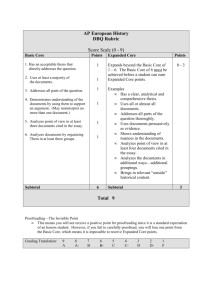
Skill Standards for Professional- Technical College Instructors
advertisement

Skill Standards for ProfessionalTechnical College Instructors 2012 Update 1 2 Copyright © 2012 State of Washington through the Center of Excellence for Careers in Education. Unless otherwise provided, data which originates from this agreement, shall be “works for hire” as defined by the U.S. Copyright Act of 1976, and shall be owned by the State of Washington. Data shall include, but not be limited to, reports, documents, pamphlets, advertisements, books, magazines, surveys, studies, computer programs, films, tapes, and/ or sound reproductions. Ownership includes the right to copyright, patent, register, and the ability to transfer these rights. For More Information Contact: Erik Tinglestad, Executive Director, Center of Excellence for Careers in Education, Green River Community College. (253) 833-9111 ext. 4359, etinglestad@greenriver.edu Project Funding Financial support for this project was provided by the Center of Excellence for Careers in Education through funding from the Workforce Education Council. Permission to Cite General permission is granted for educators to photocopy and quote limited material from this document for noncommercial instructional or scholarly use. Permission must be sought from the Center of Excellence for Careers in Education to charge for photocopies, to quote material in advertising, or to reprint substantial portions of the document in other publications. Credit should always be given to the source of the photocopies or quotes by citing a complete reference. Copies of Document Additional copies of the document can be downloaded at no cost: http://www.careersined.org/ Document Credits Project Director, Alan Hardcastle Ph.D., Washington State University (WSU) Energy Program, (360) 956-2167, hardcast@wsu.edu Research, facilitation and technical writing by Terryll Bailey, The Allison Group (206) 525-7175, tbailey@theallisongroup.com. Acknowledgements This document is the result of the collaborative efforts of industry, labor, education, and government successfully working together through the Center of Excellence for Careers in Education. A special thanks to all who contributed, and especially to the faculty members who participated in the focus groups. Their countless hours of work to help produce the skill standards are greatly appreciated. Project Development and Coordination: • Erik Tinglestad, Green River Community College • Alan Hardcastle, WSU Energy Program • Terryll Bailey, The Allison Group • Sally Zeiger Hanson and Gerry Rasmussen, WSU Energy Program 3 Focus Group Participants The focus group participants consisted of nine college faculty members from a variety of fields, representing a cross section of Washington’s 34 two-year colleges. They met over a two-day period at Kent Station to review and update the critical work functions and key activities performed by Professional Technical College Instructors. They then identified the performance indicators, technical knowledge, skills and abilities, and employability skills required to succeed in this field. Their insights were an invaluable contribution and formed the foundation of this work. Participants included: • • • • • • • • 4 Christine Beaudry – Radiologic Science – Yakima Valley Community College Greg Brazell – Early Childhood Education – Pierce College, Fort Steilacoom Rod McDonald – Welding – Grays Harbor College Jeff Ward – Business – Highline Community College Jim Howe – Computer Science – Lake Washington Institute of Technology Margaret Anderson – Physical Therapist Assistant – Whatcom Community College Mark Franklin – Diesel and Heavy Equipment – Spokane Community College Penny Woodruff – Nursing – Grays Harbor College (Original Skill Standard Participant) • Karen Strickland (observing) – Human Services – South Seattle Community College – American Federation of Teachers (AFT) WA Table of Contents National Context...................................................................................................... 7 What Are Skill Standards? ........................................................................................ 7 The Benefits and Uses of Skill Standards................................................................... 8 Pyramid of Competencies......................................................................................... 9 Background on the 2012 Skill Standards Project..................................................... 10 Skill Standards Update Process............................................................................... 10 Project Steering Committee.................................................................................... 11 Focus Group........................................................................................................... 11 Findings................................................................................................................. 12 Definitions ............................................................................................................. 12 Technical Skills, Knowledge, Abilities and Tools....................................................... 13 SCANS Employability Skills..................................................................................... 13 Skill Standards for Professional-Technical College Instructors.................................. 14 Critical Work Functions: A. Manage Learning Environments.................................................................. 16 B. Develop Outcomes, Assessments, and Curricula.......................................... 23 C. Develop and Review Programs.................................................................... 28 D. Provide Student Instruction......................................................................... 35 E. Provide Support and Guidance to Students.................................................. 40 F. Perform Administrative and Program Management Functions...................... 45 G. Create and Maintain a Professional Environment......................................... 52 H. Promote the Program and Recruit Students................................................ 57 SCANS Survey Results............................................................................................ 61 5 6 National Context The National Skill Standards Board (NSSB) was established by Congress in 1994 to encourage the creation and adoption of a national system of voluntary skill standards that would enhance the ability of the U.S. to compete effectively in a global economy. By the time the NSSB sunset in 2003, several national voluntary skill standards projects were developed by various industries in full partnership with education, labor and community-based organizations. The intent was to have voluntary skill standards that are flexible, portable, and continuously updated and improved. Washington State was an early leader in the development and use of industrydefined skill standards, contributing to the development of a national model and creating skill standards to align the needs of industry with the provision of workforce education and training. What Are Skill Standards? Skill standards are performance specifications that identify the knowledge, skills and abilities an individual needs to succeed in the workplace. They are critical to improving workforce skills, raising living standards and improving the competitiveness of the U.S. economy. To be effective, skill standards must reflect the consensus of industry professionals. Skill standards provide measurable benchmarks of skill and performance achievement. They answer two critical questions: What do workers need to know and be able to do to succeed in today’s workplace? And how do we know when workers are performing well? Without this fundamental information, employers do not know whom to hire or where to focus their limited training dollars; employees and new entrants to the workforce do not know what they need to do to improve their performance; and educators do not know how to prepare students for the challenge of the workplace. Why Are Skill Standards Important? In today’s workplaces, the only constant is change. Jobs that once were relatively simple now require high-performance work processes and enhanced skills. Because skill standards reflect changing workplace realities, they are a tool that can be used by applicants and employees to access greater career opportunities. National recognition of skill standards in career fields provides a common basis for certifying achievement against those standards, thereby allowing for the portability of skills across geographic areas, companies and careers. Updating skills and knowledge is now a lifelong endeavor, causing many employers and employees to spend more effort, time and money on education and training. Skill standards provide benchmarks for making education and training decisions, shaping curricula and directing funds toward highest value education and training investments. 7 The Benefits and Uses of Skill Standards Skill standards benefit all the stake-holders – business, labor, educators, government, and the community. The success of a skill standards development project and its usefulness to the community is dependent on the full participation and commitment of all stakeholders. These benefits can be used as a benchmark for evaluating the effectiveness of collaborative efforts. Curriculum Development • Identify necessary competencies based on the skill standards information and assessments. • Develop program outcomes for specific academic and training programs, including Tech Prep, two-year, and apprenticeship programs. • Perform gap analysis to determine changes or additions to be made to curriculum. • Revise existing curriculum to better meet the current and future needs of the industry. • Develop new curriculum and establish new programs based on these competencies. 8 Articulation • Develop models to support the articulation of program outcomes and competencies between academic and training systems. • Establish articulation agreements between existing programs to ensure portability of skills. • Connect competencies and Certificates of Competence with benchmark documentation to build national portability systems. A Continuous Updating Process A continuous updating process is necessary: all partners must revise and verify skill standards on a regular basis. For national economic development success, curriculum and current training methods must be updated to meet workplace standards. Individual workers must have access to clearly stated competency goals and direct access to skill development assistance. With cooperative effort on local and national levels, we can begin to resolve the workforce skill shortages that face us today Pyramid of Competencies The Pyramid of Competencies (see Figure 1) is a depiction of skill standards in three broad skill categories. Tier I Tier I represents the broadest level of competencies, and is the set of employability (SCANS) skills, knowledge, abilities and personal qualities required of all workers to be successful in today’s workplace. These are the universal skills that are needed to apply technical knowledge and tools effectively. Tier II Tier II represents technical skills, knowledge and abilities common to a cluster of jobs within a cluster across all industries or industry sectors. Tier III Tier III represents industry-specific technical skills, knowledge and abilities that are unique to individual jobs or clusters and are the most prone to rapid change. For example, many workers need to upgrade their skills based on sudden market shifts. 9 Figure 1 The Pyramid of Competencies Background of the 2012 Skill Standards Update Project The original Skill Standards for Professional-Technical College Instructors was produced in 2000 using specific research-based processes required by the Washington State Board for Community and Technical Colleges (SBCTC). The 2012 update project replicated the original process and updates the original document to ensure that the skill standards reflect the current skills, knowledge, technologies and practices of community and technical college instructors. This project was requested by the Workforce Education Council (WEC) and managed by the Center of Excellence for Careers in Education to ensure that a standards-based approach continues to be used as a foundation for defining competencies and measurable skills of instructors. The standards also help to ensure that proposed Applied Baccalaureate degree programs for ProfessionalTechnical Instructors incorporate current foundational skills. Skill Standards Update Process 10 Steering Committee and Focus Group A Steering Committee consisting of workforce leaders from colleges across the state was convened to provide oversight to this project. The Steering Committee nominated participants for the focus group process. The initial focus group, which was led by Terryll Bailey of The Allison Group, included nine experienced educators representing many different professional-technical disciplines, including business, technical, health, human services, and trade and industry. In addition, there was diversity in terms of the amount of teaching experience and experience in industry as well as with gender, age, and race. While the majority were full-time instructors, some part-time instructors also participated. The participants met for a two-day focus group process at Green River Community College’s Kent Station campus. The first step in the focus group process was to identify the primary functions and key activities that constitute the work of a competent entry-level professional-technical college instructor. Working with a draft of sample functions that were prepared from the original existing skill standards and research of instructor job descriptions, the group revised and adapted functions and tasks to meet the needs of professional-technical college instructors, programs and two-year college institutions throughout Washington State. Participants freely made changes and recommendations and crafted 8 basic critical functions with corollary key activities. Project Steering Committee • Christy Doyle, Spokane Community College • Curt Freed, Columbia Basin College* • Jean Watley, Bates Technical College • Jo Ann Baria, Pierce College* • Mike Kelly, Grays Harbor College* • Noreen Light, State Board for Community and Technical Colleges* • Pat Copeland, Edmonds Community College • Paulette Lopez, Yakima Valley Community College • Phil Venditti, FACTC, Clover Park Technical College * Original Skill Standard Participant Focus Group • Christine Beaudry – Radiologic Science, Yakima Valley Community College • Greg Brazell – Early Childhood, Pierce College • Rod McDonald – Welding, Grays Harbor College • Jeff Ward – Business, Highline Community College • Jim Howe – Computer Science, Lake Washington Institute Of Technology • Margaret Anderson – Physical Therapist Assistant, Whatcom Community College • Mark Franklin – Diesel And Heavy Equipment Equipment, Spokane Community College • Penny Woodruff –Nursing, Grays Harbor College (Original Skill Standard Participant) • Karen Strickland (Observing) – Human Services, South Seattle Community College – AFT WA Performance Criteria The second step was to identify the performance indicators for each key activity, answering the question: “How do you know when this is performed well?” The group also identified the tools, knowledge and foundation skills required to meet the performance criteria. The draft skill standards generated through the focus group process were reviewed by members of the Steering Committee with respect to current industry trends and requirements. Verification Thirdly, a survey of SCANS skills and personal qualities for teaching careers was administered to focus group members, and later to a larger sample of professional-technical instructors from colleges across the state. SCANS (Secretary’s Commission on Achieving Necessary Skills) are foundation employability abilities 11 required of workers in all occupations at varying levels specific to their jobs. A total of 130 SCANS surveys were returned. Finally, a survey of critical work functions and key activities was sent to professional-technical instructors at all 34 colleges in Washington State. All critical work functions and key activities were verified, and each key activity was rated for its level of importance. Response data were compiled and averaged to find the level of importance of each critical function. Surveys were returned from 130 participants from 24 colleges. The results of all the focus groups, surveys and feedback were compiled and analyzed, and a draft of the document was reviewed by the Steering Committee. These standards were accepted by the Instruction Commission in May 2012. Findings 12 The process of updating the Skill Standards for Professional Technical Instructors in 2012 underscored the strength of the original standards created in 2000. While technology, programs and students were found to have changed somewhat, the essential skills, knowledge and abilities needed to be effective in the classroom have remained constant. Three Critical Work Functions from the 2000 version are now merged or embedded into other functions: Perform Administrative Functions and Perform Program Management become one function and Learn and Adapt New Technologies is embedded throughout the other functions. These changes infer that administrative and management functions may have become more central to an instructors role and that technology is infused into all aspects of the work. Definitions Critical Work Functions Critical work functions represent the general areas that a first-year, fully competent, professional-technical instructor would perform. Key Activities Key activities are the tasks related to the critical work functions. They are made up of work activities which are measurable and observable and which result in a decision, product or service. Level of Importance Professionals who are actively working in this occupation rated the level of importance for each critical work function and key activity, ranging from not important to critical. All critical work functions were rated as important, very important or critical. Performance Indicators Performance indicators are specific behavioral evidence of a worker’s achievement of skills, knowledge and tasks. The question answered is: “How do we know when this key activity is performed well?” Performance indicators provide the standard of performance required to produce the necessary outcomes of key activities. Technical Skills, Knowledge, Abilities and Tools Technical skills, knowledge and abilities are those areas of expertise which workers must have in order to perform a given occupational task with excellence. A collection of skills, knowledge, abilities and tools make up competencies. Skills refer to proficiency in an applied activity. This activity could be physical, mental or interpersonal in nature. Knowledge is a particular set of information. Abilities are broad human characteristics that result from natural talent, training, or experience. Tools are materials, equipment and implements a worker must be able to use competently to meet the requirements of the job. SCANS Employability Skills SCANS employability skills are basic academic and personal skills that are needed to build more advanced competencies. They are competencies required by all workers in order to obtain meaningful work and participate in the modern workforce. 13 Skill Standards for Professional-Technical Instructors C. Develop and review programs D. Provide student instruction 14 B. Develop outcomes, assessments, and curricula A. Manage learning environments Critical Work Functions Key Activities A1 Research, evaluate and obtain required equipment, systems, tools, supplies, and materials A2 Set up, maintain and repair instructional systems, equipment and/or tools A3 Develop a growth and replacement plan for systems, equipment and/or tools A4 Lead students and supervise learning environments A5 Research, select, evaluate and maintain off-campus learning environments B1 Identify, evaluate, and modify outcomes B2 Create, evaluate, and modify curriculum B3 Create, evaluate, and modify assessments B4 Implement curriculum and assessments. B5 Integrate curriculum with other faculty in the department and in other instructional areas/ institutions C1 Develop, review, and update program course plan C2 Recruit and work with advisory committee and employers to meet changing needs of the program and industry C3 Identify, evaluate, and modify program outcomes and assessments C4 Identify and develop core and support courses C5 Maintain (or obtain) program accreditation D1 Prepare and/ or gather current instructional materials D2 Provide individual and group instruction D3 Initiate, develop, and implement student assessments D4 Modify instructional material and methods based on student and industry assessments and feedback D5 Promote professionalism in the learning environment A6 Evaluate and monitor the safety of the instructional areas and practices A7 Identify, evaluate, and implement new instructional strategies and technologies C6 Research, identify and evaluate trends and implement current industry standards C7 Coordinate program development with other college programs and institutions H. Promote the program and recruit students G. Create and maintain a professional environment F. Perform administrative and program management functions E. Provide support and guidance to students Critical Work Functions Key Activities E1 Provide students with access to instructor E2 Provide information or referrals to meet student needs E3 Provide students with career advising and assist with job placement E4 Provide academic advising E5 Serve as student activity advisor as applicable F1 Perform documentation and record keeping duties F2 Lead and manage instructional and program assistants F3 Mentor, orient, and support new and parttime faculty F4 Develop criteria, recruit, and make recommendations regarding hiring of faculty F5 Provide input for program, schedules, and college printed and electronic publications F6 Develop and manage budgets F7 Research and assist with writing and implementing grants and targeting financial resources 15 G1 Collaborate with college staff, faculty, students and internship/ externship site personnel G2 Work with program advisory committee G3 Maintain current knowledge of the field G4 Participate in professional networking H1 Participate in campus, high school and community organization activities and educational partnerships H2 Develop promotional plan H3 Provide program information for prospective students H4 Perform recruiting activities G5 Develop a professional development plan Critical Work Function: A. Manage Learning Environments Key Activity A1 Research, evaluate and obtain required equipment, systems, tools, supplies, and materials 16 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Requisitions, budgets and/or grant requests are submitted in a timely manner and in accordance with college policies and procedures. • Recommendations from advisory committee are accurately documented and considered. • The system, equipment and tool options are thoroughly researched and an effective selection is made to support student learning. • Ergonomic requirements are properly considered as appropriate. • Alternative sources of funds and systems/ equipment are actively pursued as appropriate. • Equipment and/or system’s impact on student learning is accurately documented in accordance with college policies and procedures. • Adequate supplies and materials are maintained. • Equipment, systems, tools, supplies and materials are properly identified and justified. • Knowledge of equipment requisitions procedures. • Knowledge of advisory committee protocols. • Knowledge of procedures for submitting budget and/or grant requests. • Knowledge of equipment and tool options and the ability to access relevant sources of information. • Ability to access alternative sources of funds and equipment/ systems. • Knowledge of student learning and the ability to determine the impact of equipment/ systems. • Knowledge of ergonomics. • Knowledge of college policies and procedures. • Understands technological requirements and results; analyzes task/technology relationship; proposes simple technological solutions. • Interprets information, selects methods of communication and summarizes. integrates and analyzes information. • Analyzes situations and information, considers risks and implications, complies multiple viewpoints, and generates alternative solutions. • Maintains job specific supplies and equipment, orders and maintains inventory and monitors safe and efficient utilization of materials. • Understands the organization and system hierarchy and follows procedures and recognizes system strengths and limitations A. Manage Learning Environments Continued Key Activity A2 Set up, maintain and repair instructional systems, equipment and/or tools Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Systems and equipment setup is completed in accordance with manufacturer’s specifications. • All safety procedures are completely followed. • Systems and equipment are set up to ensure access by students. • New systems and equipment are set up to be compatible with existing equipment/ systems and learning environment as appropriate. • Technical support is accessed when appropriate. • Maintenance schedules are properly followed. • All maintenance records and warranty requirements are maintained in an organized manner and kept current. • Equipment, tools, and systems malfunctions and repair needs are promptly diagnosed and repaired as appropriate and/or departments or personnel are informed. • Equipment and tools are properly secured. • Equipment, tools, and systems are kept clean and properly maintained. • Repair and support personnel are accurately identified. • Knowledge of sources of information regarding manufacturer’s specifications. • Knowledge of safety procedures. • Knowledge of student access issues regarding systems and equipment. • Knowledge of compatibility issues between new and existing equipment/systems. • Knowledge of existing technical support capabilities. • Knowledge of maintenance schedules and procedures and the use of tools required for maintenance of equipment and systems. • Knowledge of warranty and maintenance records requirements. • Ability to clean and secure tools. • Ability to diagnose and repair systems, equipment and tools. • Knowledge of roles and responsibilities of campus personnel and departments. • Understands the organization and system hierarchy and follows procedures and recognizes system strengths and limitations. • Monitors system performance, troubleshoots system malfunction/ failure and analyzes system operation. • Utilizes previous training and experience to predict outcomes; visually analyzes relationship between parts/whole and process/procedure and interprets charts and graphs. • Understands operation/ interaction; manipulates technology for desired results; analyzes technology output; examines task/technology relationship. • Follows specified maintenance, identifies and corrects malfunctions, troubleshoots failures, evaluates performance of technology. 17 A. Manage Learning Environments Continued Key Activity A3 Develop a growth and replacement plan for systems, equipment and/ or tools 18 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Student, program and industry needs are correctly identified, and present inventory is accurately assessed. • Funding sources and timelines are correctly identified. • Safety issues are carefully considered. • Technology changes and industry compatibility are accurately assessed. • Facilities, technological support and equipment maintenance schedules are accurately assessed. • Cost effective recommendations are included in the plan. • Plan includes implementation schedule, personnel training and responsibilities and assessment mechanism and process. • Ability to access • Records information information on funding accurately, creates sources and availability. original documents; • Knowledge of current summarizes and synindustry, student, thesizes information. program and safety • Maintains job specific requirements. supplies and equipment, orders and • Ability to access equipment maintenance maintains inventory and monitors safe and information and efficient utilization of technical support. • Knowledge of system or materials. program requirements • Predicts outcomes, anaand facility and system lyzes data, integrates capabilities. multiple items of data, contrasts conflicting • Knowledge of assessdata, and researches ment tools. • Ability to perform cost/ additional information benefit analysis. sources. • Understands the organization and system hierarchy and follows procedures and recognizes system strengths and limitations. • Understands technological requirements and results; analyzes task/technology relationship; proposes simple technological solutions. A. Manage Learning Environments Continued Key Activity A4 Lead students and supervise learning environments Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • All safety procedures are properly followed and requirements are completely met. • Students and all classroom personnel are thoroughly informed of safety procedures regarding all equipment. • Work ethics, mutual respect and leadership are modeled. • Order is observable in the classroom and instructions from instructor are followed promptly. • Rigor of the curriculum is maintained. • Students are engaged in a respectful manner. • Environmental distractions are minimized. • Learning is supported and facilitated by the appropriate use of instructional media and equipment. • Facilities needs and requests are submitted in a timely manner in accordance with college policies and procedures. • Adequate assignments and schedules are established for lab/shop activities. • Off-campus sites and activities are assessed for appropriate management and supervision of students. • Knowledge of safety requirements and procedures and all OSHA/ WISHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration/ Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act) and hazardous materials procedures. • Ability to model work ethic, leadership and mutual respect. • Knowledge of all applicable laws and regulations regarding the learning environment. • Knowledge of and ability to utilize instructional media and equipment. • Knowledge of facilities and equipment requisition procedures and timelines. • Ability to minimize environmental distractions. • Knowledge of appropriate management and supervision of students for off-campus sites and activities. • Ability to assess rigor of curriculum. • Analyzes and responds to customer needs; demonstrates commitment to customer, obtains additional resources to meet customer needs. • Leads by example, motivates others to extend their capabilities, Displays enthusiasm/positive attitudes and develops minority/majority views. • Understands operation/ interaction; manipulates technology for desired results; analyzes technology output; examines task/technology relationship. • Establishes rapport with co-workers and customers; modifies behavior to environment; shows understanding for other, works to identify/remove social barriers and encourages cooperation and negotiation. • Analyzes possible causes, generates and evaluates solutions and devises and implements plan of action. • Respects the rights of others, recognizes the value of diversity, encourages/supports individuality, supports correct course of action and responsibly challenges discriminatory practices and procedures. 19 A. Manage Learning Environments Continued Key Activity A5 Research, select, evaluate and maintain off-campus learning environments 20 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Off-campus learning sites are identified and properly recruited in accordance with the established course outcomes. • Off-campus sites are regularly visited to determine suitability for student learning. • Off-campus learning environments and their site supervisors meet established criteria. • Meetings are held with site supervisors to inform them of their roles and responsibilities and the roles and responsibilities of students and instructors. • Work-based learning environments are correctly evaluated in an ongoing manner in accordance with program specification. • Off-campus sites are researched and evaluated for distinctive needs. • Internships/externships are coordinated in an effective manner. • Knowledge of off-campus sites and site requirements of students. • Knowledge of criteria for selection of offcampus sites and site supervisors. • Ability to recruit off-campus sites which meet established criteria. • Knowledge of roles and responsibilities of site supervisors, instructors and students. • Knowledge of work-based learning environment evaluation procedures, and criteria. • Knowledge of internship/externship procedures. • Predicts outcomes, analyzes data, integrates multiple items of data, contrasts conflicting data, and researches additional information sources. • Interprets information, applies processes to new information, analyzes organization of information and transfers information between formats. • Interprets information, selects methods of communication and summarizes integrates and analyzes information. • Utilizes integrated/multiple software, locates and retrieves stored information, interprets data, integrates multiple platforms, utilizes networks and modifies information. • Analyzes situations and information, considers risks and implications, complies multiple viewpoints, and generates alternative solutions. • Follows specified maintenance, identifies and corrects malfunctions, troubleshoots failures, evaluates performance of technology. A. Manage Learning Environments Continued Key Activity A6 Evaluate and monitor the safety of the instructional areas and practices Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Students and staff are oriented to safety procedures per college policies and federal and state guidelines. • Safety rules and regulations are followed. • Incidents are appropriately reported and documented in a timely fashion. • Staff and students have current CPR (Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation) and First Aid credentials, as required. • Safety procedures are posted per Labor and Industry guidelines. • College safety departments/personnel are notified to ensure that safety supplies are readily accessible. • Safety hazards are reported immediately. • MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheets) are available as required in instructional areas. • OSHA/WISHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration/ Washington Industrial Safety and Health Act) requirements and hazardous materials procedures are completely followed. • The learning environment is maintained in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. • Knowledge of safety requirements and procedures and all OSHA/ WISHA* and hazardous materials procedures. • Ability to read, interpret, and apply MSDS data. • Knowledge of emergency telephone numbers and procedures. • Knowledge of college and state safety policies and procedures. • Ability to operate safety equipment within instructional program. • Pays attention to details, demonstrates enthusiasm & initiative, monitors performance standards and follows up on assigned tasks. • Analyzes implications of decisions, recommends ethical course of action and responsibly challenges unethical practices and decisions. • Monitors system performance, troubleshoots system malfunction/ failure and analyzes system operation. • Maintains job specific supplies and equipment, orders and maintains inventory and monitors safe and efficient utilization of materials. • Interprets information, selects methods of communication and summarizes, integrates and analyzes information. 21 A. Manage Learning Environments Continued Key Activity A7 Identify, evaluate, and implement new instructional strategies and technologies 22 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • New instructional strategies and technologies are researched by fully participating in professional conferences and consulting with advisory committees. • Industry and technology suppliers are properly consulted to stay current on new instructional strategies and technologies. • Social and information networks and professional organizations are actively pursued and effectively utilized to learn about emerging strategies and technologies for the learning environment. • New methodologies related to instructional strategies and technologies are properly evaluated. • New technologies are implemented in accordance with college policies and procedures. • Knowledge of sources of information regarding professional conferences. • Ability to access industry suppliers and knowledge of how to network with them. • Knowledge of social and information networks and professional organizations. • Ability to evaluate new methodologies related to instructional strategies and technologies. • Ability to implement new instructional strategies and technologies. • Knowledge of college policies and procedures • Understands strategies and technological requirements and results; analyzes task/ technology relationship; proposes simple technological solutions. • Understands operation/ interaction; manipulates technology for desired results; analyzes technology output; examines task/technology relationship. • Interprets information, applies processes to new information, analyzes organization of information and transfers information between formats. • Utilizes integrated/multiple software, locates and retrieves stored information, interprets data, integrates multiple platforms, utilizes networks and modifies information. • Demonstrates creative thinking process while problem solving; develops creative solutions and applies them to new situations; generates unique solutions. B. Develop Outcomes, Assessments, and Curricula Key Activity B1 Identify, evaluate, and modify outcomes Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Outcomes are properly documented in accordance with college, regulatory and accrediting body policies and procedures. • Industry standards are thoroughly researched in order to identify outcomes and competencies. • Outcomes are reviewed by the advisory committee. • Outcomes and competencies are continuously evaluated and modified as necessary based on advisory committee recommendations and/ or changing industry standards, regulatory and accrediting bodies. • Outcomes are written for learner comprehension. • All necessary skills are included in the outcomes. • Knowledge of the purpose and components of outcomes and the ability to develop clear and measurable outcomes. • Knowledge of documentation procedures to record outcomes. • Ability to access regulatory and accrediting bodies and industry and college sources of information regarding outcomes, competencies, and standards. • Knowledge of advisory committee protocols. • Knowledge of technical and non-technical skills required for success in the workplace and the ability to translate those into outcomes. • Understanding of the requirements of diverse learners. • Knowledge of outcomes definitions, competencies and requirements. • Knowledge of the implications of outcomes on assessment of learning. • Records information accurately, creates original documents; summarizes and synthesizes information. • Follows set of instructions, qualifies and analyzes information, interprets and summarizes information and researches to gain information. • Demonstrates creative thinking process while problem solving; develops creative solutions and applies them to new situations; generates unique solutions. • Interprets information, applies processes to new information, analyzes organization of information and transfers information between formats. 23 B. Develop Outcomes, Assessments, and Curricula Continued Key Activity B2 Create, evaluate, and modify curriculum 24 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Curriculum sequence supports student success at achieving outcomes and competencies. • Appropriate learning activities are selected for the curriculum. • Curriculum properly aligns with accrediting bodies, college mission, and program goals and is driven by workforce needs. • Curriculum includes a curriculum map and the following for all courses: course descriptions, learning outcomes, competencies, course content, objectives, learning assessments, ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) accommodations, course requirements, grading requirements, and prerequisites if necessary. • Curriculum is regularly reviewed by advisory committee and/or accrediting bodies as required and meets all legal requirements. • Flexibility is built into the curriculum to address multiple learning styles and individual student needs. • Curriculum is tailored to individual needs when appropriate. • Opportunities for team teaching with other disciplines are actively explored. • Knowledge of curriculum map and ability to develop course descriptions, learning outcomes, course content, content objectives, learning assessments and the ability to apply them to curriculum. • Knowledge of curriculum sequencing and prerequisites. • Ability to write competencies and performance objectives. • Knowledge of a variety of teaching and learning strategies appropriate to diverse learners. • Ability to access employers and advisory committee to determine workforce needs. • Knowledge of requirements for ADA accommodation. • Knowledge of curriculum review requirements and procedures and legal issues regarding curriculum. • Ability to team-teach among / across disciplines. • Ability to adapt curricula to various delivery modalities. • Method of delivery is taken into consideration when developing or modifying curriculum. • Pays attention to details, demonstrates enthusiasm & initiative, monitors performance standards and follow up on assigned tasks. • Records information accurately, creates original documents; summarizes and synthesizes information. • Understands continuous improvement process, suggests system modifications/ improvements and analyzes goals/ constraints. • Interprets and applies new knowledge and experience, analyzes application of learning tools, investigates new learning techniques, manipulates learning tools and formulates/ adapts learning strategies. • Analyzes situations and information, considers risks and implications, complies multiple viewpoints, and generates alternative solutions. B. Develop Outcomes, Assessments, and Curricula Continued Key Activity B3 Create, evaluate, and modify assessments Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Outcomes are assessed by a variety of measurements. • Assessments include a variety of activities including performancebased or theory-based assessments. • Assessment criteria are established in accordance with industry standards and accrediting bodies. • Assessments accurately measure student performance of specified outcomes / competencies. • Assessments are evaluated and modified based on changes in the industry, advisory committee input, objective analysis of assessment data/results. • Assessment tools and criteria provide relevant feedback for learner self-assessment and improvement. • Knowledge of assess• Conducts task-specific ment construction. training, coaches others to apply related • Knowledge of theory-based and concepts, provides conperformance-based structive feedback and assessments. develops appropriate • Knowledge of assesstraining procedures. ment measurements. • Interprets and applies • Knowledge of industry new knowledge and and accrediting body experience, analyzes standards. application of learning • Ability to modify tools, investigates new assessments based on learning techniques, objective analysis of manipulates learning assessment data/results. tools and formulates/ • Knowledge of feedback adapts learning strategies appropriate strategies. to diverse learners. • Monitors system perfor• Knowledge of formal, mance, troubleshoots informal, formative system malfunction/ failure and analyzes and summative system operation. assessments. • Records information accurately, creates original documents; summarizes and synthesizes information. • Predicts outcomes, analyzes data, integrates multiple items of data, contrasts conflicting data, and researches additional information sources. 25 B. Develop Outcomes, Assessments, and Curricula Continued Key Activity B4 Implement curriculum and assessments 26 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Outcomes assessments are performed to evaluate student performance according to appropriate criteria. • Student performance is evaluated in relation to published student outcomes and/or competencies. • Industry standards are integrated within the curriculum where appropriate. • Implementation and assessment occur in an ongoing manner to keep current with technology and trends. • Post-completion student and industry assessments are conducted and used to improve curricula and instructional practice. • Assessment tools and criteria are used to obtain relevant feedback for program improvement. • Knowledge of campus resources for student course evaluation, postcompletion follow-up and faculty evaluation surveys. • Knowledge of local employer contacts. • Knowledge of and ability to implement curriculum improvements. • Knowledge of current technology and trends. • Knowledge of published student outcomes and competencies. • Knowledge of industry standards. • Ability to use assessment data to implement improvements in curriculum. • Pays attention to details, demonstrates enthusiasm & initiative, monitors performance standards and follow up on assigned tasks. • Interprets and applies new knowledge and experience, analyzes application of learning tools, investigates new learning techniques, manipulates learning tools and formulates/ adapts learning strategies. • Conducts task-specific training, coaches others to apply related concepts, provides constructive feedback and develops appropriate training procedures. • Uses logic to draw conclusions, analyzes rules and principles and examines information for relevance and accuracy. • Utilizes integrated/multiple software, locates and retrieves stored information, interprets data, integrates multiple platforms, utilizes networks and modifies information. B. Develop Outcomes, Assessments, and Curricula Continued Key Activity B5 Integrate curriculum with other faculty in the department and in other instructional areas/ institutions Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Knowledge of course content and outcomes is shared across departments, disciplines and institutions. • Competencies are consistent in multisectioned courses and overlapping course content areas. • Cross-discipline team teaching is implemented as possible. • Instructional resources are shared across departmental and institutional areas. • Cross-discipline courses are integrated when pertinent. • Tech Prep policies are followed as applicable. • Knowledge of program and degree requirements of other programs. • Ability to access program and degree requirements of other programs and institutions. • Knowledge of and ability to access instructional resources across departments and institutions. • Knowledge of intradepartmental and interinstitution resources. • Ability to integrate cross-discipline courses. • Knowledge of standardization of competencies for multi-section courses. • Knowledge of Tech Prep policies and procedures. • Establishes rapport with co-workers and customers; modifies behavior to environment; shows understanding for other, works to identify/remove social barriers and encourages cooperation and negotiation. • Actively participates in discussion; presents complex ideas and information, analyzes group and individual response and poses critical questions. • Works to improve team skills, encourages team members, and assumes responsibility for accomplishing team goals. • Understands negotiations process; Moderates discussion, interprets complaints and concerns, analyzes group dynamics and detects underlying issues. • Understands the organization and system hierarchy and follows procedures and recognizes system strengths and limitations. 27 C. Develop and Review Programs Key Activity C1 Develop, review, and update program/ course plan 28 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Course sequence supports student success at achieving outcomes. • Program aligns with accrediting bodies and college and, where applicable, division mission. • Program meets all legal requirements. • Program meets workforce needs. • Program plan includes learning outcomes, competencies, and program assessment tools in both core and industry-specific courses. • Proper prerequisites are established if necessary. • Program is regularly reviewed by advisory committee and/or accrediting bodies as required. • Advising and accrediting bodies are notified of proposed changes and appropriate approvals are obtained. • Flexibility is built in to the program to address multiple learning styles and individual student needs. • Programs are evaluated for viability. • Knowledge of learning process. • Knowledge of regulatory and accreditation requirements and college and, where applicable, division mission. • Ability to access sources of information regarding workforce needs and the ability to apply workforce needs to program plan. • Knowledge of definition and requirements of learning outcomes, competencies, program assessment tools, core support and prerequisite courses. • Knowledge of advisory committee and/or accrediting bodies review and approval procedures and legal requirements regarding program plan. • Knowledge of alternate instructional strategies to accommodate multiple learning styles. • Knowledge of criteria for evaluating program viability. • Interprets information, applies processes to new information, analyzes organization of information and transfers information between formats. • Monitors system performance, troubleshoots system malfunction/ failure and analyzes system operation. • Analyzes and responds to customer needs; demonstrates commitment to customer, obtains additional resources to meet customer needs. • Analyzes situations and information, considers risks and implications, complies multiple viewpoints, and generates alternative solutions. • Follows set of instructions, qualifies and analyzes information, interprets and summarizes information and researches to gain information. C. Develop and Review Programs Continued Key Activity C2 Recruit and work with advisory committee and employers to meet changing needs of the program and industry Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • New advisory committee members are regularly recruited. • Advisory committee membership accurately has diverse representation and meets SBCTC (State Board for Community and Technical Colleges) requirements. • Committee member participation is actively encouraged and acknowledged. • Advisory committee meetings are held on a regular basis. • Instructors attend advisory committee meetings on a regular basis. • Advisory committee recommendations are solicited and are recorded in the minutes. • Employers are contacted on a regular basis to determine current changes in the industry. • Meeting minutes are filed and maintained in accordance with college policies and procedures. • Knowledge of advisory committee member recruitment procedures and SBCTC requirements. • Knowledge of college policy and procedures related to recording of advisory committee recommendations. • Knowledge of the employer base and the ability to access it. • Knowledge of industry and demographic diversity. • Responds to nonverbal communication; Interprets, clarifies and influences communication and compares multiple viewpoints. • Works to improve team skills, encourages team members, and assumes responsibility for accomplishing team goals. • Recognizes job tasks, analyzes work assignments and delegates responsibilities. • Understands negotiations process; Moderates discussion, interprets complaints and concerns, analyzes group dynamics and detects underlying issues. • Leads by example, motivates others to extend their capabilities, Displays enthusiasm/positive attitudes and develops minority/majority views. 29 C. Develop and Review Programs Key Activity C3 Identify, evaluate, and modify program outcomes and assessments 30 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Program outcomes are assessed by a variety of measurements. • Program assessment criteria are established per industry standards and accrediting bodies and accurately measure performance of specified outcomes. • Program assessments are correctly evaluated and modified based on changes industry, advisory committee input, and community/ student needs. • Program outcomes are properly documented in accordance with college and accrediting body policy. • Industry standards are thoroughly researched and program outcomes are reviewed by the advisory committee. • Outcomes are continuously evaluated and modified based on advisory committee recommendations, community needs, government and/or transfer requirements and changing industry standards. • All necessary technical and non-technical skills are included in the outcomes. • Knowledge of outcomes and assessment activities and criteria and relevant industry and accrediting body standards. • Knowledge of advisory committee protocols. • Knowledge of technical and non-technical skills and the ability to integrate them into outcomes/ competencies. • Ability to write assessments that accurately measure program outcomes/ competencies and to evaluate and modify program assessments. • Ability to write program outcomes/ competencies. • Knowledge of documentation procedures for program outcomes/ competencies. • Monitors system performance, troubleshoots system malfunction/ failure and analyzes system operation. • Records information accurately, creates original documents; summarizes and synthesizes information. • Interprets information, selects methods of communication and summarizes integrates and analyzes information. • Analyzes implications of decisions, recommends ethical course of action and responsibly challenges unethical practices and decisions. • Demonstrates creative thinking process while problem solving; develops creative solutions and applies them to new situations; generates unique solutions. C. Develop and Review Programs Continued Key Activity C4 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Core and support courses are reviewed Identify and by advisory comdevelop core and mittee and industry support courses and approved when appropriate. • Articulation models in the state, advisory committees, the private/ government sectors, and accreditation and/ or legal requirements are used to identify core and support courses. • Core courses and related instruction meet the requirements of the SBCTC (State Board for Community and Technical Colleges). • Core and support courses meet degree and certificate requirements. • All required approvals are obtained in a timely manner. • Knowledge of advisory committee protocols. • Knowledge of articulation models and the ability to access sources of information regarding articulation. • Knowledge of SBCTC and degree and certificate requirements. • Knowledge of state and college approval procedures and timelines. • Ability to identify and access a variety of information resources related to course development. • Pays attention to details, demonstrates enthusiasm & initiative, monitors performance standards and follow up on assigned tasks. • Understands continuous improvement process, suggests system modifications/ improvements and analyzes goals/ constraints. • Uses logic to draw conclusions, analyzes rules and principles and examines information for relevance and accuracy. • Utilizes previous training and experience to predict outcomes; visually analyzes relationship between parts/whole and process/procedure and interprets charts and graphs. • Utilizes integrated/multiple software, locates and retrieves stored information, interprets data, integrates multiple platforms, utilizes networks and modifies information. 31 C. Develop and Review Programs Key Activity C5 Maintain (or obtain) program accreditation 32 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Accrediting bodies are notified of all proposed changes as required and appropriate approvals are obtained. • Self-study is completed as required. • Program performance data is accurately and properly collected, analyzed, and documented in accordance with the accreditation standards. • Programs are modified to meet standards and recommendations of the accrediting bodies. • Site reviews are conducted in accordance with the requirements of the accrediting bodies. • Program reviews support institutional accreditation. • Accrediting body credentialing requirements are met. • Knowledge of approval procedures and the ability to contact and notify accrediting bodies of proposed changes and requests for accreditation. • Knowledge of the components of a self-study. • Ability to complete a self-study. • Knowledge of performance data collection, analysis and documentation procedures. • Ability to modify programs to meet standards. • Ability to constructively participate in site reviews. • Knowledge of requirements for institutional accreditation. • Knowledge of and ability to obtain accrediting body credentials. • Pays attention to details, demonstrates enthusiasm & initiative, monitors performance standards and follow up on assigned tasks. • Records information accurately, creates original documents; summarizes and synthesizes information. • Interprets information, applies processes to new information, analyzes organization of information and transfers information between formats. • Analyzes implications of decisions, recommends ethical course of action and responsibly challenges unethical practices and decisions. • Effectively manages time; prepares and organizes multiple schedules and manages timelines. C. Develop and Review Programs Continued Key Activity C6 Research, identify, and evaluate trends and implement current industry standards Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Advisory committees are regularly consulted on industry standards. • Industry trends and changes are identified, evaluated and incorporated with advisory committee approval. • Employers/Industries are consulted and/ or surveyed on an ongoing basis. • Retraining and backto-industry experiences are included in the professional development plan. • Research through trade and professional sources of information, industry visits and networking is conducted on a regular basis including attending professional meetings. • Licensing and standard-setting bodies are consulted on an ongoing basis. • Knowledge of advisory committee protocols. • Knowledge of current practices and issues in industry. • Ability to demonstrate the applicable and relevant skills required to implement current industry standards. • Knowledge of research theory and design. • Knowledge of applicable laws and industry standards. • Knowledge of appropriate trade and professional sources of information. • Ability to locate sites and funding for Back-to-Industry opportunities. • Understands continuous improvement process, suggests system modifications/ improvements and analyzes goals/ constraints. • Predicts outcomes, analyzes data, integrates multiple items of data, contrasts conflicting data, and researches additional information sources. • Analyzes situations and information, considers risks and implications, complies multiple viewpoints, and generates alternative solutions. • Uses logic to draw conclusions, analyzes rules and principles and examines information for relevance and accuracy. • Actively participates in discussion; presents complex ideas and information, analyzes group and individual response and poses critical questions. 33 C. Develop and Review Programs Continued Key Activity C7 Coordinate program development with other college programs and institutions 34 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • All Instructional policies and guidelines are thoroughly researched and followed. • Articulation and/or transfer agreements are established. • Graduation data from transfer institutions is procured. • Knowledge of related course content and outcomes in similar institutions is shared. • Competencies are consistent in multisectioned courses and overlapping course content areas. • Cross-discipline team teaching is implemented when possible. • Instructional resources are shared across departmental and institutional areas. • Cross-discipline courses are integrated when pertinent. • Similar outcomes are developed with other institutions. • Similar programs at other colleges are visited regularly. • Knowledge of articulation and/or transfer agreements. • Knowledge of program and degree requirements and outcomes of other programs and institutions. • Ability to access program and degree requirements of other programs and institutions. • Knowledge of and ability to access instructional resources across departments and institutions. • Knowledge of industrial outcomes / competencies. • Knowledge of college policies regarding team teaching. • Establishes rapport with co-workers and customers; modifies behavior to environment; shows understanding for other, works to identify/remove social barriers and encourages cooperation and negotiation. • Understands the organization and system hierarchy and follows procedures and recognizes system strengths and limitations. • Works to improve team skills, encourages team members, and assumes responsibility for accomplishing team goals. • Understands negotiations process; Moderates discussion, interprets complaints and concerns, analyzes group dynamics and detects underlying issues. • Responds to nonverbal communication; Interprets, clarifies and influences communication and compares multiple viewpoints. D. Provide Student Instruction Key Activity D1 Prepare and/or gather current instructional materials Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Instructional materials are clearly identified, support curriculum outcomes, and are completely reviewed on a regular basis. • Instructional materials are selected and approved in accordance with college policies and procedures. • All appropriate options are thoroughly researched to ensure quality and currency of instructional materials. • Instructional materials appeal to multiple learning styles and diverse learners. • Instructional materials comply with state/ federal requirements or guidelines as necessary. • Instructional materials are customized to meet student needs and program outcomes. • Other campus resources are consulted to ensure availability of instructional materials. • Method of delivery is taken into consideration when preparing and selecting materials. • Knowledge of instructional materials includes, but is not limited to: textbooks, reference materials, audiovisuals, websites, handouts, software and simulations. • Knowledge of curriculum outcomes. • Knowledge of sources of information regarding instructional materials and the ability to access them. • Knowledge of learning styles and diverse teaching methodologies and the ability to implement them. • Knowledge of state/ federal requirements or guidelines regarding instructional materials. • Ability to customize instructional materials to meet student needs and program outcomes. • Knowledge of campus resources. • Ability to adapt materials to method of delivery. • Understands technological requirements and results; analyzes task/technology relationship; proposes simple technological solutions. • Interprets and applies new knowledge and experience, analyzes application of learning tools, investigates new learning techniques, manipulates learning tools and formulates/ adapts learning strategies, • Conducts task-specific training, coaches others to apply related concepts, provides constructive feedback and develops appropriate training procedures. • Follows set of instructions, qualifies and analyzes information, interprets and summarizes information and researches to gain information. • Utilizes previous training and experience to predict outcomes; visually analyzes relationship between parts/whole and process/procedure and interprets charts and graphs. 35 D. Provide Student Instruction Continued Key Activity D2 Provide individual and group instruction 36 • Learning and curriculum are directed towards program and student outcomes/ competencies. • Students are encouraged to mentor other students when appropriate. Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Students and all classroom personnel are thoroughly informed of safety and operating procedures in the learning environment. • Group and individual instruction accurately and effectively model and teach industry standards and workplace requirements. • Students are effectively oriented to the learning task, including method of delivery, outcomes, assessments, syllabus and relevance of prior and related skills and abilities. • Student instruction is effective and appropriate for the method of delivery, and accommodates diverse learning styles. • Learning is facilitated with clear and effective presentations, demonstrations and active learner involvement. • Regular opportunities are provided for students to practice, perform, and receive feedback on all required skills, knowledge, competencies, and abilities. • Instruction promotes the application, transfer and retention of learning in accordance with adult learning theory. • Student behavior standards (code of conduct, students’ rights and responsibilities) are consistently and constructively reinforced. • Student learning styles, questions and discussions are effectively acknowledged, guided and integrated into the learning process in a positive way. • Knowledge of safety and operating procedures as related to individual circumstances. • Knowledge of group and individual instruction models, adult learning principles and the ability to adapt strategies to diverse learners. • Knowledge of industry standards, workplace requirements and competencies, and the ability to adapt them to instruction. • Knowledge of learning tasks, outcomes, methods of delivery, assessments and relevance of prior and related skills and abilities. • Ability to adapt student instruction to method of delivery. • Ability to develop opportunities for students to practice, perform and receive feedback on skills. • Ability to include the retention, application and transfer of learning in instruction. • Knowledge of student behavior standards and the ability to constructively reinforce them. • Ability to integrate questions from students into the learning process. • Knowledge of the subject matter and the ability to demonstrate competency in the field. • Ability to prepare a syllabus. • Ability to model mentoring. • Actively participates in discussion; presents complex ideas and information, analyzes group and individual response and poses critical questions. • Responds to nonverbal communication; Interprets, clarifies and influences communication and compares multiple viewpoints. • Establishes rapport with co-workers and customers; modifies behavior to environment; shows understanding for other, works to identify/remove social barriers and encourages cooperation and negotiation. • Interprets and applies new knowledge and experience, analyzes application of learning tools, investigates new learning techniques, manipulates learning tools and formulates/adapts learning strategies. • Conducts task-specific training, coaches others to apply related concepts, provides constructive feedback and develops appropriate training procedures. • Leads by example, motivates others to extend their capabilities, Displays enthusiasm/positive attitudes and develops minority/majority views. • Respects the rights of others, recognizes the value of diversity, encourages/supports individuality, supports correct course of action and responsibly challenges discriminatory practices and procedures. D. Provide Student Instruction Continued Key Activity D3 Initiate, develop, and implement student assessments Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Instructors are regularly available to communicate student progress as needed. • Self-assessment and peer assessment methods are taught and encouraged in an effective manner. • Assessment feedback is provided in a timely manner, is guided by assessment criteria, and is clearly supportive of student learning and success. • Assessment criteria are accurately provided to the students prior to the assessment and grading policies are provided to the students in writing in accordance to college policy. • Confidentiality and ethical guidelines are completely followed including FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act, 1974). • Assessment of student learning is formal and informal as well as formative and summative. • Assessment tools that are directly related to industry requirements are developed and implemented. • Assessment criteria are tangible, measurable and observable. • Student grades are accurately calculated according to published grading policy and assessment criteria. • Knowledge of self- and peer assessment as methods of evaluation. • Knowledge of methods of constructive feedback to students. • Knowledge of assessment tools and techniques, grading policies, methodologies, and criteria and the ability to apply them. • Knowledge of confidentiality and ethical guidelines. • Knowledge of formal, informal, formative and summative assessment. • Knowledge of grading policies and assessment criteria. • Knowledge of college policies and procedures. • Knowledge of FERPA. • Knowledge of industry requirements • Grades are submitted in accordance with college policies and procedures and state and federal laws and regulations. • Interprets and converts numerical data and predicts arithmetic results. • Understands continuous improvement process, suggests system modifications/ improvements and analyzes goals/ constraints. • Conducts task-specific training, coaches others to apply related concepts, provides constructive feedback and develops appropriate training procedures. • Analyzes implications of decisions, recommends ethical course of action and responsibly challenges unethical practices and decisions. • Uses logic to draw conclusions, analyzes rules and principles and examines information for relevance and accuracy. 37 D. Provide Student Instruction Continued Key Activity D4 Modify instructional material and methods based on student and industry assessments and feedback 38 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Student feedback is appropriately solicited, acknowledged, documented, analyzed and applied to the improvement of instruction. • Instruction is adapted to meet the needs of diverse learners, and student motivational needs. • A variety of instructional strategies is applied. • Diverse resources are consulted to identify and access alternative instructional methods, materials, and methods of delivery. • Instructional material and methods are evaluated and modified based on changes in the industry, advisory committee input and objective analysis of assessment data/results. • Knowledge of and • Respects the rights ability to solicit, of others, recognizes document and analyze the value of diversity, appropriate student encourages/supports feedback. individuality, supports • Ability to apply moticorrect course of vational techniques for action and responsibly challenges discriminadiverse learning styles. • Knowledge of a tory practices and variety of instructional procedures. strategies. • Responds to nonverbal • Knowledge of diverse communication; resources for alternative Interprets, clarifies and instructional methods influences communication and compares and materials. multiple viewpoints. • Ability to modify instructional materials • Understands conand methods based on tinuous improvement changes in the industry, process, suggests advisory committee system modifications/ input and objective improvements and analysis of assessment analyzes goals/ data/results. constraints. • Analyzes possible causes, generates and evaluates solutions and devises and implements plan of action. • Conducts task-specific training, coaches others to apply related concepts, provides constructive feedback and develops appropriate training procedures. D. Provide Student Instruction Continued Key Activity D5 Promote professionalism in the learning environment Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Professional teaching standards are identified and implemented. • Learning is cooperatively accomplished between the teacher and the student. • A positive role model is provided for the students. • Ethical and professional standards are understood and demonstrated. • Professional boundaries with students are established, modeled, and maintained. • Classroom and other instructional areas are appropriately safe and orderly. • Knowledge of and ability to implement professional teaching standards. • Knowledge of state and college policies and procedures of professional boundaries. • Knowledge of contentspecific and collegespecific code of ethics. • Ability to model ethics and professionalism. • Knowledge of safety policies, procedures and protocols. • Analyzes implications of decisions, recommends ethical course of action and responsibly challenges unethical practices and decisions. • Establishes rapport with co-workers and customers; modifies behavior to environment; shows understanding for other, works to identify/remove social barriers and encourages cooperation and negotiation. • Conducts task-specific training, coaches others to apply related concepts, provides constructive feedback and develops appropriate training procedures. • Leads by example, motivates others to extend their capabilities, Displays enthusiasm/positive attitudes and develops minority/majority views. • Respects the rights of others, recognizes the value of diversity, encourages/supports individuality, supports correct course of action and responsibly challenges discriminatory practices and procedures. 39 E. Provide Support and Guidance to Students Key Activity E1 Provide students with access to instructor 40 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Student requests for assistance are responded to in a courteous, respectful, and timely manner. • Multiple modes of communication are used. • Instructor time is properly allocated for the purpose of receiving and responding to group and individual student requests for assistance. • Instructors are regularly accessible, within professional boundaries, to students in accordance with college policies and procedures. • Instructor contact and access information is provided in writing to students in a clear manner. • Knowledge of and ability to use voicemail, email and online technologies. • Knowledge of the required and contracted office hours. • Knowledge of professional boundaries and college policies and procedures regarding student contact. • Actively participates in discussion; presents complex ideas and information, analyzes group and individual response and poses critical questions. • Analyzes and responds to customer needs; demonstrates commitment to customer, obtains additional resources to meet customer needs. • Effectively manages time; prepares and organizes multiple schedules and manages timelines. • Establishes rapport with co-workers and customers; modifies behavior to environment; shows understanding for other, works to identify/remove social barriers and encourages cooperation and negotiation. • Responds to nonverbal communication; Interprets, clarifies and influences communication and compares multiple viewpoints. E. Provide Support and Guidance to Students Continued Key Activity E2 Provide information or referrals to meet student needs Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Current files or resources of available student services and referral procedures are maintained and readily available to students. • Referrals are conducted in a respectful manner and in compliance with ethical guidelines. • Applicable procedures and guidelines for documentation and follow-up of referrals are followed. • Reasonable accommodations are provided with respect to recommendations from a service referral (e.g. disability support services or access services). • FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act, 1974) laws are followed. • Ongoing communication with student services professionals is maintained. • Knowledge of available student services, student clubs and proper procedures. • Knowledge of confidentiality / ethics (FERPA). • Knowledge of documentation procedures and the ability to follow-up on the referral. • Ability to implement reasonable accommodations in the learning environment. • Knowledge of disability support services and ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act). • Knowledge of organizations, opportunities and procedures for obtaining support for student activities and competitions. • Understands the organization and system hierarchy and follows procedures and recognizes system strengths and limitations. • Responds to nonverbal communication; Interprets, clarifies and influences communication and compares multiple viewpoints. • Analyzes and responds to customer needs; demonstrates commitment to customer, obtains additional resources to meet customer needs. • Respects the rights of others, recognizes the value of diversity, encourages/supports individuality, supports correct course of action and responsibly challenges discriminatory practices and procedures. • Interprets information, applies processes to new information, analyzes organization of information and transfers information between formats. 41 E. Provide Support and Guidance to Students Key Activity E3 Provide students with career advising and assist with job placement 42 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Students are made aware of the job search process and how to access career and employment information from multiple sources. • Advisory members and employers are consulted concerning employment opportunities and career options. • Students are accurately informed of known job opportunities and the jobs for which they currently qualify. • References and recommendations are provided on behalf of students when requested and applicable and in accordance with FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act, 1974) guidelines. • Current career information and opportunities are maintained in an organized manner. • Knowledge of the job search process for that field. • Knowledge of the advisory members and employers and the ability to contact them. • Knowledge of sources of job opportunities and job qualifications. • Ability to provide appropriate content for references and recommenda¬tions. • Knowledge of college policies regarding references and recommendations and knowledge of FERPA. • Knowledge of current career information opportunities and the ability to access that information. • Ability to instruct students in job search methodology or refer appropriately. • Knowledge of the qualifica¬tions for specific positions within the field. • Analyzes and responds to customer needs; demonstrates commitment to customer, obtains additional resources to meet customer needs. • Establishes rapport with co-workers and customers; modifies behavior to environment; shows understanding for other, works to identify/remove social barriers and encourages cooperation and negotiation. • Analyzes possible causes, generates and evaluates solutions and devises and implements plan of action. • Recognizes job tasks, analyzes work assignments and delegates responsibilities. • Leads by example, motivates others to extend their capabilities, Displays enthusiasm/positive attitudes and develops minority/majority views. E. Provide Support and Guidance to Students Continued Key Activity E4 Provide academic advising Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Student goals, experiences, and needs are accurately identified. • Student is informed of academic and transfer options to meet goals based on individual education plan. • Information about college resources to support student success is provided in an effective manner. • An accurate checklist of current college registration procedures is provided. • Waitlists are kept up to date and accurate information is provided to prospective students in a timely manner. • Program application process is communicated in a timely and effective manner. • Knowledge of academic • Responds to nonverbal and transfer options. communication; Interprets, clarifies and • Knowledge of the educational planning influences communicatool and/or process. tion and compares • Knowledge of college multiple viewpoints. resources. • Analyzes possible • Knowledge of college causes, generates and registration and waitlist evaluates solutions and procedures. devises and implements • Ability to convert plan of action. student goals, experi• Utilizes integrated/mulences, and needs into tiple software, locates appropriate program and retrieves stored and course selection. information, interprets data, integrates mul• Knowledge of course sequencing. tiple platforms, utilizes • Knowledge of program networks and modifies application process. information. • Interprets information, selects methods of communication and summarizes integrates and analyzes information. • Analyzes and responds to customer needs; demonstrates commitment to customer, obtains additional resources to meet customer needs. • Demonstrates creative thinking process while problem solving; develops creative solutions and applies them to new situations; generates unique solutions. 43 E. Provide Support and Guidance to Students Continued Key Activity E5 Serve as student activity advisor, as applicable 44 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Students are adequately advised of available activities and resources. • Information, guidance, resources and mentoring are provided. • Student club goals and objectives are identified, stated, and implemented. • Assistance in facilitating meetings and activities is provided. • Established state and college policies and procedures are followed. • Student leaders are effectively guided in conducting the business of the organization and/or activity. • Knowledge of Robert’s Rules of Order and/ or Parliamentary Procedures and the ability to apply them in a learning environment. • Knowledge of student activity advisor responsibilities and limitations per college policies and procedures. • Ability to work within the existing advisory system to accomplish stated goals. • Knowledge of constitutional by-laws of the particular activity or organization. • Ability to develop student leaders. • Knowledge of organizations, opportunities and procedures for obtaining support for student activities and competitions. • Responds to nonverbal communication; Interprets, clarifies and influences communication and compares multiple viewpoints. • Actively participates in discussion; presents complex ideas and information, analyzes group and individual response and poses critical questions. • Analyzes and responds to customer needs; demonstrates commitment to customer, obtains additional resources to meet customer needs. • Leads by example, motivates others to extend their capabilities, Displays enthusiasm/positive attitudes and develops minority/majority views. • Respects the rights of others, recognizes the value of diversity, encourages/supports individuality, supports correct course of action and responsibly challenges discriminatory practices and procedures F. Perform Administrative and Program Management Functions Key Activity F1 Perform documentation and record keeping duties Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Attendance records are documented and submitted as required. • Accurate committee files are kept as required. • Current curriculum materials are organized and accessible. • College records are kept in accordance with departmental and institutional policies and procedures. • Budget records are maintained in accordance with college policies and procedures. • Assistance is provided with writing and implementing grants as applicable. • Records pertaining to student performance and credentialing are maintained in accordance with all applicable laws, regulations and college policies. • Program-specific contracts, agreements and student records are documented and kept up to date as required for off-campus learning environments. • Knowledge of record keeping procedures. • Knowledge of college policies and procedures regarding record-keeping. • Knowledge of grant writing. • Knowledge of programspecific contract requirements and the ability to meet contractual agreements. • Knowledge of laws, regulations and policies relating to record keeping of student performance. • Knowledge of college curriculum resources and review process. • Pays attention to details, demonstrates enthusiasm & initiative, monitors performance standards and follow up on assigned tasks. • Records information accurately, creates original documents; summarizes and synthesizes information. • Utilizes integrated/multiple software, locates and retrieves stored information, interprets data, integrates multiple platforms, utilizes networks and modifies information. • Interprets information, applies processes to new information, analyzes organization of information and transfers information between formats. • Effectively manages time; prepares and organizes multiple schedules and manages timelines. 45 F. Perform Administrative and Program Management Functions Continued Key Activity F2 Lead and manage instructional and program assistants 46 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • A list of current job responsibilities is accurately provided and clarified. • An effective process is in place to clarify ongoing task assignments. • Orientation to policies, procedures, and the physical work environment is provided in an effective manner as needed. • Information about ongoing professional development opportunities is accurately provided and supported. • Job performance is properly assessed according to college policies and procedures. • Information about safety practices is adequately relayed • Information and updates are communicated in a timely and effective manner. • Assistant demonstrates appropriate workplace behavior and safety practices and performs at an effective level. • Knowledge of management techniques and current job responsibilities. • Knowledge of updated information of college policies and procedures. • Ability to orient new assistants. • Knowledge of professional development opportunities. • Ability to conduct perfor¬mance appraisals for instructional and program assistants. • Knowledge of safety practices in the learning environment. • Recognizes job tasks, analyzes work assignments and delegates responsibilities. • Works to improve team skills, encourages team members, and assumes responsibility for accomplishing team goals. • Leads by example, motivates others to extend their capabilities, Displays enthusiasm/positive attitudes and develops minority/majority views. • Conducts task-specific training, coaches others to apply related concepts, provides constructive feedback and develops appropriate training procedures. • Pays attention to details, demonstrates enthusiasm & initiative, monitors performance standards and follow up on assigned tasks. F. Perform Administrative and Program Management Functions Continued Key Activity F3 Mentor, orient, and support new and part-time faculty Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Curriculum and course materials and resources are accurately provided as required/ appropriate. • When applicable, orientation and paperwork needs are met. • All applicable laws, regulations, college policies are communicated and followed. • When applicable, performance of parttime faculty is properly assessed, feedback provided and recommendations made as appropriate. • When applicable, appropriate staffing needs are accurately identified, assessed and prioritized. • Part-time faculty questions are answered and assistance is provided as necessary in an expedient, courteous and respectful manner. • Clear and appropriate channels of communication between mentor and mentee are established and maintained. • Professional development opportunities are communicated in an effective manner. • Knowledge of curriculum, course materials, and resources. • Knowledge of employment regulations, laws and college policies. • Knowledge of student assessment and feedback techniques. • Knowledge of staffing needs and the ability to assess and prioritize them to meet program or department needs. • Knowledge of orientation procedures. • Knowledge of professional development opportunities. • Knowledge of available means of communication. • Recognizes job tasks, analyzes work assignments and delegates responsibilities. • Responds to nonverbal communication; Interprets, clarifies and influences communication and compares multiple viewpoints. • Conducts task-specific training, coaches others to apply related concepts, provides constructive feedback and develops appropriate training procedures. • Interprets information, selects methods of communication and summarizes integrates and analyzes information. • Leads by example, motivates others to extend their capabilities, Displays enthusiasm/positive attitudes and develops minority/majority views. • Analyzes possible causes, generates and evaluates solutions and devises and implements plan of action. 47 F. Perform Administrative and Program Management Functions Continued Key Activity F4 Develop criteria, recruit, and make recommendations regarding hiring of faculty 48 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Job descriptions and qualifications for faculty positions are properly identified. • Resumes and applications are thoroughly reviewed as received where applicable. • Interviews are conducted and, where applicable, recommendations are made in accordance with college policies and procedures. • Adequate sources of information are used to determine job qualifications. • Effective recruiting, screening, interviewing, and selection are performed in accordance with college policies and procedures. • Knowledge of specific job qualifications. • Ability to create job descriptions. • Ability to review applications. • Ability to access college policy and procedures regarding interview procedures. • Knowledge of college interview procedures. • Respects the rights of others, recognizes the value of diversity, encourages/supports individuality, supports correct course of action and responsibly challenges discriminatory practices and procedures. • Recognizes job tasks, analyzes work assignments and delegates responsibilities. • Responds to nonverbal communication; Interprets, clarifies and influences communication and compares multiple viewpoints. • Uses logic to draw conclusions, analyzes rules and principles and examines information for relevance and accuracy. • Establishes rapport with co-workers and customers; modifies behavior to environment; shows understanding for other, works to identify/remove social barriers and encourages cooperation and negotiation. F. Perform Administrative and Program Management Functions Continued Key Activity F5 Provide input for program, schedules, and college printed and electronic publications Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Schedules (including times, room and teaching assignments) are coordinated between program core and support courses. • Schedules and publications regarding the program are kept current and comply with all legal requirements. • Accurate program information is provided to college departments responsible for publication. • Accuracy of information in college schedules and publications is monitored and modified as necessary. • All materials about programs are consistent. • Knowledge of program requirements and courses. • Ability to schedule courses within a program. • Knowledge of legal requirements regarding college publications. • Knowledge of program information. • Knowledge of publication modification procedures. • Knowledge of publication timelines. • Knowledge of interdisciplinary college course scheduling procedures. • Monitors system performance, troubleshoots system malfunction/ failure and analyzes system operation. • Records information accurately, creates original documents; summarizes and synthesizes information. • Effectively manages time; prepares and organizes multiple schedules and manages timelines. • Understands negotiations process; Moderates discussion, interprets complaints and concerns, analyzes group dynamics and detects underlying issues. • Predicts outcomes, analyzes data, integrates multiple items of data, contrasts conflicting data, and researches additional information sources. 49 F. Perform Administrative and Program Management Functions Continued Key Activity F6 Develop and manage budgets 50 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Needs are annually • Knowledge of budgets identified and priand the budgeting oritized in accordance process. with college policies • Knowledge of and procedures. budgetary and college constraints. • Adequate resources are determined to meet the • Knowledge of equipprogram needs. ment placement plan • Resources are expended development and in a timely manner review processes. following college policies and procedures to support the program. • Equipment replacement plan is developed and reviewed annually. • Budgetary restrictions are followed and calculations are accurately formulated. • Appropriate documentation is maintained according to college policies and procedures. • Performs routine recordkeeping, reconciles accounts and develop budget proposals. • Analyzes situations and information, considers risks and implications, complies multiple viewpoints, and generates alternative solutions. • Maintains job specific supplies and equipment, orders and maintains inventory and monitors safe and efficient utilization of materials. • Summarizes and translates mathematical data and manipulates formulas. • Interprets information, applies processes to new information, analyzes organization of information and transfers information between formats. F. Perform Administrative and Program Management Functions Continued Key Activity F7 Research and assist with writing and implementing grants and targeting financial resources.* * Please note: many new instructors are not involved with writing grants. Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Appropriate campus personnel are contacted to investigate grant opportunities. • Sources of grant opportunities are thoroughly investigated. • Necessary data is procured or provided as requested. • Necessary forms and/or documents and reports are completed within established guidelines. • Funds are expended in accordance with grant proposal restrictions. • Grant proposal presentations to appropriate personnel are made as necessary. • Grant follow-up and evaluations are completed in a timely manner. • Ability to research • Interprets information, informa¬tion and write applies processes to proposals in accordance new information, with grant guidelines. analyzes organization • Ability to manage grant of information and funds. transfers information • Ability to assess progbetween formats. ress and effectiveness of • Records information the grant. accurately, creates • Knowledge of sources original documents; of grant opportunities. summarizes and syn• Knowledge of resources thesizes information. for grant writing. • Pays attention to details, demonstrates enthusiasm & initiative, monitors performance standards and follow up on assigned tasks. • Interprets information, selects methods of communication and summarizes integrates and analyzes information. • Demonstrates creative thinking process while problem solving; develops creative solutions and applies them to new situations; generates unique solutions. 51 G. Create and Maintain a Professional Environment Key Activity G1 Collaborate with college staff, faculty, students and internship/ externship site personnel 52 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Curriculum and course materials and resources are provided as required. • When applicable, performance is properly assessed, feedback is provided and recommendations are made in a respectful and appropriate manner. • Communications with college staff and faculty and internship/ externship personnel are conducted in an ongoing and effective manner. • Assistance is provided as necessary in a courteous and respectful manner. • Colleagues and staff are responded to in a timely manner. • Institution wide and interdisciplinary student learning activities and initiatives are fully supported. • Professional growth is promoted among staff and faculty. • College departments and services are accurately informed of needs in a professional and collaborative manner. • College and departmental committees are attended with full participation in accordance with college policy. • Knowledge of locations to file or post curriculum and course materials and resources. • Knowledge of procedures to request resources from library, instructional software and adoption procedures and ordering processes. • Knowledge of college depart¬ments and services available. • Knowledge of college communication tools. • Knowledge of professional growth opportunities. • Knowledge of program requirements and outcomes. • Knowledge of performance assessment, feedback and recommendation procedures. • Knowledge of college and departmental committees and college policies regarding committees. • Knowledge of employment contract provisions in regards to participation on the committee. • Establishes rapport with co-workers and customers; modifies behavior to environment; shows understanding for other, works to identify/remove social barriers and encourages cooperation and negotiation. • Effectively manages time; prepares and organizes multiple schedules and manages timelines. • Understands the organization and system hierarchy and follows procedures and recognizes system strengths and limitations. • Works to improve team skills, encourages team members, and assumes responsibility for accomplishing team goals. • Sets well defined goals, demonstrates commitment to self improvement, applies self management skills and appropriate modifies goals. G. Create and Maintain a Professional Environment Continued Key Activity G2 Work with program advisory committee Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Instructor-attended advisory committee meetings are held on a regular basis in accordance with college and SBCTC (State Board for Community and Technical Colleges) policies and procedures. • Instructors participate fully in advisory committee meetings and activities. • Advisory committee recommenda¬tions are considered and imple¬mented as appropriate. • New advisory committee members are recruited on an ongoing basis. • Advisory committee members reflect the diversity of the community and industry. • Productivity of advisory committee is encouraged. • Sets well defined • Knowledge of college and SBCTC policies and goals, demonstrates procedures regarding commitment to self advisory committee improvement, applies recommen¬dations. self management skills • Knowledge of faculty and appropriate modirole regarding advisory fies goals. committee and com• Works to improve mittee protocols. team skills, encourages • Ability to utilize adviteam members, and sory board in industry assumes responsibility trades for students. for accomplishing team • Knowledge of the goals. relevant field of study, • Respects the rights program requirements of others, recognizes and accreditation the value of diversity, requirements. encourages/supports • Ability to implement individuality, supports committee recommencorrect course of dations into program. action and responsibly • Ability to recruit new challenges discriminaand diverse members tory practices and to the committee. procedures. • Conducts task-specific training, coaches others to apply related concepts, provides constructive feedback and develops appropriate training procedures. • Leads by example, motivates others to extend their capabilities, Displays enthusiasm/positive attitudes and develops minority/majority views. 53 G. Create and Maintain a Professional Environment Continued Key Activity G3 Maintain current knowledge of the field 54 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Working relationships with college staff, faculty and administrators, are maintained to stay current on education and training resources and methods. • Working relationships with employers/ industry, graduates/ former students, and advisory committees are professionally maintained to stay current on industry trends and emerging technologies. • Memberships in appropriate professional organizations are obtained and maintained. • Professional publications are accessed and properly utilized. • Local, regional and national seminars, workshops and meetings are attended as appropriate. • College procedures are followed regarding attendance at professional functions. • A variety of resources is utilized to network with people working and/ or teaching within the field. • Emerging industryspecific equipment is incorporated into the learning environment. • Knowledge of methods for fostering professional relationships. • Knowledge of appropriate professional organizations in the field. • Knowledge of roles and responsibilities of membership in a professional organization. • Ability to access relevant sources of information regarding professional publications and professional development opportunities. • Knowledge of travel request procedures and professional development reimbursement procedures. • Knowledge of industry leaders and technology suppliers related to emerging technology. • Ability to evaluate new technology in regards to its usefulness, effectiveness and long-range implications. • Ability to obtain and maintain certification on industry-specific equipment. • Sets well defined goals, demonstrates commitment to self improvement, applies self management skills and appropriate modifies goals. • Predicts outcomes, analyzes data, integrates multiple items of data, contrasts conflicting data, and researches additional information sources. • Works to improve team skills, encourages team members, and assumes responsibility for accomplishing team goals. • Defends own viewpoints, accepts constructive criticism, accepts responsibility for own behavior and understands own impact on others. • Follows set of instructions, qualifies and analyzes information, interprets and summarizes information and researches to gain information. G. Create and Maintain a Professional Environment Continued Key Activity G4 Participate in professional networking Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Working relationships with graduates, college staff, faculty, administrators, internship/ externship personnel, employers, and advisory committees are maintained in an effective manner. • Memberships in appropriate professional organizations are obtained and maintained in an effective manner. • Seminars, workshops and local, regional, and national meetings are attended as appropriate. • All college procedures are completely followed regarding attendance at professional functions. • A variety of resources is utilized to interact with people teaching and working in the related field. • Knowledge of methods for fostering professional relationships. • Knowledge of appropriate organizations in the field. • Knowledge of roles and responsibilities of membership in a professional organization. • Knowledge of travel request procedures and professional development reimbursement procedures. • Utilizes integrated/multiple software, locates and retrieves stored information, interprets data, integrates multiple platforms, utilizes networks and modifies information. • Works to improve team skills, encourages team members, and assumes responsibility for accomplishing team goals. • Sets well defined goals, demonstrates commitment to self improvement, applies self management skills and appropriate modifies goals. • Interprets and applies new knowledge and experience, analyzes application of learning tools, investigates new learning techniques, manipulates learning tools and formulates/ adapts learning strategies, • Actively participates in discussion; presents complex ideas and information, analyzes group and individual response and poses critical questions. 55 G. Create and Maintain a Professional Environment Continued Key Activity G5 Develop a professional development plan 56 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Files and resources for all applicable certification and professional development requirements are kept current and maintained in an orderly and effective manner. • Appropriate activities are thoroughly researched and properly identified and completed. • Documentation is accurately maintained in accordance with college policy and procedures. • Plan includes activities to address areas for improvement and professional growth. • All approvals are obtained as required. • Tenure-track faculty complete all assessments and professional development activities required by their campus and tenure committee. • Professional Technical College Instructor Skill Standards are used as a resource to develop PDP. • Knowledge of sources of information for applicable certification and professional development activities and requirements. • Knowledge of college policies and procedures regarding professional development and required elements of a professional development plan. • Ability to develop a plan that addresses areas for improve¬ment and professional growth. • Knowledge of documentation and approval procedures. • Ability to fulfill the require¬ments of certification. • Knowledge of the campus tenure track process. • Ability to access and use the skill standards. • Ability to access relevant sources of information regarding professional development opportunities. • Sets well defined goals, demonstrates commitment to self improvement, applies self management skills and appropriate modifies goals. • Analyzes possible causes, generates and evaluates solutions and devises and implements plan of action. • Interprets information, applies processes to new information, analyzes organization of information and transfers information between formats. • Records information accurately, creates original documents; summarizes and synthesizes information. • Understands the organization and system hierarchy and follows procedures and recognizes system strengths and limitations. H. Promote the Program and Recruit Students Key Activity H1 Participate in campus, high school and community organization activities and educational partnerships Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Community and campus activity offerings are researched. • Activities and organizations that promote the program and recruitment of students are identified. • Promotional information is made available. • Activities are properly set up and organized. • College policies and procedures regarding recruitment events are met. • Participation in appropriate high school advisory committees is carried out in an effective manner. • Accurate and complete program information is provided at the high school advisory committee meetings. • Participation in related Tech Prep activities initiations carried out in an effective manner. • Articulation agreements are properly created and maintained with high schools, colleges and universities and state agencies. • Knowledge of relevant campus and community activities. • Ability to select appropriate activities to enhance student learning. • Knowledge of college policies and procedures regarding campus and community activities. • Knowledge of setup and organization procedures for campus and community activities. • Knowledge of procedures for establishing articulation agreements. • Knowledge of Tech Prep. • Knowledge of contacts for high school advisory committees, feeder programs and Tech Prep consortia members. • Works to improve team skills, encourages team members, and assumes responsibility for accomplishing team goals. • Actively participates in discussion; presents complex ideas and information, analyzes group and individual response and poses critical questions. • Establishes rapport with co-workers and customers; modifies behavior to environment; shows understanding for other, works to identify/remove social barriers and encourages cooperation and negotiation. • Responds to nonverbal communication; Interprets, clarifies and influences communication and compares multiple viewpoints. • Effectively manages time; prepares and organizes multiple schedules and manages timelines. • Analyzes and responds to customer needs; demonstrates commitment to customer, obtains additional resources to meet customer needs. 57 H. Promote the Program and Recruit Students Continued Key Activity H2 Develop promotional plan 58 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • The appropriate institutional resources are utilized to develop an effective marketing strategy. • Potential students are correctly identified. • Coordination with feeder programs to identify perspective students is carried out in an effective manner. • Plan includes how to market, what marketing tools to use, schedule of marketing events, and the target population. • Marketing budget is accurately and completely developed. • All appropriate approvals are obtained in accordance with college policies and procedures. • Accurate information is provided to appropriate college entities for creation and modification of published materials regarding programs. • Information in published materials is continuously monitored for currency and accuracy and appropriate departments are informed of errors and updates. • Knowledge of contacts for high school advisory committees, feeder programs and Tech Prep consortia members. • Ability to identify potential students. • Knowledge of college policies and procedures. • Ability to develop a marketing plan and budget. • Knowledge of the institutional resources that relate the marketing plan. • Knowledge of marketing strategies, tools, scheduling and the target population. • Effectively manages time; prepares and organizes multiple schedules and manages timelines. • Utilizes previous training and experience to predict outcomes; visually analyzes relationship between parts/whole and process/procedure and interprets charts and graphs. • Demonstrates creative thinking process while problem solving; develops creative solutions and applies them to new situations; generates unique solutions. • Performs routine recordkeeping, reconciles accounts and develop budget proposals. • Respects the rights of others, recognizes the value of diversity, encourages/supports individuality, supports correct course of action and responsibly challenges discriminatory practices and procedures H. Promote the Program and Recruit Students Continued Key Activity H3 Provide program information for prospective students Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Group information sessions are scheduled, advertised, and conducted on a regular basis. • Individual informational meetings are scheduled as needed. • Accurate information materials are developed and disseminated in an effective manner. • Access is made available through a variety of methods such as mail, phone, email. • Prompt responses are made to contacts through a variety of channels (email, phone, etc.). • Prospective students are referred to other programs or college services as appropriate. • Industry and career information are provided. • Knowledge of program information and options. • Knowledge of procedures for scheduling, advertising and conducting group information sessions. • Knowledge of procedures for individual information meetings. • Knowledge of contents of information materials. • Knowledge of college and other program options. • Knowledge of industry career options and job opportunities. • Knowledge of means of communication available through the college. • Responds to nonverbal communication; Interprets, clarifies and influences communication and compares multiple viewpoints. • Analyzes and responds to customer needs; demonstrates commitment to customer, obtains additional resources to meet customer needs. • Effectively manages time; prepares and organizes multiple schedules and manages timelines. • Interprets information, applies processes to new information, analyzes organization of information and transfers information between formats. • Sets well defined goals, demonstrates commitment to self improvement, applies self management skills and appropriate modifies goals. • Respects the rights of others, recognizes the value of diversity, encourages/supports individuality, supports correct course of action and responsibly challenges discriminatory practices and procedures. 59 H. Promote the Program and Recruit Students Continued Key Activity H4 Perform recruiting activities 60 Performance Indicators Technical Knowledge Employability Skills How do we know when the task is performed well? Skills, Abilities, Tools SCANS Skills and Foundational Abilities • Appropriate records of student, program, and placement success stories and data are properly maintained and disseminated. • Presentations to high school students, teachers, parents and community organizations are provided on a regular basis. • Program information is compiled and given to appropriate college recruiter on a regular basis. • Knowledge of students • Responds to nonverbal who have completed communication; the programs Interprets, clarifies and successfully. influences communica• Knowledge of contacts tion and compares in the high schools multiple viewpoints. and in community • Respects the rights organizations. of others, recognizes • Knowledge of materials the value of diversity, to be used in promoencourages/supports tional activities. individuality, supports • Ability to prepare matecorrect course of rials for presentation. action and responsibly challenges discriminatory practices and procedures. • Analyzes and responds to customer needs; demonstrates commitment to customer, obtains additional resources to meet customer needs. • Interprets information, applies processes to new information, analyzes organization of information and transfers information between formats. • Actively participates in discussion; presents complex ideas and information, analyzes group and individual response and poses critical questions. SCANS Survey Results: Professional-Technical College Instructors Foundation Skills and Personal Qualities Key: 1 = Basic Competency Level; 5 = Advanced Competency Level. 1 2 3 4 Critical Competencies 5 Basic Skills Demonstrates Effective Reading Strategies Identifies relevant details, facts, specifications, follows set of instructions, probes to gain knowledge/information and qualifies/analyzes information. Demonstrates Effective Writing Strategies Records information accurately, writes simple documents and summarizes/ paraphrases information. Applies Arithmetic Processes Performs basic computations and measurements, converts numerical data and predicts arithmetic results. Applies Mathematics Processes Utilizes mathematical formulas and processes, summarizes and translates mathematical data. Demonstrates Effective Listening Skills Listens attentively, responds to non-verbal communication and confirms, interprets, clarifies and influences communication. Demonstrates Effective Speaking Skills Actively participates in discussion, explains concepts and presents complex ideas and information. Thinking Skills Applies Creative Thinking/ Generates Ideas Recognizes patterns and relationships, demonstrates creative thinking process while problem solving and develops creative solutions. Applies Decision Making Strategies Analyzes situations and information, considers risks and implications and compiles multiple viewpoints. Recognizes and Solves Problems Identifies the problem, analyzes possible causes/reasons, recommends action plan and generates/evaluates solutions. Demonstrates Visualization Utilizes previous training and experience to predict outcomes; visually analyzes relationship between parts/whole and process/procedure and interprets charts and graphs. Knows How to Learn Draws upon experiences and prior knowledge, interprets and applies new knowledge and experience and interprets symbols, diagrams and schematics. Applies Reasoning Skills Applies rules/principles to process, uses logic to draw conclusions and analyzes rules and principles. 61 SCANS Survey Results: Professional-Technical College Instructors – Continued Foundation Skills and Personal Qualities Key: 1 = Basic Competency Level; 5 = Advanced Competency Level. 1 2 3 4 Critical Competencies 5 Personal Qualities 62 Demonstrates Responsibility Follows policies and procedures, pays attention to details, works with minimal supervision, demonstrates initiative and monitors performance standards. Demonstrates Belief in Self Worth Responds assertively, defends own viewpoints, accepts constructive criticism and responsibility for own behavior and understands own impact on others. Demonstrates Sociability in Groups Responds appropriately to others, takes active interest in others, establishes rapport with co-workers and customers, modifies behavior to environment and shows understanding/empathy for others. Demonstrates Self-Management Accepts responsibility for own behavior, accepts constructive criticism, sets welldefined/realistic goals, demonstrates commitment to self improvement, and applies self-management skills. Demonstrates Integrity/ Honesty Demonstrates honesty and trustworthiness, accepts responsibility for own behavior, analyses societal implications of decisions and recommends ethical course of action. Management of Resources Manages Time Effectively manages time; prepares and organizes multiple schedules and manages timelines. Manages Money Performs routine recordkeeping. Manages Materials/ Facilities Maintains job-specific supplies and equipment, orders and maintains inventory and monitors safe and efficient utilization of materials. Manages Human Resources Analyzes work assignments, assesses individual knowledge and skills, determines workload and monitors performance. Management / Use of Information Acquires and Evaluates Information Selects relevant data, identifies the need for data, predicts outcomes, and integrates multiple items of data. Organizes and Maintains Information Interprets information and applies processes to new information. Interprets and Communicates Information Recognizes accuracy of information, interprets information, and prepares basic summaries. SCANS Survey Results: Professional-Technical College Instructors – Continued Foundation Skills and Personal Qualities Key: 1 = Basic Competency Level; 5 = Advanced Competency Level. 1 2 3 4 Critical Competencies 5 Interpersonal Skills Participates as Team Member Demonstrates commitment, works to improve team skills, encourages team members, assumes responsibility for accomplishing team goals. Teaches Others Conducts task-specific training, coaches others to apply related concepts, provides constructive feedback and develops appropriate training procedures. Serves Customers Demonstrates sensitivity to customer concerns and interests; analyzes and responds to customer needs; obtains additional resources to meet customer needs; makes exceptional effort on behalf of customer. Exhibits Leadership Leads by example, motivates others to extend their capabilities, displays enthusiasm/positive attitudes and develops majority/minority views. Negotiates Agreements Understands negotiations process; identifies conflicts and demonstrates composure; interprets complaints and concerns and analyzes group dynamics. Works with Diversity Understands the legal aspects of discrimination; respects the rights of others and demonstrates awareness of diversity; recognizes the value of diversity. Understanding/Management of Systems Understands System Understands the organization and system hierarchy and follows procedures and recognizes system strengths and limitations. Monitors/Corrects System Performance Monitors system performance, analyzes system operation, and distinguishes trends in performance. Improves/Designs Systems Suggests system modifications/improvements and determines system components to be improved. Use of Technology Selects Appropriate Technology Understands the requirements of the task and technological results and analyzes task/ technology relationship. Applies Technology to Task Understands technology applications, manipulates technology for desired results and analyzes technology output. Maintains/ Troubleshoots Technology Follows specified maintenance, identifies and corrects malfunctions, troubleshoots failures, evaluates performance of technology. 63 64