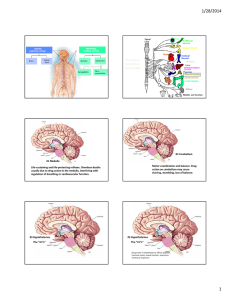
9/29/2015 Neuron Synapse Synapse Under Electron Microscope
advertisement

9/29/2015 Neuron Synapse Synapse Under Electron Microscope Presynaptic Terminal Synapse Postsynaptic membrane Best Known Small Molecule Neurotransmitter Groups • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7irX53PZuAE go to 1:11 • (ignore the Vietnamese subtitles ! ) • Acetylcholine (ACh) • Monoamines • Norepinephrine (NE) • Dopamine (DA) These 3 are “catecholamines” • Epinephrine (E) • Serotonin (5HT) (an “indoleamine”) • Amino Acids • • • • Glutamate GABA Aspartate Glycine 1 9/29/2015 Large molecules Large Molecule Transmitters Small transmitters synthesized right in synaptic ending • Neuropeptides (small proteins) • • • • • Pituitary peptides – like LH Hypothalamic peptides – like oxytocin Brain-gut peptides- like insulin Opiate peptides – like endorphins Miscellaneous others Synapse Unconventional Transmitters Presynaptic Terminal • Unconventional in their chemistry, their release and their effects • Soluble Gases • Nitric Oxide (NO) – causes blood vessels to dilate • Carbon Monoxide (CO) • Endocannabinoids Synapse • Anandamide Postsynaptic membrane Autoreceptors are presynaptic receptors! • Neurons using different neurotransmitters as their messenger are not evenly distributed throughout the nervous system. • Most neurotransmitters serve as messengers just in particular areas or systems, and thus are related to particular behaviors or functions. 2 9/29/2015 • ACh: parasympathetic neurons; motor neurons; many cortical neurons • NE: sympathetic n.s.; reticular formation; hypothalamus; limbic system • 5HT: limbic system; sleep system; pain suppression system • DA: basal ganglia; reward system; prefrontal cortex; hypothalamus-pituitary Transmitter Precursor Comes from: Acetylcholine Choline or lecithin Cauliflower, milk Yolk, liver, soy, peanuts, butter Catecholamines Phenylalanine or tyrosine Proteins, almonds, avocados, bananas, seeds Serotonin Tryptophan Poultry, dairy, beef, soy, peanuts, barley, brown rice Released Transmitter Removed or Cleaned Up By: • 1. Reuptake back into the presynaptic ending and/or • 2. enzymatic breakdown Presynaptic membrane contains proteins that serve as transporters. Excess transmitter inside neuron also broken down by enzymes. The Action of Neurotransmitters The effect produced at the synapse depends not only on the type of neurotransmitter but also the type of receptor. We now know each neurotransmitter fits multiple types of receptors – e.g. at least 5 types of DA receptors and 6 types of 5HT receptors have been discovered. Example: ACh • 2 types of ACh receptors: • Nicotinic – e.g. motor neuron to muscle fibers • Muscarinic – e.g. parasympathetic nerves to organs and glands • Different drugs bind to each type of receptor 3 9/29/2015 Drug Actions Psychoactive drugs act by affecting 1 or more of the steps of chemical transmission (synthesis, storage, release, receptor binding, breakdown or reuptake) Some drugs enhance transmitter action (“agonists”) Some interfere with transmitter action (“antagonist”) AGONIST examples: Narcotic pain relievers fit and activate opiate receptors mimicking the action of normal endorphin. Nicotine fits into & stimulates ACh receptor sites, arousing the cortex like ACh ANTAGONIST examples: Haldol blocks DA receptors in schizos Naloxone blocks opiate receptors Atropine blocks muscarinic ACh receptors & curare or botox block nicotinic ACh receptors L-dopa MAOI Reserpine Amphet • For example, the first drug we’ll encounter in our discussion of Parkinson’s disease, l-dopa, affects the first step (synthesis of neurotransmitter). • L-dopa is a “precursor” or ingredient DA neurons can use to make DA. Botox Nicotine, endorphins Cocaine Parkinson’s Disease THC Antipsychoticsl • About 1-2/100 of those over 50 have PD (about 1,000,000 total in US) • Progressive loss of DA cells in substantia nigra which normally send messages to basal ganglia • We all gradually lose neurons but those with PD may have accelerated loss (70% or more gone) • Symptoms: Difficulty initiating movements, slow movements, muscle rigidity & tremors-at-rest • Also cognitive slowing & depression in many Substantia nigra of midbrain contains the cell bodies of DA neurons whose axons go to the basal ganglia & other forebrain areas 4 9/29/2015 Basal Ganglia or “Striatum” PD vs normal SN Normal # of DA cells vs PD Possible Causes • Early Parkinson’s disease – strong genetic link (weak association in late-life form of PD- identical twins not more concordant than frats) • Environmental toxin of some sort (herbicides, pesticides): IA, MN, ND, SD, & NEB have highest rates in US! • Head injury may be associated with up to 11 fold increase in risk & earlier age of onset. • Caffeine or nicotine use may decrease your risk Or basal ganglia In midbrain Bundle of axons from midbrain to basal ganglia is called the nigrostriatal pathway Treatments • Increase DA production with l-dopa • L-dopa is having an “agonist” action • Problems: l-dopa induced side effects & loss of effectiveness over time • Variety of new meds being tried • DA agonists, antioxidants, nerve growth factors •When Drug Therapy Fails • When drug effectiveness declines, experimental options include: • Deep brain (thalamic or subthalamic) stimulation to block activity in these same regions • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WYDoHmg9ECI • Lesion other parts of motor control system • Pallidotomy ; thalamotomy (Michael J. Fox) • Transplant of DA producing cells into brain http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=puJCjUsgq7o 5