HIT THE GROUND RUNNING MS WORD INTRODUCTION
advertisement
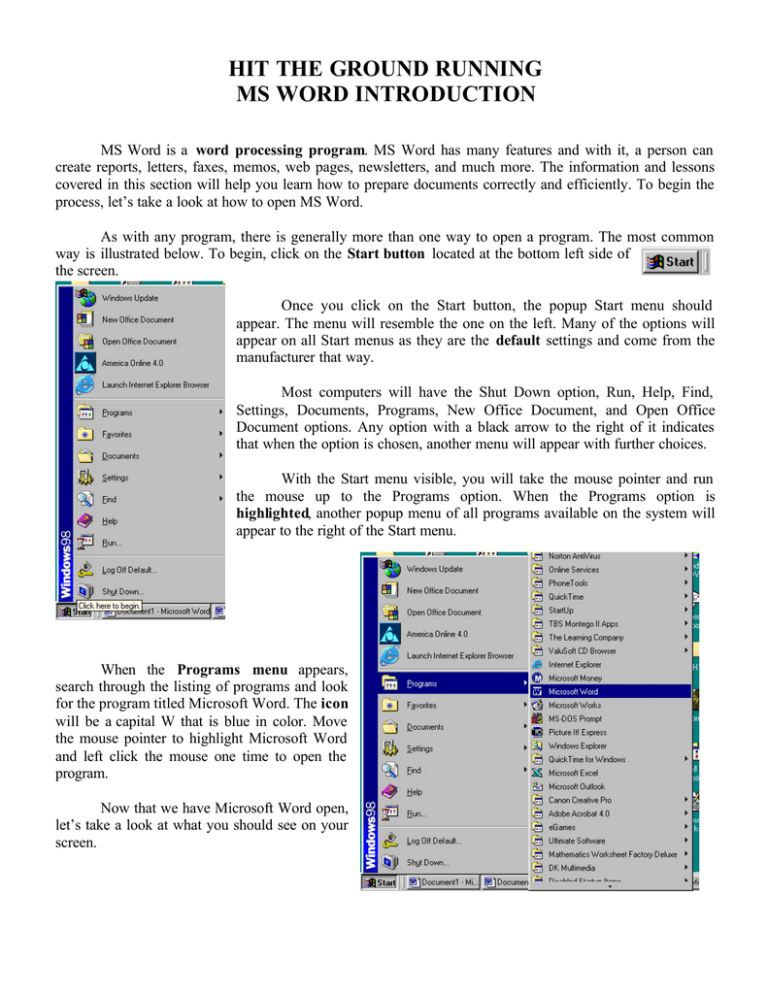
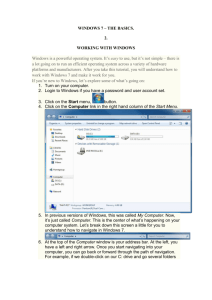
HIT THE GROUND RUNNING MS WORD INTRODUCTION MS Word is a word processing program. MS Word has many features and with it, a person can create reports, letters, faxes, memos, web pages, newsletters, and much more. The information and lessons covered in this section will help you learn how to prepare documents correctly and efficiently. To begin the process, let’s take a look at how to open MS Word. As with any program, there is generally more than one way to open a program. The most common way is illustrated below. To begin, click on the Start button located at the bottom left side of the screen. Once you click on the Start button, the popup Start menu should appear. The menu will resemble the one on the left. Many of the options will appear on all Start menus as they are the default settings and come from the manufacturer that way. Most computers will have the Shut Down option, Run, Help, Find, Settings, Documents, Programs, New Office Document, and Open Office Document options. Any option with a black arrow to the right of it indicates that when the option is chosen, another menu will appear with further choices. With the Start menu visible, you will take the mouse pointer and run the mouse up to the Programs option. When the Programs option is highlighted, another popup menu of all programs available on the system will appear to the right of the Start menu. When the Programs menu appears, search through the listing of programs and look for the program titled Microsoft Word. The icon will be a capital W that is blue in color. Move the mouse pointer to highlight Microsoft Word and left click the mouse one time to open the program. Now that we have Microsoft Word open, let’s take a look at what you should see on your screen. Before we actually create a document, let’s take a look at the parts of the Microsoft Word window. Take some time to review the picture below to become familiar with the different parts of the Word window. As you continue on with the lessons for MS Word, you can refer back to this graphic if you need help remembering the names of the parts of the window. Title Bar Standard toolbar Menu Bar Formatting toolbar Insertion point Ruler End-of-file marker Menu Bar Menu Bar Vertical scroll bar Menu Bar Horizontal scroll bar View buttons Status bar The graphic above shows the parts of the Word application window in general terms, but let’s take a closer look at several parts of the window to better understand what function they perform. First let’s take a look at the title bar. The Title Bar indicates the name of the program that is currently running and in the case of Word, indicates the number of the document at which you are currently looking. When you first open up the Word application, it creates document one. The next document that is created will be called document two. You can have multiple documents open; however, you can only work in one at a time. Directly under the title bar, you will find the Menu Bar. The menu bar contains words and when an option on the menu bar is activated, it displays a list of commands. Some of the commands have images next to them so you can quickly associate the command with the image on a toolbar. Most menus are located on the menu bar at the top of the Word window. Shortcut menus are available when you right-click text, objects, or other items. Notice the image of an open folder beside of the Open option. Once you can associate the images with the commands, it is often quicker and/or easier to use the Standard Toolbar and the Formatting Toolbar to achieve the same result. Many of the more common or widely used commands from the Menu Bar are listed are the next page. File Button – Options 1. New – Creates new document 2. Open – Opens a document saved on hard drive or disk 3. Save – Saves document to hard drive or disk 4. Save As – Saves a document to hard drive or disk. Allows you to change name when revising 5. Page Setup – Allows you to change margins, paper size, and paper orientation 6. Print Preview – Allows you to see a preview of what the printed page would look like You cannot make changes in Print Preview. Click on the close button to close print preview 7. Print – Allows you to print document, page range, number of copies, and collate Edit Button – Options 1. Undo – Erases last action 2. Redo – Puts back last action that has been erased. 3. Cut – Deletes a highlighted section of text or a picture 4. Copy – Copies a highlighted section of text or a picture 5. Pastes – Actually puts copied text into a new document 6. Find – Allows you to search through a document for a certain word 7. Replace – Allows you to replace a given word for another Insert Button – Options 1. Break – Insert a page or column break 2. Page Number – Allows you to number pages 3. Date/Time – Allows you to insert current date 4. Auto Text Picture – Allows you to insert pictures, drawings, or clip art 5. Picture – Inserts clip art, photos, or other art work into documents Format Button – Options 1. Font – Allows you to change Font, font size, font color, and effects 2. Paragraph – Allows you automatically indent first line of paragraph, line spacing – double space 3. Bullets and Numbering – Allows you to insert numbers or bullets to as accents 4. Columns – Inserts columns on page 5. Tabs – Allows you to set tabs Tools Button – Options 1. Spelling and Grammar – Allows you to check for spelling and grammar errors. Be careful with this option. If the dictionary on the hard drive doesn’t include a word then the computer thinks the word is spelled incorrectly. 2. Language - Contains a thesaurus to help you vary your vocabulary 3. Envelopes – Allows you to print envelopes and labels Options – You can change many defaults here such as, spelling and grammar check Table Button – Options 1. Draw a Table Help Button – Options 1. Microsoft Word Help The default position of the Standard Toolbar is directly under the menu bar. A toolbar can contain buttons with images (the same images you see next to corresponding menu commands), menus, or a combination of both. Microsoft Word includes many built- in toolbars that you can show and hide as needed. Tool buttons that are in color are active. This means that the function completed by the tool button is an available option. Tool buttons that are light grey, like the two arrows above, are inactive. The function these buttons activate is not available at this time. Notice in the graphic below, the Undo Button is now blue which indicates it is active. The graphic below also indicates the name or function of each tool button. Drawing Toolbar The “New” tool button on the Standard tool bar is the same command that is found under File on the Menu bar. You can use either option to open a new document. Most applications have at least two methods of completing the same function. Refer back to page three of your handout if you cannot remember what each function does. The Formatting Toolbar is generally located to the right of the Standard toolbar or directly underneath the Standard toolbar. The Formatting toolbar allows you to change the look of your document. Below is a graphic that identifies each tool button. A brief explanation of what each tool button does is located on page 5. To change the Style, Font, or Font size of your text, you put the mouse pointer over the black down arrow beside of the current selection and left click one time. A drop down menu will appear, and your other options will be indicated. You can activate tool buttons on the Formatting toolbar before you type the text by putting the mouse pointer over the tool button and left clicking one time. When you finish the text you want formatted, you can turn off the tool button by putting the mouse pointer over the button and left clicking one time again. Formatting Toolbar definitions: 1. Style - A style is a set of formatting characteristics that you can apply to text in your document to quickly change its appearance. When you apply a style, you apply a whole group of formats in one simple task. For example, you may want to format the title of a report to make it stand out. Instead of taking three separate steps to format your title as 16 pt, Arial, and center-aligned, you can achieve the same result in one step by applying the Title style. When you start Microsoft Word, the new blank document is based on the Normal template, and text that you type uses the Normal style. This means that when you start typing, Word uses the font, font size, line spacing, text alignment, and other formats currently defined for the Normal style. The Normal style is the base style for the Normal template, meaning that it’s a building block for other styles in the template. 2. Font - A set of type characters of a particular typeface design and size. Two of the most commonly used fonts are Times New Roman and Arial. There are many different types of fonts that can be used. Specialized fonts have been developed and are often used for decoration or for emphasis. Examples of fonts are as follows: Algerian Harlow Solid Brush Script MT Georgia Castellar Monotype Corsiva EngraversMT Old English Text Chiller 3. Font size – This option changes the size of the letters within a document. Sizes range from 8 point to 72 point. The larger the number, the larger the text. Examples of font sizes: 14 point 16 point 18 point 20 point 22 point 4. Bold – Text typed with the bold option on is printed in thick heavy type 5. Italic - Of or being a style of printing type patterned on a Renaissance script with the letters slanting to the right: This sentence is printed in italic type. 6. Underline – This function will add an underline to all selected text. 7. Left Align – This function begins any text on the left hand side of the page. 8. Center Align – This function centers text in the middle of a page. 9. Right Align – This function begins any text on the right hand side of the page and moves toward the left hand side of the page. 10. Justify – This function spreads out the text typed to even out where each sentence ends. This function is most obvious when reading a book. 11. Numbering – This function allows you to create numbered lists or outlines. 12. Bullets – This function allows you to create bulleted lists. 13. Font Color – This function allows you to change the color of the text. The Ruler allows you to see the amount of space available on a page to enter text. The white area shown on the ruler below is available space for text or graphics. The grey area to the right of the ruler is the margin indicator. This area is not available for use. If a graphic is placed in this area it will not print out. To activate the ruler options, click on View and then on the drop down menu click on Ruler. The Insertion Point or curser as it is more commonly known indicates where the text or graphics will be placed within a document. You can move the insertion point by hitting enter or using the arrow keys. The Vertical and Horizontal Scroll Bars allow you to move around the page to see all of the text that is written on a page. To move a page up or down, use the Vertical Scroll Bar. Place the mouse pointer on the black up or down arrow and click the left mouse button. You can also move the page up or down by left clicking on the grey square on the scroll bar, holding down the left mouse key and drag the square up or down as desired. To move a page to the right or left, use the same action except on the Horizontal Scroll Bar. The View buttons , located at the bottom left hand side of the window, allow you to change the way you look at a document. Normal view is a simplified layout of the page. Print Layout view shows how a document will look when it is printed. It is recommended that you use the Print Layout view when creating documents. The Status Bar is a horizontal area at the bottom of the document window in Microsoft Word. It provides information about the current state of what you are viewing in the window and any other contextual information. The Status Bar indicates which page is currently being shown in the window, the section of the page being shown in the window, the number of the page in the current window in relation to the total number of pages in the document, the distance from the top of the page to your insertion point, the line of text where the insertion point is located, and the distance, in number of characters, from the left margin to the insertion point. The key concepts in this section include: v Identifying the major parts of the Microsoft Word Window v Identifying what commands are listed on the Menu Bar v Identifying what commands are listed on the Standard and Formatting toolbars If you can identify all the concepts above, you are doing great!!!! If you cannot, you might want to go over this section of the text again. Lesson One MS Word Key Concepts: v Creating a new document v Working in multiple documents v Entering text into a document v Navigating through a document v Saving a document v Looking at a document in print preview mode v Printing a document To create a new document in Microsoft Word you must first open the program Microsoft Word. To open the program, left click on the Start button, highlight the Programs option on the Start Menu, and left click once on Microsoft Word on the Programs Menu. When MS Word opens a new blank document is displayed. The document is currently titled Document One. The file name will remain Document One until the document is saved using the ‘Save As” command and a new file name is assigned. Several documents can be opened at the same time. However, only one document can be actively worked on at a time. Any other opened documents can be viewed on the task bar at the bottom of the window. To open one of these windows, left click on the name of the document to be opened, and it will open up in a new window. You can toggle back and forth between these windows. The several purposes of this feature is to allow the user to have access to other information that might be helpful in creating a new document, copy and paste information, or multitask. As you enter text into your document, the cursor will move towards the right margin, and the status bar will change to reflect the position of the cursor. To place a space between words in a sentence, strike the space bar at the bottom of the keyboard. It will place one empty space each time it is struck. Striking the enter key is not necessary as you type in the text. Unlike a typewriter, MS Word has a default function* called Word Wrap. This feature allows you to continuously type in text and the program automatically moves down to the next line when no further space is available for the text. *(A default function is one that occurs each time you open up a document in MS Word.) The enter key is struck when you want to start a new paragraph or you want to insert a blank line between lines of text. If you hit the enter key at the end of each line, the program assumes that you are starting a new sentence or paragraph and that the first word of the sentence should be capitalized. The program will also assume that there should be some type of punctuation at the end of the previous sentence or paragraph. As text is entered into the document, another default function of MS Word is being performed. The program automatically checks for spelling and grammatical errors. Spell check is used to check the spelling of the text. When a word is misspelled, it will be underlined in red. MS Word uses a preset dictionary to check the spelling of the text. If a word is not in the dictionary, spell check assumes that the word is misspelled. You will often see last names underlined because of this. The city of Parkersburg is also often underlined because it is not in the dictionary the computer uses. New words can be added to the dictionary to help correct this. You will often find that spell check often makes mistakes. Do not rely solely on spell check. Grammar check is used to determine if a sentence is grammatically correct. It is completed with the Spell Check. When a sentence’s structure is grammatically incorrect, MS Word will underline the sentence with a green line. The grammar check feature will identify sentence fragments and misplaced or missing punctuation. Grammar check also identifies passive sentences. Again, while this feature is helpful, it is not perfect so do not solely rely on it. Double check all work. If you make a mistake while entering text, and you catch the mistake quickly, hit the backspace key to go back and correct the mistake. If however you have typed a whole paragraph before finding a mistake in the first sentence, you have two main options. (And no one does not involve a hammer.) One option is that you can erase the entire paragraph, fix the mistake, then retype the paragraph. This however is very time consuming and aggravating. The second option involves knowing how to navigate through the page so that you can go immediately back to the area that is incorrect, (without losing any other text), fixing the mistake, and then returning to the end of the text to continue entering text. Which one would you prefer? There are many options that can be used to move through a document. One of the most common is to use the Vertical and Horizontal Scroll bars to move within a document. Left click on the black, single arrows to move up, down, right or left. You can hold down the left mouse key to move more quickly. You can also put the mouse pointer on the grey squares on the scroll bars, hold down the left mouse key, and drag the squares up, down, right or left to view different areas of the page. Another method of navigating is Click and Type. Use the mouse to move the cursor to a different position in a document and fix a mistake. The mouse pointer in a word document is called an I-beam. It is called this because it looks like a capital I. Move the I-beam to the point in the document where changes need to be made and click the left mouse button once. This will insert a cursor where the I-beam is located. Then use the backspace button to erase a mistake or start typing to include further text. The rest of the text will move down the page to allow for the new text. When the text is correct, move the I-beam to the end of the text, left click the mouse, and continue entering text into the document.* * To use the Click and Type feature you must be working in the Print Layout View. You can change the view by clicking on the view buttons with the mouse or by clicking on the View option on the menu bar. A third method of moving through a document is to use the keyboard. Below is a list of the buttons that will help you with navigation and the function of each button or set of buttons. If two buttons need pressed, press them at the same time. Left Arrow Right Arrow Up Arrow Down Arrow End Home Page Up Page Down Control & Left Arrow Control & Right Arrow Control & Up Arrow Control & Down Arrow Control & End Control & Home Control & Page Up Control & Page Down Moves one character to the left Moves one character to the right Moves up one line Moves down one line Moves to end of a line Moves to the beginning of a line Moves up one screen Moves down one screen Moves one word to left Moves one word to right Moves up one paragraph Moves down one paragraph Moves to the end of a document Moves to the beginning of a document Moves to the top of the previous page Moves down to the top of the next page Once you have all the information typed in the document, you will want to save it. As a precaution, you might want to save the document every 5-10 minutes as you work on it. The reasoning behind this is that sometimes accidents happen and you can lose all of your information. Power surges, power outages, or the program freezing up are only three possible problem you might run across when working on a computer. As the old saying goes “Better to be safe than sorry”. To save a document you can use the Save As feature or the Save feature. However, the two features are different. Use the Save As feature the first time you save a document. It allows you to rename the file. To save a file using the Save As command, move the mouse pointer to the word File on the Menu Bar and left click. Move down the drop down menu and highlight the Save As option and left click. When the Save As window opens, move the pointer down to the text box beside of File Name and type in the name you wish to save the file as. Do not use punctuation or symbols in the file name. Letters and numbers only should be used to avoid conflict with the program. Save can be used after you have renamed a file. However, if you click Save any changes you have made to the document overwrites what information was in the document when it was last saved. If you wish to keep the first copy and save the document with the changes, you will need to click on Save As and rename the document. Often when versions of a document are being created, additional versions will have numbers after the file name. An example might be Version 1, Version 2, Version 3. Version 1 is the original document. Version 2 has some changes from Version 1 and Version 3 has changes from both Version 1 and Version 2. It is recommended that if you are unsure of any changes you have made to a document, you should save the document using Save As and rename it. That way if the changes are not what was needed or something in the original document was accidentally deleted, it will be easier to fix the document. Once a document has been saved, you can then print it. You do not need to save a document to print it, however, if something goes wrong you would have to retype it before you could print it out again. So just to be safe, save the document before you do anything else. It is recommended that before you print out a document you look at the document in the Print Preview mode. Print Preview allows you to see how the document will print out before you actually print it out. It allows you to see mistakes with spacing or with the margins. To activate the Print Preview command, you can move the mouse pointer to the File option on the Menu Bar and click the left mouse button. On the drop down menu highlight Print Preview and left click again. This will take you to the Print Preview screen. This is a cropped version of a Print Preview Screen. Notice that the title bar indicates that this is a preview of what is to be printed. The Print Preview Screen has a menu bar and the Print Preview Tool Bar. The options on the Print Preview Tool bar are from left to right v v v v v v v v v v Print Magnifier – This allows you to click on part of the page and increase it to read it better One Page – Allows you to see one page in a document Multiple Pages – Allows you to look at several pages in the same document at the same time. However the pages will be smaller and you may need to magnify them to see them better. Zoom – This allows you to shrink a page to see the entire page at one time or increase the page to view just a small section of it. View ruler – puts the ruler on the print preview screen Shrink to Fit – This option shrinks the document so that it fits in your field of view on screen Full screen – This option increases document to fit entire field of view on screen. Close – This option takes you back to the Normal or Print Layout View where you can make any necessary changes. * No changes to a document can be made in the Print Preview Mode. Help Once you have previewed the document and determined that it is correct, you can use the Print tool button on the toolbar to print out the document. Once you have printed out the document you are finished. Congratulations! You have just created, saved, and printed your first document. Activity One Creating, Saving, and Printing a document. Follow all instructions. If an activity is completed incorrectly, it will have to be redone. You have just read an advertisement for a two-day workshop on Anger Management and Conflict Resolution. The workshop is one that you would like to attend but you would need time off from work to go to the workshop. Write the following memo to your shift supervisor requesting two days off to attend the conference. Instructions: 1. Create a new document. 2. Type in the text below. Any text in parenthesis is an action and the correct information should be entered. Example: (Today’s Date) current date should be entered here not “Today’s Date”. 3. Place one blank line between each paragraph. You will need to hit the enter key twice to place the blank line in the document. 4. Save the document as Word Activity One. 5. View the document in Print Preview to determine if there are any mistakes. Make any necessary corrections to the document. 6. Print one copy of the document. 7. Submit the letter to your online ins tructor. (Today’s Date) (Instructor’s Name), Shift Supervisor Anger Management and Conflict Resolution Workshop At my last review session, it was commented that all area supervisors should have up to date methods of dealing with employees temperamental or who have problems dealing with other employees or management. It has come to my attention that a two-day workshop is being offered at West Virginia University at Parkersburg next month. The workshop will include seminars on 10 Effective Ways to deal with an Angry Employee, How to Solve Employee Conflicts through Discussion, and Handling Difficult Situations. I believe that this workshop will be extremely helpful in updating my skills and will allow me to bring back the most current information to be discussed and reviewed at the next area supervisors’ meeting. I would like your permission to attend this workshop at West Virginia University at Parkersburg. Please contact me when you have reached a decision so that I can send in the reservation form and workshop fee. Thank you, (Your Full Name) Activity Two Creating, Saving, and Printing a document. Follow all instructions. If an activity is completed incorrectly, it will have to be redone. Your instructor has requested a document from you. The document will contain three paragraphs. In the first paragraph, you have been instructed to tell about yourself. In the second paragraph, you have been asked to write about your educational goal. (If you do not plan on attending further schooling, write about your family) The last paragraph is to contain your employment goals. What type of job, where you would work, and expected salary are but three examples of things you can discuss in this paragraph. Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Create a new document. Create the three paragraphs listed above. Place one blank line between each paragraph. Save the document as Word Activity two. View the document in Print Preview to determine if there are any mistakes. Make any necessary corrections to the document. 6. Print one copy of the document. 7. Submit to your online instructor.