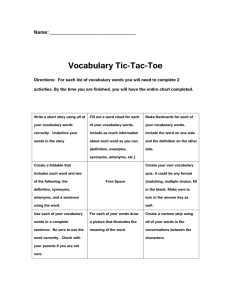
QCC COURSE ASSESSMENT FORM QCC C A
advertisement

QCC COURSE ASSESSMENT FORM (SHORT) QCC COURSE ASSESSMENT FORM Spring 2011 Prepared by Professor Jilani Warsi Date: March 30, 2011 Department: Basic Educational Skills Course: BE-226 College Reading and Study Skills for ESL Students Curriculum or Curricula: PART I. STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES For Part I, attach the summary report (Tables 1-4) from the QCC Course Objectives Form. TABLE 1. EDUCATIONAL CONTEXT BE226 is the second course in a tw o-semester sequence designed for students w ho speak English as a Second Language, but w ho are in need of intensive instruction in reading and study skills related to their content courses. Emphasis is on the development of w ord recognition skills, know ledge of complex English idioms, listening skills, and study techniques. The objective is to develop w ord recognition, comprehension, listening skills, and study strategies, not only in general material, but also as they apply to students’ content courses. A student enrolled in BE226 has either tested into this level by scoring betw een 58 – 69 on the A CT Reading Exam, or has successfully fulfilled the course requirements for BE225, a prerequisite for BE226. Students are required to score a minimum of 70% on the CUN Y standardized reading test to meet the exit criteria for BE226. TABLE 3. GENERAL EDUCATION OBJECTIVES Gen Ed objective’s ID number from list (1-10) General educational objectives addressed by this course: Select from preceding list. (1.) Write, read, listen and speak clearly and effectively. In this course, students practice all four language skills by reading, writing and talking about current issues. They discuss the issues, read about topics in newspaper and magazine articles, essays, stories or on the Internet, listen to various viewpoints and write responses which clearly state their own point of view. 1(14) (2.) Use personal and collaborative skills for personal growth to establish constructive relationships in a diverse society. In this course, students from a wide range of cultural backgrounds read about diverse customs and cultures. They collaborate in groups to share knowledge, learn the traditions of different peoples, and develop academic and personal relationships. TABLE 5: COURSE OBJECTIVES AND STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES Course Objectives Learning Outcomes Reading Comprehension: 1) Students will recognize conventional patterns of English sentence structure, grammar and syntax. a) Students will identify sentence and syntactic patterns in a variety of texts in genres such as essays, memoirs, short works of fiction and non-fiction. b) Students will reinforce their knowledge of grammar by reading a variety of academic and literary texts and responding orally and in written assignments and tests. 2) Students will recognize an author’s stated or implied thesis, major ideas and supporting information. a) Students will identify and an author’s stated thesis, major ideas and supporting information in discussions, written assignments, oral presentations, debates and tests. b) Students will infer an author’s implied thesis from a text’s major ideas and supporting information and demonstrate that knowledge in written and oral activities. 3) Students will analyze a text in relation to a) Students will compare and contrast other texts and general knowledge. a text’s meaning with societal norms, other texts. Reading Comprehension (continued) b) Students will compare and contrast a text with their own and others’ personal experiences, beliefs and value systems in class 2(14) assignments and activities, tests and situations beyond the classroom. Vocabulary: 1) Students will recognize known vocabulary and idiomatic expressions in a variety of texts. a) Students will identify known vocabulary in a range of texts studied in class as well as beyond the classroom. b) Students will identify idiomatic expressions they have studied in other texts and sources beyond the classroom such as the media. 2) Students will determine the meaning of new vocabulary and idioms from word analysis, contextual clues and appropriate reference sources. a) Students will refer to dictionaries and thesauruses for definitions of unknown vocabulary and idioms when preparing academic assignments. b) Students will analyze prefixes, roots and suffixes or infer them from contextual clues to determine the meaning of unknown words and idioms in texts within and beyond the classroom. Critical Thinking 1) Students will analyze a text by formulating questions, making inferences, drawing conclusions, and distinguishing an author’s stated and implied ideas. a) Students will critically analyze a text to determine its stated or implied thesis, major ideas and supporting information in individual assignments and on tests. b) Students will critically analyze a text’s stated or implied thesis and supporting material in group activities such as class discussions, oral presentations and debates. a) Students will question an author’s ideas individually in assignments and on 3(14) 2) Students will evaluate an author’s ideas by comparing and contrasting them with other texts and their own or others’ experiences, beliefs and value systems. Critical Thinking (continued) 3) Students will extrapolate an author’s ideas and apply them to new texts and situations. tests in order to judge the validity of those ideas with respect to their own or others’’ experiences, beliefs and value systems. b) Students will question an author’s ideas in group activities such as discussions, oral presentations and debates to judge their validity with respect to others’ experiences, beliefs and value systems. They will appreciate the subjective differences and distinctions of co-existing points-ov-view. a) Students will extrapolate the ideas of a text and apply them to other texts and situations such as current events, in individual assignments and tests in order to test their validity and usefulness. b) Students will argue the merits and demerits of an author’s ideas in group activities such as discussions, oral presentations and debates. In these activities, students will consider the validity and usefulness of the author’s ideas in various situations outside the classroom. Writing: 1) Students will summarize, paraphrase, quote and outline the main ideas and supporting information of various texts. a) Students will write summaries that paraphrase and quote the main ideas and supporting information of a text for homework assignments, oral presentations and debates. b) Students will write outlines of a text as study guides for tests. 2) Students will explain and respond to an author’s ideas and information in a variety of writing projects. a) Students will explain and respond to an author’s ideas in letters, journals, book reports and term papers which critically evaluate the author’s ideas. These 4(14) assignments will be compiled in a term portfolio. b) Students will incorporate their written responses to various texts into oral presentations and debates. Listening and Speaking 1) Students will listen to lectures in class and take accurate class notes. a) Students will listen to class lectures to determine the major ideas and supporting information being communicated. b) Students will take accurate notes that distinguish between the major ideas and supporting information of a lecture. 2) Students will communicate orally with the instructor and each other in various class activities. a) Students will use listening and speaking skills to respond to an instructor’s queries and pose questions of their own. b) Students will use listening and speaking skills to communicate with other students in class discussions, group work and debates. 3) Students will apply listening and speaking skills acquired in class in a variety of settings outside the classroom. a) Students will speak and listen to spoken English in performing common daily activities outside the classroom such as workplace communication. b) Students will listen to spoken English in the media and engage in conversations regarding topics of current interest. Study Skills 5(14) 1) Students will preview a text to gain an overview of its thesis and major ideas. . a) Students will preview a text by reading titles, headings, subheadings, marginal notes, key words and glossaries, and reading the introduction and conclusion to form a general understanding of a text. b) Students will preview a text for an overview of its thesis and major ideas by examining graphs, charts and illustrations that are included to enhance the reader’s understanding. Study Skills (continued) 2) Students will summarize, paraphrase and outline the thesis, major ideas and supporting information of a text. a)Students will write summaries of a text to prepare for tests by outlining, paraphrasing and quoting the author’s major ideas and supporting information . b)Students will prepare for oral presentations and debates by outlining summarizing, paraphrasing and outlining the major ideas and supporting information of a text. PART II. ASSIGNMENT DESIGN: ALIGNING OUTCOMES, ACTIVITIES, AND ASSESSMENT TOOLS For the assessment project, you will be designing one course assignment, which will address at least one general educational objective, one curricular objective (if applicable), and one or more of the course objectives. Please identify these in the following table: TABLE 5: OBJECTIVES ADDRESSED IN ASSESSMENT ASSIGNMENT 6(14) Course Objective(s) selected for assessment: (select from Table 4) Vocabulary: Students will determine the meaning of synonyms and antonyms using context clues. Curricular Objective(s) selected for assessment: (select from Table 2) Vocabulary: Students will determine the meaning of synonyms and antonyms using context clues. General Education Objective(s) addressed in this assessment: (select from Table 3) (1.) (2.) Write, read, listen and speak clearly and effectively. In this course, students practice all four language skills by reading, writing and talking about current issues. They discuss the issues, read about topics in newspaper and magazine articles, essays, stories or on the internet, listen to various viewpoints and write responses which clearly state their own point of view. Use personal and collaborative skills for personal growth and to establish constructive relationships in a diverse society. In this course, students from a wide range of cultural backgrounds read about diverse customs and cultures. They collaborate in groups to share knowledge, learn the traditions of different peoples, and develop academic and personal relationships. In the first row of Table 6 that follows, describe the assignment that has been selected/designed for this project. In writing the description, keep in mind the course objective(s), curricular objective(s) and the general education objective(s) identified above, The assignment should be conceived as an instructional unit to be completed in one class session (such as a lab) or over several class sessions. Since any one assignment is actually a complex activity, it is likely to require that students demonstrate several types of knowledge and/or thinking processes. Also in Table 6, please a) identify the three to four most important student learning outcomes (1-4) you expect from this assignment b) describe the types of activities (a – d) students will be involved with for the assignment, and c) list the type(s) of assessment tool(s) (A-D) you plan to use to evaluate each of the student outcomes. (Classroom assessment tools may include paper and pencil tests, performance assessments, oral questions, portfolios, and other options.) Note: Copies of the actual assignments (written as they will be presented to the students) should be gathered in an Assessment Portfolio for this course. 7(14) TABLE 6: ASSIGNMENT, OUTCOMES, ACTIVITIES, AND ASSESSMENT TOOLS Briefly describe the assignment that will be assessed: For this assessment, the students will be taught how to determine the meaning of a word by examining context clues so that they understand it is not necessary to look up every word they don’t know in the dictionary. Desired student learning outcomes for the assignment (Students will…) List in parentheses the Curricular Objective(s) and/or General Education Objective(s) (1-10) associated with these desired learning outcomes for the assignment. 1. Students will examine the context surrounding new vocabulary words to draw logical conclusions about their meaning. 2. Students will listen to class lectures and take accurate notes. 3. Students will be given a passage to read and will be asked to find a synonym of the highlighted word by using context clues. 4. Students will be given another passage to read and will be asked to find an antonym of the highlighted word by using context clues. Briefly describe the range of activities student will engage in for this assignment. What assessment tools will be used to measure how well students have met each learning outcome? (Note: a single assessment tool may be used to measure multiple learning outcomes; some learning outcomes may be measured using multiple assessment tools.) 1. First, the instructor will provide a lesson to explain the concept of synonyms. The instructor will also explain how to use the context clues to find the correct synonyms of the highlighted words in the text. 1. While explaining synonyms and antonyms, the instructor will call on students in the class to respond to questions that lead students to the correct answer. 2. While the students work in groups, the instructor will circulate to guide 2. In small groups in class and assist students in students will participate in finding the correct an exercise that will require synonyms and antonyms. them to use the context to After the group work has find appropriate synonyms been completed, the class of the highlighted words in will discuss their multiple-choice questions. findings. The students This will be followed by a will be provided a homework assigned whereby follow-up activity that students will read a passage will be completed at and answer multiple-choice home. During the next questions finding the correct class this activity will be synonym of the highlighted reviewed as a class. word. The assignment will give students the opportunity 3. The effectiveness of the to practice this new skill. lecture will be assessed 3. In a follow-up session the instructor will provide a lesson on antonyms. Again, the instructor will explain how to use the context clues to find the correct antonym 8(14) when the instructor circulates to assist the small groups of students as they attempt to determine the meaning of new vocabulary words. of the highlighted words in the text. 4. The instructor will circulate to determine if the students are able to find the correct synonyms and antonyms. 5. A reading passage and multiple-choice questions 4. In small groups in class, students will practice will be utilized to assess reading a text and answer the students’ ability to find the correct synonyms multiple-choice questions finding the correct and antonyms of the highlighted word in the antonyms using the context clues. text. 5. They will be given a homework assignment, which will require them to read a selection and answer multiple-choice questions, finding the correct antonym of the highlighted word. The multiple-choice questions will be used to assess their understanding of antonyms. PART III. ASSESSMENT STANDARDS (RUBRICS) Before the assignment is given, prepare a description of the standards by which students’ performance will be measured. This could be a checklist, a descriptive holistic scale, or another form. The rubric (or a version of it) may be given to the students with the assignment so they will know what the instructor’s expectations are for this assignment. Please note that while individual student performance is being measured, the assessment project is collecting performance data ONLY for the student groups as a whole. TABLE 7: ASSESSMENT STANDARDS (RUBRICS) Brief description of assignment: For this assessment, the students will be taught how to determine the meaning of a word by examining context clues so that they understand it is not necessary to look up every word they don’t know in the dictionary. Desired student learning outcomes from the assignment: (Copy from Column 1, Table 6 above; Assessment measures for each learning outcome: (Copy from Column 3,Table 6 above) 9(14) Standards for student performance: Describe the standards or rubrics for measuring student achievement of each outcome in the assignment. include Curricular and /or General Education Objectives addressed) 1. While explaining context 1. Students will examine clues, the instructor will call the context surrounding on various students in the new vocabulary words to class to respond to questions find correct synonyms that will lead the students to and antonyms. the correct answer. 1. The instructor will assess the students’ understanding as he/she hears the students’ responses to her questions. 2. Students will discuss the 2. While the students work in groups, the instructor will possible answers in circulate to guide and assist small groups in the class. students in determining the meaning of new vocabulary. After the group work is complete, the entire class will discuss their findings. The students will be provided a follow-up activity that will be completed at home. During the next class this activity will be reviewed as a class. 3. Students will listen to class lectures and take accurate notes. 3. When the instructor teaches this lesson on synonyms and antonyms to the class, the students will be expected to take notes. 4. Students will be given a homework assignment to 4. The instructor will circulate practice the new skill to determine if the students they have learned in are able to find the correct class. synonym and antonym of the highlighted word in the text. 4. Students will be given a passage to read and will 5. A reading passage and multiple-choice questions be asked to determine will be utilized to assess the the new vocabulary students’ ability to find the words by using context correct synonym and clues. antonym using context clues. 10(14) Give the percentage of the class that is expected to meet these outcomes If needed, attach copy(s) of rubrics. 2. The instructor will circulate to determine if his/her learners are writing down the correct answers. If they have mistakes, the teacher will guide and correct them. 3. When students encounter problems they will review their notes with the members of their group and with the instructor when he/she circulates. 4. The instructor will circulate to determine if his/her learners are writing down the correct answers. If they have mistakes, the teacher will guide and correct them 5. Rubric for Test a) A grade of 100 indicates that the student showed a complete mastery of finding the correct synonyms and antonyms using context clues. b) A grade of 90 indicates that the student demonstrated a good mastery of the skill of finding the correct synonyms and antonyms using context clues. c) A grade of 80 indicates that the students displayed an adequate mastery of determining the correct synonyms and antonyms from context clues. d) A grade of 70 indicates that the student showed a basic knowledge of finding the correct synonyms and antonyms from context clues. e) A grade of 60 indicates that the student displayed an elementary knowledge of the skill of finding the correct synonyms and antonyms from context clues. f) A grade of 50 or below indicates that the student demonstrated an insufficient knowledge of finding the correct synonyms and antonyms from context clues. PART IV. ASSESSMENT RESULTS TABLE 8: SUMMARY OF ASSESSMENT RESULTS Use the following table to report the student results on the assessment. If you prefer, you may report outcomes using the rubric(s), or other graphical representation. Include a comparison of the outcomes you expected (from Table 7, Column 3) with the actual results. NOTE: A number of the pilot assessments did not include expected success rates so there is no comparison of expected and actual outcomes in some of the examples below. However, projecting outcomes is an important part of the assessment process; comparison between expected and actual outcomes helps set benchmarks for student performance. TABLE 8: SUMMARY OF ASSESSMENT RESULTS SCORE RECEIVED 0 20 40 60 80 100 NUMBER OF STUDENTS 0 7 27 38 56 34 TOTAL 162 SYNONYMS PERCENTAGE THAT RECEIVED THIS SCORE 0% 4.32% 16.66% 23.45% 34.56% 20.98% 11(14) SCORE RECEIVED 0 20 40 60 80 100 SCORE RECEIVED 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 NUMBER OF STUDENTS 9 12 22 43 36 40 TOTAL 162 ANTONYMS PERCENTAGE THAT RECEIVED THIS SCORE 5.55% 7.40% 13.58% 26.54% 22.22% 24.69% SYNONYMS AND ANTONYMS COMBINED NUMBER OF PERCENTAGE THAT RECEIVED THIS SCORE STUDENTS 0 0.00% 0 0.00% 2 1.23% 5 3.08% 5 3.08% 21 12.96% 22 13.58% 36 22.22% 35 21.60% 20 12.34% 16 9.87% TOTAL 162 TABLE 9. EVALUATION AND RESULTING ACTION PLAN In the table below, or in a separate attachment, interpret and evaluate the assessment results, and describe the actions to be taken as a result of the assessment. In the evaluation of achievement, take into account student success in demonstrating the types of knowledge and the cognitive processes identified in the Course Objectives. 12(14) A. Analysis and interpretation of assessment results: What does this show about what and how the students learned synonyms and antonyms? • While 0 percentage scored 0 on the synonym test, 9 students or 5.555% of the BE226 population received a score of 0 out of a possible 100 on the antonyms test. • 7 students or 4.32% of the BE226 population received a score of 20 on the synonyms test, but 12 students or 7.40% received the same score on the antonyms test. • 27 students or 16.66% of the population scored 40 on the synonyms test whereas only 22 students or 13.58% received the same score (40). • 38 students or 23.45% of the BE226 population scored 60 out of a possible 100 on the synonyms test. The number of students scoring 60 on the antonyms test was slightly higher (43 or 26.54%. • 56 students or 34.56% of the BE226 population displayed a good command of synonyms. They scored 80 on the synonyms test. However, the number of students scoring 80 on the antonyms test was relatively lower. Only 36 students or 22.22% of the BE226 population scored 80. • While only 34 students or 20.98% displayed excellent knowledge of synonyms by scoring 100, a slightly higher number of students (40 or 24.69%) scored 100 on the antonyms test. • Taken together, 0 students or 0.00% of the BE226 population scored 0 or 10 out of 100 points. A total of 2 students or 1.23% scored 20, and 5 students or 3.08% scored 30 points. 5 students or 3.08% of the BE226 population scored 40 out of 100 points. 21 students or 12.96% scored 50 points, and 22 students or 13.58% of the BE226 population scored 60 points. A total of 36 students or 22.22% scored 70 points, and 35 students or 21.60% displayed an adequate mastery of the skill of finding correct synonyms and antonyms from context clues by scoring 80 points. Compared to this, 20 students or 12.34% scored 90 points. Finally, 16 students or 9.87% displayed a complete mastery of finding the correct synonyms and antonyms from context clues by scoring 100 out of 100 points. B. Evaluation of the assessment process: What do the results suggest about how well the assignment and the assessment process worked both to help students learn and to show what they have learned? The synonyms and antonyms lessons were designed by a deputy reader and three experienced full-time faculty members who have taught English as a Second Language (ESL) students for a number of years. The assignment was carefully designed to address the level of synonyms and antonyms knowledge BE226 students are supposed to display before taking the CUNY standardized reading test. The results indicate that while 16 students or 9.87% of the BE226 population scored 100 points, 20 students or 12.34% received 90 points altogether. While 35 students or 21.60% scored 80 points, 36 students or 22.22% of the BE226 population received a score of 70 points, which is the minimum score to pass the exit test for BE226. It should be noted that while 55 students or 33.93% of the BE226 population scored 60 points or below, failing to meet the minimum requirement for passing the exit test, 107 students or 66.03% scored 70 points and above. 13(14) C. Resulting action plan: Based on A and B, what changes, if any, do you anticipate making? These results will be shared with all the BE-226 reading instructors so that they can understand that it is important for the BE226 students to improve their knowledge of synonyms and antonyms. Since 33.93% of the students were unable to receive the minimum passing score, it would be reasonable to assume that one third of the BE226 population would have difficulty achieving mastery of synonyms and antonyms before they take the exit test. QCC 03/30/11 14(14)