRT1sh C) MDA-MB-231 ΔKen FOXM1 WT FOXM1 S DM SIRT1 O T1 R S 72 M) u 1 0( D O MS S 1 RT 72 M) u 1 0( WT FOXM1 FOXM1 Human Breast Cancer Samples: Inverse Relationship Between FoxM1 and Sirt1 FOXM1sh ΔKen FOXM1sh/SIRT1sh MMP9 Ac-p53 MMP2 Actin MMP9 OGT Controlsh Actin 1.0 SIRT1sh 0.48 0.99 0.95 Skp2 Actin C) Downregulation of SIRT1 expression in breast cancer tissues vs. normal breast tissue O G 50 µM Ti + SR OG T7 Ti 20 FOXM1 Breast Tissue and Tumor IHC: SIRT1 O-GlcNAc Normal Modified from: Wang et al, Cancer Cell (2008) Cancer D) SIRT1 Deacetylase: Longevity Protein, Nutrient Sensor and Tumor Suppressor Conclusion and Model 50 µM SR T7 FOXM1sh/SIRT1sh DM FOXM1sh SO D) 20 MDA-MB-231 • OGT regulation of FOXM1 is dependent on SIRT1 • OGT regulates FOXM1 through SIRT1 to promote invasion • OGT regulates FOXM1 in TNBC cell lines such as MDA-MB-231, MDAMB-157, as well as MDA-MB-468. b E) Targeting OGT Inhibits Cancer Cell Invasion via regulation of oncogenic transcription factor FOXM1. OGT Actin cancer cell AMPKa ? g SIRT1 ? Ac invasion/metastasis? FOXM1 P M M P2 ECM Proteins Figure 2: OGT and SIRT1 cooperate to promote invasion in TNBCs The reduction of SIRT1 levels using stably expressed SIRT1 shRNA induces the upregulation of FOXM1 in MDA-MB-231 adenocarcinoma cells (A). 3D culture of MDAMB-231 cells stably expressing SIRT1 and FOXM1 shRNA and fluorescently stained with DAPI (blue) and Green fluorescence protein (GFP, green) showing that SIRT1 is required for FOXM1 regulation of 3D growth (B). The upregulation of SIRT1 in response to the SIRT1 activator SRT720 induces the downregulation of FOXM1 WT when compared to DMSO treated and no downregulation in a mutant version of FOXM1 (ΔKEN) (C). Combined treatment of OGT inhibitor with SIRT1 activator (SRT1720) synergizes to reduce FOXM1 levels in MDA-MB-231 cells (D). Caldwell et al, Oncogene (2009) Lynch, TP, Ferrer, CM, et al, J. Biol Chem (2012) Future Directions • Determine whether OGT regulation of SIRT1 promotes breast cancer cell metastasis (in progress) • Determine whether FOXM1 is directly deacetylated by SIRT1, if so, map-out acetylation sites • Determine whether SIRT1 regulates FOXM1 phosphorylation state