Glaucoma and Vision-Related Quality of Life
advertisement

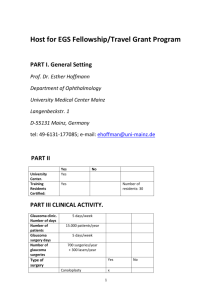
Glaucoma and Vision-Related Quality of Life Paul M. Gentile, MPH(c); Anneclaire De Roos, PhD, MPH; Lisa A. Hark, PhD, RD; Rebecca Gensure, MD; Deiana Johnson, MPH Drexel University School of Public Health, Wills Eye Hospital Department of Research, Philadelphia, PA Purpose The severity of glaucoma can lead to overall poorer quality Results Table 1: Comparison of baseline NEI-VFQ-25 Subscale Scores and glaucoma diagnosis Patients aged 50 years and over were examined and interviewed at the community and main sites and of life (QoL). This study aimed to assess and identify factors were diagnosed with some form of glaucoma. Overall, 208 (73.8%) accounted for Black or African related to quality of life among a high-risk group of patients American. Females 187 (66.3) and males 95 (33.7) were accounted for in the study population. A review with a variety of glaucoma related diagnosis in Philadelphia. of quality of life scores among the patients was examined utilizing the NEI-VFQ-25 and GDS-15. From We wish to investigate how baseline assessment of QoL, the NEI-VFQ-25, 196 (69.5%) patients had subscale scores in 76-100 range, indicating a high QoL. In demographics, and type of glaucoma might together provide the GDS-10,198 (87.2%) had an overall score in the 0-4 range, indicating no depression. Across all the useful information on whether or not future patients might sites, only 2 people were screened positive on the GDS-15 for being suspected clinically depressed. benefit from additional services such as a patient navigator These individuals were referred to a social worker. Glaucoma patients that were female were also noted or social worker to address their overall QoL. as having lower QoL than males (p<0.1). Type of glaucoma diagnosis has also indicated that patients with some form of glaucoma are more likely to have overall poorer QoL (p<.001). Methods • The study included 282 enrolled patients from previous Figure 1: Distribution of GDS-15 scores across all community and hospital sites Figure 2: Distribution of NEI-VFQ-25 scores across community and hospital sites community sites that were used in a previous CDC-funded study, and from Wills Eye Hospital. • Each patient underwent a baseline assessment utilizing the National Eye Institute (NEI) Visual Function Questionnaire (VFQ) and Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) to measure quality of life. • Information captured from patient, and electronic medical Mean= 2.01 SD=2.49 Mean= 78.55 SD= 15.90 Table 2: Univariate/Multiple Linear Regression of Association of the NEI-VFQ with patient demographics and diagnosis Estimate (linear regression) Variable Estimate (multiple linear * p≤.05 regression) Age Race White/Caucasian Black or African-American Other Diagnosis Primary Open-Angle Narrow-Angle Other Gender Male Female records included: Race/ethnicity, age, gender, marital status, medications, and glaucoma diagnoses. • 0.02 (CI: -0.17, 0.21) Reference -3.54 (CI: -9.00, 1.92) -10.04 (CI: -17.25, -2.84)* Reference -3.64 (CI: -9.10,1.82) -10.59 (CI: -17.84, -3.34)* -2.98 (CI: -7.247, 1.287) 1.61 (CI: -2.744, 5.976) -6.02 (CI: -12.33, .281) -4.162 (CI:-8.83, .510) -.717 (CI, -5.473, 4.04) -7.39 (CI: -14.04,-.74)* Reference -2.72 (CI: -6.66,1.21) Reference -3.38 (CI: -7.30, .54) Conclusions A univariate and multi-variate analyses was used to assess the relationship between glaucoma diagnosis, race/ethnicity, gender, age, and overall quality of life. • 0.04 (CI: -0.15, 0.24) As suggested by the literature a score for the GDS-15 was chosen as a significant value indicating that the patient may have a severe form of depression and would be referred by the patient navigator. Funded by the Partridge Foundation The findings from this study emphasize the need to continue early detection and treatment of glaucoma in order to maintain a high QoL among high-risk populations in Philadelphia. Many of the patients in this study indicated higher QoL and were diagnosed early which was representative in their overall composite score from the baseline assessment. Given that there were patients whose scores were indicative of mild and severe depression were associated with glaucoma and later stages of the disease. The later stages leads an individual to experience vision-loss and development of clinical depression. This study was able to determine and support the literature on how there is a relationship between the severity of glaucoma and overall QoL. Contact: Paul Gentile at pgentile1@gmail.com