FREC 410 HW Assignments #2 Basic Trade Theory
advertisement

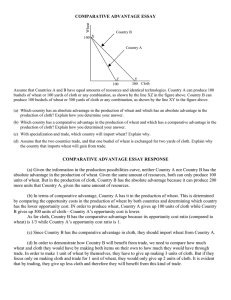
FREC 410 HW Assignments #2 Basic Trade Theory NOTE: Carefully review and provide detailed responses to the following questions. These questions are mostly based on materials covered in our class lectures and the assigned readings from the textbook. 1) Briefly explain the following terms: a) Absolute versus comparative advantage b) Factor price equalization theorem c) Terms of trade d) Factor intensity e) Internal economy of scale 2) Free Trade Equilibrium a) U.S., a major importer of coffee has demand and supply curves given below as: Dm = 200 – 40P Sm = 40 + 40P i) Derive and graph U.S import (excess) demand curve. ii) What would the price of coffee be in the absence of trade? b) Colombia, an exporter of coffee has demand and supply curves given below as: Dx = 160 – 40P Sx = 80 + 40P i) Derive and graph Colombia’s export (excess) supply curve. ii) What would the price of coffee be in the absence of trade? c) Assume U.S. and Colombia now trade in coffee and transportation cost is zero (negligible). Find and graph the equilibrium under free trade: i) What is the world price and volume (quantity) of trade? 3) Ricardian Theory of comparative Advantage Assuming the following: 2 countries (USA and Thailand); 2 commodities (cloth and wheat); and 30 million laborers in the USA and 60 million laborers in Thailand. The production possibilities frontier (PPF) in these 2 countries are given below: USA Thailand Wheat (mil. Bushels) 36 or 12 or Cloth (mil. yards) 12 18 a) State three main assumptions of the Ricardian theory of comparative advantage b) Graph the PPF for each country showing the production of wheat and cloth. c) Calculate the marginal or opportunity costs of producing wheat and corn in each country (Hint: Compute ratios of unit labor requirements) – see class notes d) Determine the terms of trade (TOT) for both countries. e) Which country has comparative advantage in the production and export of which commodity? Who export and import which commodity? 1





![저기요[jeo-gi-yo] - WordPress.com](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005572742_1-676dcc06fe6d6aaa8f3ba5da35df9fe7-300x300.png)