Measurable Annual Goals Reminders
advertisement

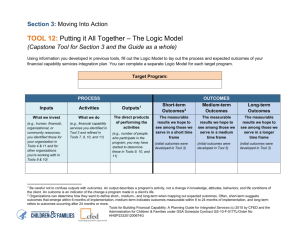
Activity 4.4 Measurable Annual Goals Reminders Note: The focus of these modules is intentionally scaled to address a narrow component of the IEP development process – creating measurable annual goals. When developing an actual IEP, please remember that it is important to consider all areas (present levels, measurable annual goals, summary of services, etc.) in the context of the entire IEP and the student’s individual needs, rather than considering each component in isolation. Measurable Annual Goals “Reminders” Measurable annual goals are used to guide instructional decisions for an individual student. Attributes include: Clear Positive Easily Understood Specific Realistic Quantifiable Measurable annual goals should reflect the identified needs of the student. They: Align with statements from the Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance (PLAAFP). Bridge the Gap Demonstrate relevance to the student’s academic, (social, and vocational) needs. Describe what the student can reasonably be expected to do in one year. Measurable annual goals prioritize learning based on the following: Close the gap between the student’s present level of performance and the grade-level expectation Prioritize standards, Determined to be necessary for the student’s ability to access Skills, and general education curriculum Knowledge Inclusion of specially designed instruction (SDI) needed to progress. Facilitate access to the general education curriculum. Measurable annual goals set a target for instruction for the year. They: Set Attainable May be informed by grade level standards or extensions when Targets appropriate. Advance the student more than one year’s growth when possible. What are four critical components of a measurable annual goal? Four Components 1. 2. 3. 4. Timeframe (in what length of time?) Conditions (under what context?) Who (the student) Behavior (will do what?) Evaluation (through what assessment) Criterion (to what degree/level?) The components include: timeframe (in what amount of time), under what conditions (given/context), who (date, time frame), behavior (will do what), evaluation (through what), criterion (to what degree or level). Activity 4.4 Measurable Annual Goals Reminders The example below illustrates six components for a 3rd grade student. Statement of when goal will be achieved (e.g., By Annual Review Date) Conditions (e.g., given an oral reading probe at grade level [3rd grade]) Observable Behavior (e.g., will read aloud; will complete assignment) Criterion/Evaluation (e.g., 115 wpm with no more than 5 errors; 90% accuracy on teacher-made tests; 85% completion rate on homework) NOTE: IDEA 04 removed the requirement to include short-term objectives in IEPs for all students, and only requires short-term objectives for those who take alternate assessments aligned to alternate achievement standards. Who Sue Bob Tracey Time Frame By Annual Review Date By Annual Review Date By Annual Review Date Conditions given an oral reading fluency assessment (ORF) at grade level, given who, what, when, where, and how questions from a grade level selection, given 3 digit subtraction problems with regrouping, Who/Behavior Sue will read Bob will read the selection and respond either orally or in writing Mark will correctly solve with 80% accuracy on standardized tests with 75% accuracy on teacher-made tests Criterion/Evaluation From 95 wpm to 115 wpm with no more than 5 errors