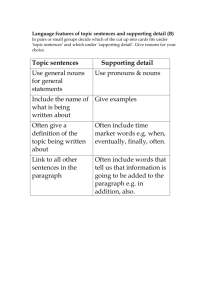
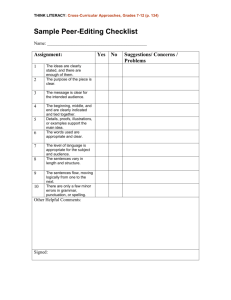
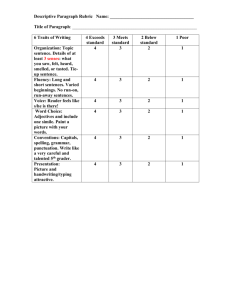
WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST READING
advertisement

WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST READING Federal Functioning Level 1 – Beginning Literacy (0–1.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: R.1 PHONEMIC AWARENESS/ WORD ANALYSIS Date & Initial 1.1.1 Recognize the concepts of print (left to right, top to bottom, front to back, return sweep). 1.1.2 Recognize upper and lower case manuscript letters of the alphabet and their sounds. 1.1.3 Identify words with the same consonants/sounds in initial word positions (e.g., car, cow, cat). 1.1.4 Manipulate initial sounds to recognize, create, and use rhyming words (e.g., may, say, ray). 1.1.5 Identify single consonants/sounds in initial, medial, and final word positions. 1.1.6 Identify short and long vowels and their sounds. 1.1.7 Use short vowel sounds to decode one-syllable words. 1.1.8 Identify “r-controlled” vowel sounds (e.g., ur, ar, ir). 1.1.9 Identify two-letter consonant blends in initial and final word positions (e.g., br-, sp-, cl-, -nd, -sk) and use these to decode one-syllable words. 1.1.10 Identify two-letter consonant digraphs in initial and final word positions (e.g., ch, sh, th, wh) and use these to decode one-syllable words. 2.1.5 2.1.6 2.1.7 R.3 COMPREHENSION 3.1.1 3.1.2 3.1.3 3.1.4 3.1.5 3.1.6 R.2 VOCABULARY 2.1.1 2.1.2 2.1.3 2.1.4 Demonstrate ability to read personal information (name, address, zip code, phone number, age). Identify common functional and survival signs and labels with one word or symbol (e.g., danger, hospital, restroom, poison). Read written numbers (one, two), clock time, prices, sizes, and isolated words and phrases in familiar contexts (e.g., traffic signs, store ads, clothing tags, fast food menus). Identify and match common symbols (e.g., dollar sign) and abbreviations (e.g., days, months, clothing size) to full form of the word. Use picture clues to identify unfamiliar words. Use context clues to determine word meaning (e.g., by identifying missing words from sentences). Read a minimum of 80% of sight words from an appropriate level word list (e.g., 100 most frequently used words). Date & Initial Locate pertinent information in simple, familiar materials (e.g., want ads, job listings, schedules, signs, food packages). Respond to instructional level text (1) by distinguishing between fact and opinion and (2) by comparing and contrasting ideas. Respond to instructional level text (1) by identifying sequence and (2) by making predictions (e.g., by using illustrations and titles). Read and interpret simple and compound sentences in a short paragraph containing familiar vocabulary. Interpret and follow very simple visual instructions that utilize pictures and diagrams. Demonstrate self-monitoring strategies (e.g., self-correct when an incorrectly identified word does not fit). R.4 FLUENCY 4.1.1 Date & Initial Date & Initial Read orally, with accuracy and comprehension, texts designed for this instructional level. (Rubrics will be developed to measure this consistently.) 1 Performance Descriptors READING – BEGINNING LITERACY – LEVEL 1 Each IGO must be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Phonemic Awareness/Word Analysis R.1.1.1 Read a few very simple sentences with familiar learned words pointing to each word as it is read; demonstrating movement from left to right and top to bottom; and movement from the end of a line to the beginning of the next (return sweep) with continuation on to the back of the page. R.1.1.2 Look at a list with a mixture of at least forty upper and lower case manuscript letters of the alphabet that are not in alphabetical order, say the names of the letters for your instructor, and indicate the sounds the letters make. R.1.1.3 Listen to twenty sets of words and identify the one word in each set of four that has a beginning sound different from the other three words in the set (e.g., cat, cow, car, dog). R.1.1.4 For twenty sets of words, listen to the first word in the set and identify one of the following three words that rhymes. Listen to ten key words and make at least two rhyming words for each. For five words, listen to the word, identify a rhyming word, and make a sentence using both words. R.1.1.5 Identify the single consonants/sounds in initial, medial, and the final word positions of fifty or more words. R.1.1.6 Identify five vowels of the English language and make the five short and five long vowel sounds using picture words with the vowel sounds in them. R.1.1.7 Decode twenty or more one syllable words that use the five short vowel sounds. R.1.1.8 Identify twenty or more “r-controlled” vowel sounds (e.g., ur, ar, ir) and use them to read the words orally. R.1.1.9 Identify the two-letter consonant blends in the initial and the final word positions (e.g., br-, sp-, cl-, -nd, -sk) of twenty or more one-syllable words and use them to read the words orally. R.1.1.10 Identify two-letter consonant digraphs in the initial and the final word positions (e.g., ch, sh, th, wh) of twenty or more one-syllable words and use them to read the words orally. Vocabulary R.2.1.1 Read personal information labels (name, address, zip code, phone number, age, etc.) and match to own personal information or complete the personal information sheet for WC.1.1.6. (See also WC.1.1.6) R.2.1.2 Identify a graphic of ten or more common functional signs, survival signs, and labels with one word or symbol (e.g., danger, hospital, restroom, poison). R.2.1.3 Read twenty-five or more written numbers (one, two), clock time, prices, sizes, and isolated words and phrases in familiar contexts (e.g., traffic signs, store ads, clothing, tags, fast food menus). R.2.1.4 Identify and match ten or more common symbols (e.g., dollar sign) and abbreviations (e.g., days, months, clothing size) to full form of the word. R.2.1.5 Use picture clues to identify ten unfamiliar words. R.2.1.6 Use context clues to determine ten word meanings (e.g., by identifying missing words from sentences). R.2.1.7 Read a minimum of 80% of twenty-five or more sight words from an appropriate level word list (e.g., 100 most frequently used words). Comprehension R.3.1.1 Locate pertinent information in two or more simple materials (e.g., want ads, job listings, schedules, signs, food packages). R.3.1.2 Respond to instructional level text (1) by distinguishing between fact and opinion in one passage and (2) by comparing and contrasting ideas in one passage. R.3.1.3 Respond to instructional level text (1) by identifying sequence in one passage and (2) by making predictions (e.g., by using illustrations and titles) in one passage. R.3.1.4 Read and interpret simple and compound sentences in a short paragraph containing familiar vocabulary by answering five comprehension questions. R.3.1.5 Interpret and follow a very simple set of visual instructions that utilize pictures and diagrams for one task. R.3.1.6 Demonstrate self-monitoring strategies (e.g., self correct when an incorrectly identified word does not fit) by reading three or more passages for the teacher. Fluency R.4.1.1 Read orally, with accuracy and comprehension, texts designed for this instructional level. Use the rubric developed for this IGO to measure this consistently. 2 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST READING Federal Functioning Level 2 – Beginning Basic (2–3.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: NOTE: Essential IGOs related to the GED Tests are underlined. R.1 PHONEMIC AWARENESS/ WORD ANALYSIS Date & Initial Identify two and three letter consonant blends (e.g., str, spl, thr) and digraphs in initial, medial, and final word positions and use them to decode onesyllable words. 1.2.2 Identify long vowel combinations and use them to decode one-syllable words. 1.2.3 Identify diphthongs (e.g., ou, aw, ay) and use to decode one-syllable words. 1.2.4 Identify the schwa sound (e.g., away) and use to decode simple words. 1.2.5 Identify and use silent consonants (e.g., kn, gh). 1.2.6 Identify words with inflectional endings (e.g., -s, -es, -ed,-ing, -er, -est). 1.2.7 Identify and use contractions and be able to match them to the two words being replaced (e.g., I’m for I am). 1.2.8 Identify and use compound words. 1.2.9 Identify root words, prefixes (e.g., pre-, un-, dis-), and suffixes (e.g., -less, -ly, -ment) and use them to decode multisyllabic words. 1.2.10 Use decoding strategies to identify and count syllables in multi-syllable words. suffixes, and root words). R.3 COMPREHENSION 1.2.1 R.2 VOCABULARY 2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.3 2.2.4 2.2.5 Read a minimum of 80% of sight words from an appropriate level word list (e.g., 300 most frequently used words). Recognize synonyms, antonyms, homonyms, and homophones (e.g., dear-deer) for identified vocabulary words presented in isolation or within a group of words. Recognize the correct meaning of multiple-meaning words (e.g., bill, train) when presented in text. Use context clues to determine the meaning of an unknown word. Use structural analysis to determine the meaning of words (e.g., prefixes, Date & Initial 3.2.1 Date & Initial Locate explicitly stated information in functional reading (e.g., invitations, bulletins). 3.2.2 Locate specific items in an alphabetical listing (e.g., class list, phone directory, dictionary) or in a topical listing (e.g., picture dictionary, table of contents). 3.2.3 Distinguish between fact and opinion in a short paragraph. 3.2.4 Use comparison and contrast to draw conclusions in a story. 3.2.5 Evaluate information from simple charts, graphs, labels, and payroll stubs to answer questions. 3.2.6 Use newspaper headlines or other titles to draw conclusions and make inferences about simple written materials. 3.2.7 Paraphrase a simple written passage. 3.2.8 Follow a set of simple written directions. 3.2.9 Determine the sequence (e.g., events in a story, set of directions, and/or a missing item) in a process. 3.2.10 Identify the author’s purpose in a selection when it is not explicitly stated. 3.2.11 Use graphic organizers, such as story maps and Venn diagrams, to determine meaning in texts written for this instructional level. 3.2.12 Self-monitor and clearly identify specific words or wordings that are causing comprehension difficulties (e.g., by circling or underlining difficult words). R.4 FLUENCY 4.2.1 Date & Initial Read orally with accuracy and comprehension, texts designed for this instructional level. (Rubrics will be developed to measure this consistently.) 3 Performance Descriptors READING – BEGINNING BASIC – LEVEL 2 Each IGO must be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Phonemic Awareness/Word Analysis R.1.2.1 Identify two and three letter consonant blends and digraphs in one-syllable words. Find initial blends in twenty words, final blends in ten words, and the blends and digraphs in five words that have the combinations in the initial, end, or both positions. Use the sounds of the digraphs and blends to help you pronounce all the words. R.1.2.2 Identify long vowel combinations and use them to decode twenty one-syllable words. R.1.2.3 Identify diphthongs (e.g., ou, aw, ay) and use them to decode twenty one-syllable words. R.1.2.4 Identify the schwa sound (e.g., a as in away) and use them to decode ten simple words. R.1.2.5 Identify and use silent consonants to read ten simple words. R.1.2.6 Identify the inflectional endings (e.g., s, es, ed, ing, er, est) from a list of twenty words. R.1.2.7 Match ten contractions to the two words being shortened (e.g., I’m for I am.) and identify ten contractions in a paragraph. R.1.2.8 Identify compound words in twenty sentences and make five compound words from ten one-syllable words. R.1.2.9 Identify the prefixes and roots in ten words, the suffixes and roots in ten words, and identify the prefixes, suffixes (or both), and roots in five words. Say the words for the teacher. R.1.2.10 Use decoding strategies to identify and count syllables in twenty multi-syllable words. Vocabulary R.2.2.1 Read a minimum of 80% of the English words listed as the final 200 words of the 300 most frequently used words. R.2.2.2 Recognize eight synonyms, fifteen antonyms, and twenty homonyms and homophones (e.g., dear-deer) for identified vocabulary words presented in isolation or with-in a group of words. R.2.2.3 Recognize the correct meaning of multiple-meaning words (bill, train) when presented in ten sentences. R.2.2.4 Use context clues to determine the meaning of ten or more unknown words. (See also R.2.1.6) R.2.2.5 Use the meaning of prefixes and suffixes to determine which prefixes and suffixes to add to root words to give meaning to a paragraph. Comprehension R.3.2.1 Look at one functional reading (invitations, bulletins, signs) and answer at least five questions from information explicitly stated in the reading. (See also WC.2.4.3) R.3.2.2 Locate five specific items in one alphabetical listing (e.g., class list, phone directory, dictionary) and five items in one topical listing (e.g., picture dictionary, table of contents). (See also WC.1.1.3) R.3.2.3 Distinguish between fact and opinion in one short paragraph. (See also WC.2.4.7) R.3.2.4 Use comparison and contrast to draw conclusions in one short story. (See also WC.2.5.3, WC.2.3.4) R.3.2.5 Evaluate information from one simple chart, graph, label, and payroll stub by answering fifteen questions. R.3.2.6 Use five newspaper headlines or other titles to draw at least two conclusions for each about simple written material that would follow. R.3.2.7 Paraphrase one, simple written passage. Use a rubric to evaluate. (See also WC.2.3.1) R.3.2.8 Follow at least two sets of simple written directions. (See also WC.2.3.1) R.3.2.9 Determine the sequence (e.g., events in a story, set of directions, and/or a missing item) in two or more processes. (See also WC.2.2.5) R.3.2.10 Identify the author’s purpose in one selection when it is not explicitly stated. R.3.2.11 Use a graphic organizer such as a story map or a Venn diagram to determine meaning in a text written for this instructional level. (See also WC.2.2.3, WC.3.3.8, WC.2.5.3) R.3.2.12 Demonstrate self-monitoring techniques to clearly identify specific words or wordings that are causing comprehension difficulties (e.g., by circling or underlining difficult words) in one short selection taken from a text on instructional level. (See also WC.5.4.1) Fluency R.4.2.1 Read orally, with accuracy and comprehension, a text designed for this instructional level. Use the rubric to measure consistently. 4 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST READING Federal Functioning Level 3 – Low Intermediate (4–5.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: R.2 VOCABULARY 2.3.1 2.3.2 2.3.3 2.3.4 Use prefixes, suffixes, root words, antonyms, and synonyms to determine meaning of unfamiliar words. Use context clues to determine meaning of unfamiliar words. Read a minimum of 80% of sight words from an appropriate level word list. Identify the meaning of frequently used synonyms, antonyms, and homographs. R.3 COMPREHENSION 3.3.1 3.3.2 3.3.3 3.3.4 3.3.5 3.3.6 3.3.7 Date & Initial Identify the main idea of a passage and relevant supporting details. Identify cause/effect signal words in sentences (e.g., as a result, because, consequently, thus). Follow simple written multi-step instructions and diagrams. Locate pertinent information in multiparagraph passages and apply it to answer a question. Locate pertinent information in print materials (e.g., ads, labels, pay stubs, public signs) and apply it to answer a question. Read and interpret simplified policies/procedures (e.g., simple employee handbooks, payroll stubs, driver’s manual). Use comparison and contrast to determine the best purchase of an advertised item. 3.3.8 Date & Initial Evaluate information from simple graphic materials such as charts, pictures, maps, signs, diagrams, tables, or graphs. 3.3.9 Locate information on a given topic in several types of reference materials (e.g., dictionary, atlas, encyclopedia, newspaper). 3.3.10 Draw conclusions and make inferences about short passages (such as by identifying correct multiple choice answers or by writing short answers to questions). 3.3.11 Determine the appropriate reading strategy to acquire specific information (rereading, skimming, scanning). 3.3.12 Identify and apply appropriate strategies to aid comprehension (e.g., graphic organizers, outlining). R.4 FLUENCY 4.3.1 Date & Initial Read instructional level narrative and expository text aloud with fluency and accuracy, and with appropriate pacing, intonation, and expression. (Rubrics will be developed to measure this consistently.) 5 Performance Descriptors READING – LOW INTERMEDIATE – LEVEL 3 Each IGO must be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Vocabulary R.2.3.1 Use prefixes to determine the meaning of ten unfamiliar words; use suffixes to determine the meaning of ten unfamiliar words; use prefixes, suffixes, and root words to determine the meaning of ten unfamiliar words; use prefixes, suffixes, and root words to determine the antonyms of five unfamiliar words. (See also R.2.2.5) R.2.3.2 Use the context of a paragraph to determine the meaning of ten unfamiliar words at this level. (See also R.2.2.4) R.2.3.3 Read a minimum of 80% of the sight words from the 300-500 group of most frequently used words. R.2.3.4 Identify the meaning of ten frequently used synonyms, five antonyms, and five homographs. Comprehension R.3.3.1 Identify the main idea and two relevant supporting details of one passage. (See also WC.2.2.1, WC.2.2.2) R.3.3.2 Identify cause and effect signal words in ten sentences (e.g., as a result, because, consequently, thus). (See also WC.5.4.1) R.3.3.3 Follow the simple written multi-step instructions or diagrams for one task. (See also WC.2.2.5) R.3.3.4 Locate pertinent information in one multi-paragraph passage and apply it to answer ten questions. (See also WC.2.3.6, WC.2.3.7, WC.2.3.8) R.3.3.5 Locate pertinent information in one print material (e.g., ad, label, pay stub, public sign) and apply it to answer ten questions. R.3.3.6 Read and interpret simplified policies/procedures (e.g., simple employee handbook, payroll stub, driver’s manual) to answer ten questions. (See also WC.2.5.4) R.3.3.7 Use comparison and contrast to determine the best purchase of an advertised item. List at least four qualities that compare or contrast, and determine the best buy based on the information. (See also WC.2.3.4, WC.2.6.3) R.3.3.8 Answer at least ten questions from information gathered from one simple graphic material such as a chart, picture, map, sign, diagram, table, or graph. (See also R.3.2.11) R.3.3.9 Locate information on a given topic in two or more types of reference materials (e.g., dictionary, atlas, encyclopedia, newspaper). (See also WC.2.6.5, R.2.4.2, R.3.5.2 (Partial) R.3.3.10 Draw conclusions and make inferences to answer five questions on each of two short passages (such as by identifying correct multiple choice answers or by writing short answers to questions) for a total of ten questions. R.3.3.11 Look at two different passages and determine the appropriate reading strategies needed to acquire specific information from those passages (rereading, skimming, scanning, etc.). (See also WC.2.2.2, Advanced R.3.6.9) R.3.3.12 Identify and apply appropriate strategies to aid comprehension of one short paragraph (e.g., graphic organizers, outlining). (See also WC.2.5.3) Fluency R.4.3.1 Read aloud one passage from an instructional level narrative and/or expository text, with fluency and accuracy, and with appropriate pacing, intonation, and expression. Use the rubric to measure consistently. 6 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST READING Federal Functioning Level 4 – High Intermediate (6–8.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: R.2 VOCABULARY 2.4.1 2.4.2 2.4.3 2.4.4 2.4.5 Recognize and comprehend the meaning of moderately complex occupational, technical, and contentspecific vocabulary using word, sentence, and paragraph clues to determine meaning. Use a dictionary to locate the meaning of words used in a statement. Identify and interpret basic figurative language (e.g., similes, metaphors, pun, alliteration). Identify idioms and their use in passages. Recognize and understand clipped and shortened words (e.g., exam – examination). R.3 COMPREHENSION 3.4.1 3.4.2 3.4.3 3.4.4 Date & Initial Read and interpret information in common manuals and legal forms (e.g., driver’s manual, rental agreement). Read and interpret expository writing on common topics in newspapers, periodicals, and non-technical journals. Gather information from at least three reference materials (e.g., tables of contents, magazines, catalogs, Internet) and evaluate which information best serves the student’s purpose. Identify the implied main idea and supporting details from an instructionallevel passage. 3.4.5 3.4.6 3.4.7 3.4.8 3.4.9 3.4.10 3.4.11 Date & Initial 3.4.12 3.4.13 3.4.14 Determine the sequence of events in a written passage. Identify cause and effect implied in a paragraph. Predict probable outcomes from knowledge of events obtained from a reading selection. Determine author’s purpose (e.g., to entertain, inform, persuade) from a variety of written pieces (e.g., newspaper article, travel brochure, store catalog, ad). Distinguish factual information from opinion or fiction. Determine the meaning of persuasive language and propaganda used in functional text (e.g., advertisement). Integrate information from texts, charts, and graphs to draw a conclusion based on a given task. Use stated and suggested information to infer the meaning of a phrase used in context. Identify and use the structural features (e.g., headlines, table of contents, graphics) of newspapers, magazines, and editorials to gain meaning from text. Clarify understanding of non-fictional passages by creating outlines, graphic organizers, logical notes, summaries, or reports. 7 Performance Descriptors READING – HIGH INTERMEDIATE – LEVEL 4 Each IGO must be mastered with a minimum score of 80% Vocabulary R.2.4.1 Recognize and comprehend the meaning of ten moderately complex occupational, technical, and content-specific vocabulary words using word, sentence, and paragraph clues to determine meaning. (See also WC.2.5.4) R.2.4.2 Use a dictionary to locate the meaning of ten words used in a statement. (See also R.3.3.9) R.2.4.3 Identify and interpret ten basic figurative language expressions (e.g., similes, metaphors, pun, alliteration). R.2.4.4 Identify ten idioms and their uses in one short passage. R.2.4.5 Recognize and understand ten clipped and shortened words (e.g., exam-examination). Comprehension R.3.4.1 Read and answer five comprehension questions taken from a common manual or legal form (e.g., driver’s manual, rental agreement). (See also WC.2.5.4) R.3.4.2 Read and interpret one expository writing on a common topic in a newspaper, periodical, or non-technical journal. (See also WC.2.4.3, WC.2.5.3, R.3.4.4) R.3.4.3 From at least three reference materials (e.g., tables of contents, magazines, catalogs, Internet), collect information for one assignment and tell which information best serves the purpose of the assignment. (See also WC.2.6.5) R.3.4.4 Identify the implied main idea and at least two supporting details from an instructional level passage. R.3.4.5 Determine the sequence of events in one written passage. (See also WC.2.4.8) R.3.4.6 Identify cause and effect implied in one paragraph. (See also WC.2.6.3) R.3.4.7 Predict five or more probable outcomes from a knowledge of events obtained from one reading selection. R.3.4.8 Determine the author’s purpose (e.g., to entertain, inform, persuade) from any two of a variety of written pieces (e.g., newspaper article, travel brochure, store catalog, ad). (See also WC.2.4.3) R.3.4.9 Distinguish fact from opinion and fiction in ten or more sentences. (See also WC.2.4.5, WC.2.4.7) R.3.4.10 Determine the meaning of persuasive language and propaganda used in one functional text (e.g., advertisement) by identifying ten words and/or phrases as persuasive, emotional, and/or propaganda. (See also WC.2.4.7) R.3.4.11 Using at least two sources of information (texts, charts, and/or graphs), draw conclusions for two questions. R.3.4.12 Use stated and suggested information to infer the meaning of five phrases used in the context of sentences or paragraphs. R.3.4.13 Identify and use the structural features (e.g., headlines, table of contents, graphics) of newspapers, magazines, and editorials to gain meaning from text necessary to answer ten questions. R.3.4.14 Use an outline, graphic organizer, logical notes, summary, or report to show the meaning of a non-fictional passage. (See also WC.2.4.4, R.3.3.12) 8 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST READING Federal Functioning Level 5 – Low Adult Secondary (9–10.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: NOTE: Essential IGOs related to the GED Tests are underlined. R.2 VOCABULARY 2.5.1 Demonstrate understanding of specialized vocabulary from student’s chosen occupational field (e.g., electronics manual or nursing text). R.3 COMPREHENSION 3.5.1 Date & Initial Identify the inferred main idea from a multi-paragraph passage and restate it in your own words. 3.5.2 Locate information on a research topic from resources such as bibliographies and footnotes. 3.5.3 Read a technical manual or similar document and explain a sequential process about a complex and unfamiliar work procedure. 3.5.4 Identify the central idea or theme of a literary work (e.g., short story, drama, poetry). 3.5.5 Identify and interpret common figurative language (e.g., simile, metaphor, personification, exaggeration) found in a literary work. 3.5.6 Recognize literary devices (e.g., rhythm, rhyme) used in poetry. 3.5.7 Interpret information in real-life contexts (e.g., medical, occupational, parenting) and apply that information to a new situation. 3.5.8 Follow directions necessary to perform a moderately complex sequential task, then perform the task (e.g., review directions of a household task, perform the task, and report what happened). 3.5.9 Identify relationships between similar documents (e.g., order form and invoice) and compare information for accuracy. 3.5.10 Determine the writer’s point of view based on clues about the writer’s background, vocabulary used, or details that point toward the writer’s likes or dislikes. Date & Initial 3.5.11 Recognize differences in structure, content, and tone (feeling that the writer is trying to convey) of various texts (e.g., expository versus persuasion as in job applications, technical manual, almanac, advertisement). 3.5.12 Identify opinions, propaganda, and bias within written publications (e.g., newspaper, journals, magazines). 3.5.13 Create an illustration/graphic organizer to demonstrate the importance of, and relationship between, ideas. 3.5.14 Use context clues to establish word meaning, identifying specific words or wordings that are causing comprehension difficulties. 3.5.15 Identify a cause-effect relationship in a written passage by asking why something happened and what its results were. ADDITIONAL GED IGOS (not required for completion of FFL) Date & Initial GED.5.1 Identify the elements of a plot (beginning-exposition, middlecomplications and climax, endresolution) within a literary work. GED.5.2 Predict what a character might say or do based on the character’s actions and how he/she reacts to events in a story. 9 Performance Descriptors READING – LOW ADULT SECONDARY – LEVEL 5 Each IGO must be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Vocabulary R.2.5.1 Demonstrate understanding of ten specialized vocabulary words from the student’s chosen occupational field (e.g., electronics manual or nursing text). (See also WC.2.3.1, R.2.4.1) Comprehension R.3.5.1 Identify the inferred main idea from one multi-paragraph passage and restate it in student’s own words. R.3.5.2 Locate at least one fact on a research topic from a bibliography or footnote and write the sources for the information and the bibliography (or footnote). (See also WC.2.6.5, WC.2.6.6, R.3.3.9) R.3.5.3 Read and explain a sequential process about a complex and unfamiliar work procedure found in a technical manual or similar document. (See also WC.2.2.5, WC.2.4.2, WC.2.5.4) R.3.5.4 Identify the central ideas or themes of three literary works (short story, drama, poetry). (See also WC.2.3.2) R.3.5.5 Identify and interpret ten examples of common figurative language (e.g., simile, metaphor, personification, exaggeration) in one or more literary works. R.3.5.6 Recognize five examples of literary devices (rhythm, rhyme) used in a poem. R.3.5.7 Interpret information in one real-life context (e.g., medical, occupational, parenting) and apply that information to a new situation. R.3.5.8 Follow directions necessary to perform a moderately complex sequential task with at least five steps, then perform the task (e.g., review directions of a household task, perform the task, and report what happened). R.3.5.9 Identify five relationships between two similar documents (e.g., order form and invoice) and compare five items for accuracy. (See also WC.2.3.4) R.3.5.10 Determine a writer’s point of view based on clues about the writer’s background, vocabulary used, or details that point toward the writer’s likes or dislikes in one or more of the writer’s literary pieces. R.3.5.11 Recognize the differences in structure, content, and/or tone (feeling that the writer is trying to convey) in at least four various texts (e.g., expository versus persuasion as in job applications, technical manual, almanac, advertisement). R.3.5.12 Identify five opinions, propaganda, and/or biased statements within written publications (e.g., newspaper, journals, magazines). R.3.5.13 Create an illustration/graphic organizer to demonstrate the importance of and relationship between two or more ideas. (See also WC.2.5.3) R.3.5.14 Use context clues to establish ten word meanings in ten sentences, identifying specific words or wordings that are causing comprehension difficulties. R.3.5.15 Identify a cause-effect relationship in a written passage by asking why something happened and what its results were. 10 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST READING Federal Functioning Level 6 – High Adult Secondary (11–12.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: NOTE: Essential IGOs related to the GED Tests are underlined. R.2 VOCABULARY 2.6.1 Demonstrate understanding of specialized vocabulary from a research periodical. R.3 COMPREHENSION 3.6.1 3.6.2 3.6.3 3.6.4 3.6.5 3.6.6 3.6.7 3.6.8 Date & Initial Follow complex instructions or directions that include conditionals (e.g., if and then statement) and multiple steps. Identify directly stated and inferred main ideas based on stated and suggested information. Put together clues or details to reach a logical conclusion when facts are not stated directly. Draw conclusions substantiated by text (e.g., read two educational catalogs to determine which offers the best program of study for a particular career choice). Make generalizations from implicit ideas (e.g., first paragraph of The Declaration of Independence). Locate specific information in a text, classifying the information as necessary or unnecessary to understanding the text (e.g., essential facts versus supplementary description, author’s biographical background). Analyze a character in a fictional passage by identifying the character’s appearance, behaviors, actions, and dialogue with other characters. Differentiate between fact and opinion in order to make decisions by comparing facts (e.g., consumer magazines, travel brochures, letters to the Editor). 3.6.9 3.6.10 Date & Initial 3.6.11 3.6.12 3.6.13 3.6.14 Skim for overall understanding and scan for keywords and ideas (e.g., yellow pages, classified job ads). Identify the writer’s style (e.g., repetition of a key word, use of a string of opposites) used to convey ideas. Determine the tone (feeling that the writer is trying to convey) of real-life writing samples (e.g., brochures, editorials, magazine articles). Create graphic organizers to compare and contrast ideas within text. Use context clues to establish word meaning, identifying specific words or wordings that are causing comprehension difficulties. Summarize the main idea of a passage by answering who, what, when, why, and how questions. ADDITIONAL GED IGOS (not required for completion of FFL) Date & Initial GED.6.1 Compare and contrast the personalities of two characters in a story. GED.6.2 Identify the theme or moral of a short story and a play. GED.6.3 Identify a symbol used in a poem to represent a person, place, or thing. GED.6.4 Identify phrases or words that the author used to create an image or mental picture in a poem. GED.6.5 Determine a character’s motivation (the reason a character does or says something) in a play by examining the character’s dialogue, actions, and stage directions. 11 Performance Descriptors READING – HIGH ADULT SECONDARY – LEVEL 6 Each IGO must be mastered with a minimum score of 80% Vocabulary R.2.6.1 Write the meaning of ten specialized vocabulary words from a research periodical. Comprehension R.3.6.1 Follow complex instructions or directions that include conditionals (e.g., if and then statement) and multiple steps for one task. (See also Preliminary WC.2.2.5, Preliminary WC.2.4.2, Preliminary R.3.2.8) R.3.6.2 Identify directly stated and inferred main ideas based on stated and suggested information in one passage. R.3.6.3 List clues or details to reach two logical conclusions when facts are not stated directly in passages. R.3.6.4 Draw conclusions substantiated by text (e.g., read two educational catalogs to determine which offers the best program of study for a particular career choice). (See also R.3.6.12, Preliminary R.3.2.4) R.3.6.5 Make five generalizations from implicit ideas (e.g., first paragraph of The Declaration of Independence). R.3.6.6 Locate specific information in a text, classifying and explaining at least five pieces of information as necessary or unnecessary to the understanding of the text (e.g., essential facts versus supplementary description, author’s biographical background). R.3.6.7 Analyze a character in one fictional passage by identifying the character’s appearance, behaviors, actions, and dialogue with other characters. (See also WC.2.6.1) R.3.6.8 Using real-life materials (e.g., consumer magazines, travel brochures, letters to the Editor), make a decision by differentiating between the facts and the opinions expressed in the documents. List at least five facts and five opinions found in the documents. (See also WC.2.6.3, Preliminary R.3.2.3) R.3.6.9 Skim a passage for overall understanding of a page and scan a page for five key words and ideas (e.g., yellow pages, classified job ads). (See also Preliminary WC.3.3.11) R.3.6.10 Identify the writer’s style in two short passages (e.g., repetition of a key word, use of a string of opposites) used to convey ideas. R.3.6.11 Determine the tone (feeling that the writer is trying to convey) of five real-life writing samples (e.g., brochures, editorials, magazines articles). (See also R.3.5.11) R.3.6.12 Use an appropriate graphic organizer to compare and contrast ideas within one passage of a text on student’s level. (See also Preliminary WC.2.3.4, WC.2.5.3, WC.2.6.3) R.3.6.13 Using context clues to identify and establish the word meanings of ten specific words or wordings that are causing comprehension difficulties. (See also Preliminary R.3.4.12, R.3.5.12) R.3.6.14 Summarize the main idea of one passage by answering who, what, when, why, and how questions. (See also Preliminary WC.2.3.1) 20 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST ABE WRITING/COMPOSITION Federal Functioning Level 1 – Beginning Literacy (0-1.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: WC.1 READABILITY/ACCURACY Date & Initial 1.1.1 Recognize and copy manuscript letters of the alphabet and numerals to 100. 1.1.2 Write numerals (0 – 20) from memory. 1.1.3 Write uppercase and lowercase letters from memory. 1.1.4 Recognize and write common symbols (+, -, $, #, @). 1.1.5 Write words identifying objects in the classroom, home, or workplace. 1.1.6 Write personal information (name, age, address, phone number, date of birth, Social Security number) and dates (words, abbreviations, and numbers) accurately on a simple form and from dictation. 1.1.7 Space words to form sentences. 1.1.8 Accurately copy at least one paragraph of written material. WC.2 COMPOSITION Date & Initial 4.1.1 Distinguish among declarative, imperative, interrogative, and exclamatory sentences when presented orally by the instructor. 4.1.2 Correctly punctuate simple sentences with commas and end punctuation including periods, question marks, and exclamation marks. 4.1.3 Correctly punctuate abbreviations of common titles such as Mr., Mrs., Ms., etc. WC.5 GRAMMATICAL CONCEPTS/SENTENCE STRUCTURE Date & Initial 2.1.1 Use the freewrite strategy (without regard to punctuation and capitalization) to compose simple, original sentences. 2.1.2 Revise simple sentences for completeness, punctuation, and capitalization. WC.3 CAPITALIZATION WC.4 PUNCTUATION 5.1.1 Identify nouns and verbs in a sentence. 5.1.2 Identify the subject and predicate in a sentence. 5.1.3 Make subjects and verbs agree in sentences. 5.1.4 Write three related sentences which are correctly capitalized, punctuated, and grammatically correct (i.e., simple story, phone message, etc.). WC.6 VERB TENSE Date & Initial Date & Initial Date & Initial 6.1.1 Compose simple sentences (about self, family, country, work, etc.) in both present and past tense. 3.1.1 Correctly capitalize simple sentences including sentence beginnings and the pronoun “I”. 3.1.2 Capitalize proper nouns which include names, titles, places, and abbreviations. 21 Performance Descriptors WRITING/COMPOSITION – BEGINNING LITERACY – LEVEL 1 Each IGO must be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Readability WC.1.1.1 Using a reference model (for either standard or D’Nelian manuscript), copy the twenty-six uppercase and twenty-six lowercase letters of the manuscript alphabet. Using a reference model, copy at least ten missing numerals in a chart of numbers from 1-100. (See also R.1.1.2) WC.1.1.2 From memory, write the numerals from zero to twenty in sequence without prompts. (See also R.2.1.3) WC.1.1.3 From memory, write the twenty-six uppercase and twenty-six lowercase letters of the manuscript alphabet in sequence. (See also R.1.1.2, R.3.2.2) WC.1.1.4 Identify and write ten common symbols (+, -, $, #, @, %, &, *, =, ¢). (See also R.2.1.4) WC.1.1.5 Copy two or more sentences of written material using correct spacing between letters, word, and sentences to make them clear, neat, and readable. (See also WC.1.1.8) WC.1.1.8 Accurately copy one paragraph of five sentences or more of written material using correct spacing, spelling, and clear, neat, and readable handwriting. (See also WC.1.1.7) Composition WC.2.1.1 Use the freewrite strategy (without regard to punctuation and capitalization) to compose five or more simple, original sentences. (See also WC.2.1.2) WC.2.1.2 Revise five or more simple sentences of the writer’s composition for completeness, punctuation, and capitalization. Use the freewrite composition in WC.2.1.1 or the provided sentences. (See also WC.2.1.1) Capitalization WC.3.1.1 Edit the beginnings of sentences and the pronoun “I” for capitalization in five or more sentences. (See also WC.3.1.2) WC.3.1.2 Edit twenty proper nouns including names, titles, places, and abbreviations for capitalization. (See also WC.3.1.1) Punctuation WC.4.1.1 When a minimum of ten sentences are read by the instructor, identify each sentence as either “telling” (for declarative), “commanding” (for imperative), “questioning” (for interrogative), or “exclaiming” (for exclamatory). WC.4.1.2 Correctly punctuate ten or more simple, written sentences with commas for dates, and the correct end punctuation for declarative, interrogative, exclamatory, and imperative sentences. (See also WC.4.1.3) WC.4.1.3 In ten or more sentences, correctly punctuate abbreviations of titles such as Mr., Mrs., Ms., Dr., Jr., Sr., and any other titles that are used commonly when writing to people or when addressing them. Grammatical Concepts/Sentence Structure WC.5.1.1 Identify the nouns (common and proper) in ten sentences and the verbs in ten sentences. WC.5.1.2 Identify the simple subject and the simple predicate in ten or more written sentences. WC.5.1.3 Make simple subjects and simple verbs agree in ten or more written sentences. WC.5.1.4 Choose an idea and compose three related sentences that are correctly capitalized, punctuated, and grammatically correct (i.e., short story, phone message, etc.) or edit three sentences composed for WC.6.1.1. (See also WC.6.1.1) Verb Tense WC.6.1.1 Compose three simple, original sentences in the present tense and three in the past tense about self, family, country, work, etc. 22 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST ABE WRITING/COMPOSITION Federal Functioning Level 2 – Beginning Basic Education (Level 2.0–3.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: WC.1 READABILITY/ACCURACY 1.2.1 1.2.2 Write short sentences from dictation. Recognize and copy both capital and lowercase cursive letters of the alphabet. WC.2 COMPOSITION 2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.3 2.2.4 2.2.5 Date & Initial WC.4 PUNCTUATION 4.2.1 4.2.2 Date & Initial Compose topic sentences on five selected topics. Generate at least two supporting sentences for five topic sentences. Use the brainstorming, clustering, and freewriting steps of the writing process to create three original paragraphs that include topic sentences and at least two supporting details each. Use the proofreading step of the writing process to edit original paragraphs for spelling and capitalization. Compose a simple set of instructions for common tasks sequencing at least four steps. 4.2.3 5.2.2 6.2.1 3.2.1 Date & Initial Date & Initial Change fragments and run-ons to complete sentences. Combine simple sentences to form compound sentences using commas and conjunctions. WC.6 VERB TENSE AND USAGE 6.2.2 WC.3 CAPITALIZATION Use commas to correctly punctuate items in a series, dates, and addresses. Use commas to correctly punctuate the salutation and the closing of a personal letter. Use apostrophes to form contractions. WC.5 GRAMMATICAL CONCEPTS/SENTENCE STRUCTURE 5.2.1 Date & Initial Date & Initial Write the appropriate forms of common regular and irregular verbs (am/is, was/were, has/have, go/went). Make pronouns and antecedents agree in number and gender. Capitalize the inside address, salutation, and closing of a letter. 23 Performance Descriptors WRITING/COMPOSITION – BEGINNING BASIC EDUCATION – LEVEL 2 Each IGO must be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Readability WC.1.2.1 Correctly write from dictation five or more simple sentences which use phonetically regular words or words from high frequency word lists for Levels 1 and 2. (The 300 most frequently used words are available on the Internet.) WC.1.2.2 Using a reference model (for either standard or D’Nelian cursive), copy both the twenty-six capital and twenty-six lowercase cursive letters of the alphabet. Composition WC.2.2.1 Compose a minimum of five complete, original topic sentences. (See also R.3.3.1) WC.2.2.2 Compose a minimum of two supporting sentences for each of the five topic sentences composed in WC.2.2.1. (See also R.3.2.1) WC.2.2.3 Use the brainstorm process to list ideas for the development of a minimum of three different paragraph topics. Follow with clusters (idea maps) and the freewriting technique to compose three paragraphs. Include a minimum of two supporting details in each paragraph. (See also R.3.2.11) WC.2.2.4 Use the proofreading step of the writing process to edit for completeness, spelling, and capitalization the three original paragraphs composed in WC.2.2.3 or edit another set of three paragraphs composed by the student. WC.2.2.5 Compose a simple set of instructions for one or more common tasks by sequencing at least four steps. (See also R.3.1.3, R.3.1.5, R.3.2.8, R.3.2.9, R.3.3.3) Capitalization WC.3.2.1 Capitalize the inside address, greeting (salutation), and closing of one personal and one business letter. (See also WC.4.2.2) Punctuation WC.4.2.1 Use commas to correctly punctuate seven or more sentences with items in a series, in dates, and in addresses. WC.4.2.2 Use commas to correctly punctuate the salutation and closing of four different types of personal letters. (See also WC.3.2.1) WC.4.2.3 Use apostrophes to form common contractions in twenty-five or more sentences. (See also WC.4.2.1, WC.4.2.2 – may be put into a combined exercise) Grammatical Concepts/Sentence Structure WC.5.2.1 Change the fragments and run-ons in a paragraph to make ten complete sentences. WC.5.2.2 Combine a minimum of ten simple sentences to form five compound sentences using commas and conjunctions as needed. Verb Tense and Usage WC.6.2.1 Write the correct form of regular verbs (walk, want, etc.) and irregular verbs (swim, bring, dive, take, etc.) in at least twenty sentences. (See also WC.2.2.3) WC.6.2.2 Make pronouns and their antecedents agree in number and gender when used in at least ten or more sentences. 24 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST ABE WRITING/COMPOSITION Federal Functioning Level 3 – Low Intermediate Basic Education (Level 4.0–5.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: WC.1 READABILITY/ACCURACY Date & Initial 2.3.1 2.3.2 2.3.3 2.3.4 2.3.5 2.3.6 2.3.7 2.3.8 2.3.9 Write a short summary for each of three separate paragraphs on topics of interest to the student. Write correctly punctuated and constructed (with topic sentence, at least two supporting sentences, and a conclusion sentences) narrative paragraphs from personal stories using chronological order. Write correctly punctuated and constructed (with topic sentence, at least two supporting details, and a conclusion sentence) descriptive paragraphs on places visited or other familiar topics. Compare and contrast three sets of objects using correctly punctuated and complete sentences. Define and identify the elements of an essay (introductory paragraph, supporting body paragraphs, and a conclusion paragraph). Develop an introductory paragraph on a familiar topic. Develop three support paragraphs for the topic in 2.3.6. Write a conclusion paragraph for the topic and support paragraphs in 2.3.6 and 2.3.7. Compose a business letter (i.e., thank you letter, letter of application, etc.). Date & Initial 3.3.1 Capitalize proper nouns as in the days of weeks, months, holidays, book titles, television shows, and continents. Not at this level WC.2 COMPOSITION WC.3 CAPITALIZATION Date & Initial WC.4 PUNCTUATION Date & Initial 4.3.1 Correctly punctuate a series of sentences using apostrophes for both possessives and contractions. 4.3.2 Use commas to correctly punctuate complex sentences. WC.5 GRAMMATICAL CONCEPTS/SENTENCE STRUCTURE Date & Initial 5.3.1 Combine simple sentences to form complex sentences. WC.6 VERB TENSE AND USAGE Date & Initial 6.3.1 Identify phrases and clauses. 6.3.2 Make pronouns and antecedents agree in number and gender, as well as with the verb. 25 Performance Descriptors WRITING/COMPOSITION – LOW INTERMEDIATE – LEVEL 3 Each IGO must be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Readability Not at this level. Composition WC.2.3.1 Write three short summaries on three individual paragraphs that are on topics of interest to the student. (See also R.3.2.7, R.3.3.10, R.2.5.1) WC.2.3.2 Using the writing process of brainstorming, clustering (mapping), freewriting, proofreading, and revising, write two or more correctly punctuated and constructed narrative paragraphs (with topic sentence, at least two supporting sentences, and a conclusion sentence) from personal stories using chronological order. (See also R.3.2.9) WC.2.3.3 Using the writing process of brainstorming, clustering (mapping), freewriting, proofreading, and revising, write three or more correctly punctuated and constructed descriptive paragraphs (with topic sentence, at least two supporting details, and a conclusion sentence) on familiar topics. WC.2.3.4 Using the writing process, compare and contrast three sets of objects. Write four sentences for each set, which include two contrast sentences and two comparison sentences, and at least one compound and one complex sentence in each set. (See also R.3.1.2, R.3.37, R.3.3.12, Advanced R.3.5.9) WC.2.3.5 Define and label the elements of one essay including the introductory paragraph, the supporting paragraphs body, and a conclusion paragraph. WC.2.3.6 Using the writing process, develop one well-constructed introductory paragraph (a topic sentence, two supporting sentences, and a transition sentence [carries the reader into the essay]) on a familiar topic. (See also R.3.3.1) WC.2.3.7 Following the writing process, develop three well-constructed supporting paragraphs (topic sentence, two supporting sentences, and a transition/conclusion sentence) for the topic in WC.2.3.6. (See also R.3.3.4) WC.2.3.8 Following the writing process, write a well-constructed conclusion paragraph (a topic sentence, re-statement of the three supporting details, and a conclusion sentence) for the topic and support paragraphs in WC.2.3.6 and WC.2.3.7. WC.2.3.9 Write a business letter with real-life content (i.e., thank you letter, letter of application, etc.) containing the date, inside address, salutation, body, complimentary close, and signature. (See also R.3.3.10) Capitalization WC.3.3.1 Capitalize proper nouns as in the days of weeks, months, holidays, book titles, television shows, and continents in fifty or more examples. Punctuation WC.4.3.1 Correctly punctuate a minimum of twenty examples of using apostrophes for both possessives and contractions in sentences. (See also WC.4.2.3) WC.4.3.2 Use commas to correctly punctuate at lease five complex sentences. (See also WC.5.3.1) Grammatical Concepts/Sentence Structure WC.5.3.1 Combine simple sentences to form at least five complex sentences. (See also WC.4.3.2) Verb Tense and Usage WC.6.3.1 Identify prepositional phrases, independent clauses, and dependent clauses in ten or more sentences. WC.6.3.2 Make singular and plural pronouns agree with their antecedents in number and gender, as well as with the verb in ten or more sentences. (See also WC.6.2.2) 26 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST ABE WRITING/COMPOSITION Federal Functioning Level 4 – High Intermediate Basic Education (Level 6.0–8.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: NOTE: Essential IGOs related to the GED Tests are underlined. WC.1 READABILITY/ACCURACY Date & Initial 2.4.8 Not at this level. WC.2 COMPOSITION 2.4.1 2.4.2 2.4.3 2.4.4 2.4.5 2.4.6 2.4.7 Compose sentences including simple, compound, complex, compoundcomplex using commas, semicolons, and colons. Synthesize (process and condense) and write oral instructions. Write correctly punctuated and constructed (topic sentence, at least two supporting sentences, and a conclusion sentence) expository paragraphs detailing recipes, how to do a project, etc. Write for different audiences (children, utility company, lawyer). Using the writing process, brainstorm and cluster ideas to develop a topic for an expository essay. Compose a personal opinion letter to the editor of a newspaper which consists of at least three paragraphs. Using the writing process, freewrite an expository essay (using an introduction paragraph, at least two supporting paragraphs, and a conclusion paragraph). Using correct essay structure, write a persuasive piece based upon a personal opinion. Date & Initial Following the writing process, proofread and re-write expository essays to assure correct punctuation, spelling, grammar, cohesiveness (remaining on topic), clarity, and logical organization. WC.3 CAPITALIZATION 3.4.1 Appropriately use all forms of capitalization. WC.4 PUNCTUATION 4.4.1 6.4.2 Date & Initial Recognize how parts of a sentence are used to manipulate meaning in sentences (independent clauses, introductory clauses and phrases, etc.). WC.6 VERB TENSE AND USAGE 6.4.1 Date & Initial Appropriately use all forms of punctuation. WC.5 GRAMMATICAL CONCEPTS/SENTENCE STRUCTURE 5.4.1 Date & Initial Date & Initial Demonstrate mastery of past and present tense. Establish and maintain tense in a writing piece. 27 Performance Descriptors WRITING/COMPOSITION – HIGH INTERMEDIATE – LEVEL 4 Each IGO must be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Readability Not at this level. Composition WC.2.4.1 Correctly identify and compose sentences of various types, including at least two examples of each of the following: simple, compound (using commas and semi-colons), complex (using commas), and compoundcomplex (using commas and either semi-colons or colons). (See also previous activities WC.5.1.4, WC.5.2.2, WC.4.3.2, WC.5.3.1) WC.2.4.2 From dictation, write a minimum of two sets of instructions. WC.2.4.3 Using the writing process, compose a minimum of two independent, correctly punctuated and constructed expository paragraphs (containing a topic sentence, at least two supporting sentences, and a conclusion sentence) that explain, inform, or instruct (such as a recipe). (See also R.3.4.8, R.3.4.2, previous activity WC.3.2.1) WC.2.4.4 Using the writing process, brainstorm and cluster ideas to develop at least one topic for an expository essay. (See also R.3.4.14) WC.2.4.5 Compose at least one personal opinion, three-paragraph letter to the editor of a local newspaper. WC.2.4.6 Using the writing process, freewrite at least one expository essay (using an introduction paragraph, at least two supporting paragraphs, and a conclusion paragraph). (See also previous activities R.3.2.3, WC.2.4.4) WC.2.4.7 Using correct essay structure (an introductory paragraph, at least two supporting paragraphs, and a conclusion paragraph), write one persuasive piece based upon a personal opinion. (See also R.3.4.9, previous activities WC.3.2.3) WC.2.4.8 Using the writing process, proofread and re-write two expository essays to assure correct punctuation, spelling, grammar, cohesiveness (remaining on topic), clarity, and logical organization. (You may use essays written for WC.2.4.6 and WC.2.4.7). Capitalization WC.3.4.1 Appropriately use all forms of capitalization in twenty or more sentences that contain level-appropriate vocabulary. (See also WC.3.1.2, WC.3.1.1, WC.3.2.1, WC.3.3.1) Punctuation WC.4.4.1 Appropriately use all forms of punctuation in twenty or more sentences that use level-appropriate vocabulary. (See also WC.4.1.1, WC.4.1.2, WC.4.2.3, WC.4.3.1, WC.4.3.2) Grammatical Concepts/Sentence Structure WC.5.4.1 Use sentence parts to manipulate emphasis or meaning in ten or more sentences (independent clauses, introductory clauses and phrases, etc.) Verb Tense and Usage WC.6.4.1 Correctly apply past and present tenses for regular and irregular verbs in a minimum of twenty sentences. WC.6.4.2 Establish and maintain correct verb tense throughout at least one paragraph. 28 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST ABE WRITING/COMPOSITION Federal Functioning Level 5 – Low Adult Secondary Education (Level 9.0–10.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: NOTE: Essential IGOs related to the GED Tests are underlined. WC.1 READABILITY/ACCURACY Date & Initial WC.3 CAPITALIZATION 3.5.1 Not at this level. WC.2 COMPOSITION 2.5.1 2.5.2 2.5.3 2.5.4 doc 2.5.5 2.5.6 Using the writing process (brainstorm, cluster, freewrite, and correct essay structure), compose a persuasive essay. Following the writing process, proofread and re-write the persuasive essay in 2.5.1. to assure sentence variety, correct punctuation, correct grammar usage, cohesiveness, and relevant supporting details. Write an analysis of articles from primary sources or professional journals using cause and effect or comparison and contrast. Analyze and write critiques of business and technical documents. Compose an expository writing piece from a given prompt. Compose a formal business letter. Date & Initial Appropriately use all forms of capitalization in all composition pieces within the instructional level (i.e., events, titles of books, etc.). WC.4 PUNCTUATION 4.5.1 Date & Initial Use the Edited American English rules to edit all documents (in particular, sentence structure and intended meaning) as well as unity in the writing. WC.6 VERB TENSE AND USAGE 6.5.1 Date & Initial Appropriately use all forms of punctuation (including quotations, parentheses, and brackets) in all composition pieces within the instructional level. WC.5 GRAMMATICAL CONCEPTS/SENTENCE STRUCTURE 5.5.1 Date & Initial Date & Initial Use tense change in narrative writing to maintain cohesiveness. 29 Performance Descriptors WRITING/COMPOSITION – LOW ADULT SECONDARY EDUCATION – LEVEL 5 Each IGO should be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Readability Not at this level. Composition WC.2.5.1 Using the writing process (brainstorm, cluster, freewrite) and correct essay structure (one introduction paragraph, at least two supporting paragraphs, and at least one conclusion paragraph), compose one persuasive essay. (See also WC.2.4.7) *WC.2.5.2 Following the writing process, proofread, revise, and re-write the persuasive essay in WC.2.5.1 to assure sentence variety, correct punctuation, correct grammar usage, correct capitalization, cohesiveness, and relevant supporting details. (See also WC.2.5.1, WC.2.4.8) *WC.2.5.3 Either use cause and effect to analyze one article from a primary source or use comparison and contrast to analyze two articles from professional journals. Be sure to use the entire writing process (brainstorming, clustering, freewriting, proofreading, revising, and re-writing) in composing the analysis. (See also previous activities R.3.2.4, R.3.2.11, R.3.3.12, R.3.4.2, R.3.4.6) *WC.2.5.4 Using the entire writing process (brainstorming, clustering, freewriting, proofreading, revising, and re-writing), analyze and compose one critique of a business document and one critique of a technical document. (See also previous activities R.3.2.11, R.3.3.6, R.3.4.1, R.3.4.1, Advanced R.3.5.3) *WC.2.5.5 Using the entire writing process (brainstorming, clustering, freewriting, proofreading, revising, and re-writing), write one expository writing piece from a given prompt. (See also previous activities WC.2.4.3, WC.4.5.1) WC.2.5.6 Compose at least one formal business letter using block format or modified/semi-block format and correct letter structure. Capitalization WC.3.5.1 Appropriately use all forms of capitalization (including sentence beginnings, planets, geographic regions, days, months, books, movies, proper adjectives, proper pronouns, quotations, continents, and proper nouns) on an exercise or in an essay with at least 40 examples. (See also previous activities WC.3.1.1, WC.3.2.1, WC.3.3.1) Punctuation WC.4.5.1 Appropriately use all forms of punctuation in an exercise with at least 36 examples (including titles of books, movies, ships, etc.; compound, complex, or compound-complex sentences; contractions and possessives; commas in a series, in dates, and in addresses; quotation marks for quotes and/or references; and parentheses and/or brackets) or in composition settings addressing the same. Grammatical Concepts/Sentence Structure WC.5.5.1 Edit a minimum of two narrative, expository, persuasive, or general information documents using the Edited American English rules. Verb Tense and Usage WC.6.5.1 Use correct tense change in one narrative paragraph or essay to maintain cohesiveness. *Students must be required to show the entire writing process on only one of these activities. 30 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST ABE WRITING/COMPOSITION Federal Functioning Level 6 – High Adult Secondary Education (Level 11.0–12.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: NOTE: Essential IGOs related to the GED Tests are underlined. WC.1 READABILITY/ACCURACY Date & Initial Not at this level. WC.2 COMPOSITION 2.6.1 2.6.2 2.6.3 2.6.4 2.6.5 2.6.6 Write character analyses including role, impact, personality traits, physical attributes, and symbolic meaning. Write a parody of a famous speech or short literary work. Develop up-to-date personal resume or write an autobiographical sketch. Use compare and contrast to write an advertisement marketing a new product. Identify the parts of a research paper. Using electronic resources, complete a research project on a career or a parenting issue which includes a bibliography. WC.3 CAPITALIZATION 3.6.1 Date & Initial Appropriately use all forms of capitalization in all composition pieces (especially in references, quotations, and the bibliography). WC.4 PUNCTUATION 4.6.1 Date & Initial Use the Edited American English rules to edit all documents. WC.6 VERB TENSE AND USAGE 6.6.1 Date & Initial Appropriately use all forms of punctuation in all composition pieces (including the use of punctuation for sentence variety, the titles of literary works, etc.). WC.5 GRAMMATICAL CONCEPTS/SENTENCE STRUCTURE 5.6.1 Date & Initial Date & Initial Control verb and language usage to maintain cohesiveness, tone, and unity. 31 Performance Descriptors WRITING/COMPOSITION – HIGH ADULT SECONDARY EDUCATION – LEVEL 6 Each IGO should be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Readability Not at this level. Composition WC.2.6.1 After reading a short fictional passage with at least two characters, write a character analysis of the characters to include role, impact, personality traits, physical attributes, and symbolic meaning. (See also R.3.6.7) WC.2.6.2 Write a parody of at least one famous speech or at least one short literary work. WC.2.6.3 Develop one up-to-date personal resume that is usable in the workplace for a desired position, or write an autobiographical sketch. WC.2.6.4 Use a compare and contrast organizational model such as a Venn diagram or an H-map to develop advertisement marketing for one or more new products. (See also Preliminary R.3.3.7, R. 3.6.8) WC.2.6.5 Using a prepared paper, identify the parts of a research paper by naming them. WC.2.6.6 Using electronic resources such as the Internet, write one 500-word research paper with bibliography on a career of choice or on a parenting issue using the entire writing process. (See also Preliminary R.3.3.9, R.3.4.3, R.3.5.2) Capitalization WC.3.6.1 Appropriately use all forms of capitalization in compositions especially research papers that have references, quotations, and a bibliography. Coordinate with WC.2.6.6. (See also WC.2.6.6) Punctuation WC.4.6.1 Appropriately use all forms of punctuation in one or more composition pieces written for Level 6 IGOs, including WC.2.6.1, WC.2.6.2, WC.2.6.4, WC.2.6.6. (See also WC.2.6.1, WC.2.6.2, WC.2.6.4, WC.2.6.6) Grammatical Concepts/Sentence Structure WC.5.6.1 Use the Edited American English rules to edit one or more documents created for Level 6 IGOs, such as WC.2.6.1, WC.2.6.2, WC.2.6.4, WC.2.6.6 WC.6.61, or a newly created document. (See also WC.2.61, WC.2.6.2, WC.2.64, WC.2.6.6, WC.6.6.1) Verb Tense and Usage WC.6.6.1 Control verb and language usage to maintain cohesiveness in one or more documents or essays. (See also WC.6.5.1) 32 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST ABE MATHEMATICS Federal Functioning Level 1 – Beginning Literacy (0–1.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: M.0 PRE-COMPUTATIONAL MATH SKILLS 0.1.1 0.1.2 0.1.3 0.1.4 Recognize and count numbers through 999. Count by twos, fives, and tens to 100. Identify even and odd numbers. Identify missing numbers in a sequence. M.1 WHOLE NUMBERS 1.1.1 1.1.2 1.1.3 Date & Initial M.3 FRACTION 3.1.1 Identify fractional parts (1/4, 1/3, 1/2) and whole. M.9 UNITS OF TIME AND MEASUREMENT Date & Initial Add whole numbers up to three digits (without carrying). Subtract whole numbers up to three digits (without borrowing). Multiply whole numbers through twelve using numerals. 9.1.1 9.1.2 9.1.3 2.1.1 2.1.2 Date & Initial Date & Initial Read time to the nearest hour and half hour. Understand use of standard linear measurements (inches, feet). Understand use of standard measurements (cups, pints, quarts, and gallons). M.13 GEOMETRY M.2 COUNT MONEY AND MAKE CHANGE Date & Initial Date & Initial 13.1.1 Identify and describe triangles, squares, rectangles, and circles. Recognize currency (up to $20.00) and coins; count and trade pennies, nickels, dimes, and quarters to 100 cents. Count back change (up to $5.00) using coins and currency. (Ex., The student will count change to be received from a $5.00 bill used for a $1.70 purchase.) 33 Performance Descriptors MATHEMATICS – BEGINNING LITERACY – LEVEL 1 Each IGO should be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Pre-Computational Math Skills M.0.1.1 Recognize and count numbers through 999 by completing a number chart with random prompts. M.0.1.2 Count by twos, fives, and tens to one hundred, either orally or through a written exercise. M.0.1.3 Identify a minimum of ten even and odd numbers. M.0.1.4 Identify a minimum of ten missing numbers in a sequence. Whole Numbers M.1.1.1 Complete a minimum of ten problems that require adding whole numbers up to three digits (without carrying). M.1.1.2 Complete a minimum of ten problems that require subtracting whole numbers up to three digits (without borrowing). M.1.1.3 Complete a minimum of ten problems that require multiplying whole numbers through twelve using numerals. Count Money and Make Change M.2.1.1 Complete a minimum of ten problems that require recognizing currency (up to $20.00) and coins; complete a minimum of ten problems that require counting and trading pennies, nickels, dimes, and quarters to 100 cents. M.2.1.2 Given a minimum of ten different situations, count back change (up to $5.00) using coins and currency. (Ex., The student will count change to be received from a $5.00 bill used for a $1.70 purchase.) Fractions M.3.1.1 Identify a minimum of two examples each of the fractional parts (1/4, 1/3, 1/2) and whole. Units of Time and Measurement M.9.1.1 Complete a minimum of five problems that require reading time to the nearest hour and five problems to the nearest half hour. M.9.1.2 Complete a minimum of ten statements that demonstrate an understanding of linear measurement. (For example, the length of a book is measured in (a) inches (b) feet.) M.9.1.3 Complete a minimum of ten problems that demonstrate an understanding of standard measurements (cups, pints, quarts, and gallons). For example, a glass of milk is measured in (a) quarts (b) cups (c) pints. Geometry M.13.1.1 Identify a triangle, square, rectangle, and circle; draw an example of each. 34 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST ABE MATHEMATICS Federal Functioning Level 2 – Beginning Basic (Level 2–3.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: M.1 WHOLE NUMBERS 1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3 1.2.4 1.2.5 1.2.6 Identify place value to at least the thousands place. Add whole numbers up to three digits using carrying. Subtract whole numbers up to three digits using borrowing. Multiply whole numbers up to three digits using carrying. Divide whole numbers up to hundreds by one digit. Solve single-step, real-life word problems involving addition and subtraction using up to three-digit whole numbers. M.3 FRACTIONS 3.2.1 Use rounding and estimation for tens and hundreds. M.9 UNITS OF TIME AND MEASUREMENT 9.2.1 9.2.2 9.2.3 Date & Initial 9.2.4 Date & Initial Identify clock time and calendar dates using both words and numbers. Identify fourths, halves, and whole numbers on a ruler (inches) and weight scales (pounds). Identify and select appropriate measures for capacity (cups, pints, quarts, and gallons) and weight (ounces and pounds). Interpret temperature from Fahrenheit scale in various situations. M.10 TABLES, CHARTS, GRAPHS, AND MAPS Date & Initial Date & Initial Date & Initial 10.2.1 Solve problems using simple graphs (pictograph, bar, line, and circle), tables or distances on maps. Identify and write amounts of money using decimals and words. M.6 APPLY MATH IN A FUNCTIONAL CONTEXT 6.2.1 M.8 ESTIMATION 8.2.1 Identify and demonstrate an understanding of fractional parts including ¼, ⅓, ½, and whole. M.4 DECIMALS 4.2.1 Date & Initial Date & Initial Solve simple addition and subtraction problems by computing costs from a restaurant menu. 35 Performance Descriptors MATHEMATICS – BEGINNING BASIC – LEVEL 2 Each IGO should be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Whole Number M.1.2.1 Complete a minimum of ten problems that require identifying place value to at least the thousands place. M.1.2.2 Complete a minimum of ten problems that require adding whole numbers up to three digits using carrying. M.1.2.3 Complete a minimum of ten problems that require subtracting whole numbers up to three digits using borrowing, including borrowing from zeroes. M.1.2.4 Complete a minimum of ten problems that require multiplying whole numbers up to three digits using carrying. M.1.2.5 Complete a minimum of ten problems that require dividing whole numbers up to hundreds by one digit, including problems with remainders. M.1.2.6 Solve a minimum of ten single-step, real-life word problems involving addition, and ten similar problems involving subtraction using up to three-digit whole numbers. Fractions M.3.2.1 Identify at least one example of the following: 1/4, 1/2, 1/3, and whole. Demonstrate at least one of each. For example, the student will fold paper or cut a candy bar into the designated parts. Decimals M.4.2.1 Solve a minimum of ten problems that require identification of money using decimals (e.g., $5.45); solve a minimum of ten problems that require identification of money using words (e.g., five dollars and forty-five cents). Apply Math in a Functional Context M.6.2.1 Solve a minimum of five problems that require simple addition and subtraction by computing costs from a restaurant menu. Estimation M.8.2.1 Round a minimum of five numbers to tens and a minimum of five numbers to hundreds. Solve a minimum of five problems using estimation that involves tens and hundreds. For example, estimate the sum of 406 and 798 (nearest hundred) or estimate the difference between 836 and 425 (nearest ten). Units of Time and Measurement M.9.2.1 Identify clock time using both words and numbers in a minimum of ten problems; identify calendar dates using both words and numbers in a minimum of ten problems. M.9.2.2 Solve a minimum of five problems that require the identification of fourths, halves, and whole numbers on a ruler (inches); solve a minimum of five problems that require the identification of fourths, halves, and whole numbers on weight scales (pounds). M.9.2.3 Solve a minimum of five problems that require the identification and selection of appropriate measures for capacity (cups, pints, quarts, and gallons) and five problems with appropriate measures for weight (ounces and pounds). M.9.2.4 Identify a minimum of five temperatures on a Fahrenheit scale and complete a minimum of five statements 0 that demonstrate an understanding of temperatures in various situations. Example: A very cold day is (a) 70 0 0 F (b) 56 F (c) 16 F. Tables, Charts, Graphs, and Maps M.10.2.1 Complete at least five questions each on three of the following: simple pictograph, bar graph, line graph, circle graph, table, or map. 36 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST ABE MATHEMATICS Federal Functioning Level 3 – Low Intermediate (4.0–5.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: M.1 WHOLE NUMBERS 1.3.1 1.3.2 1.3.3 1.3.4 1.3.5 1.3.6 Add whole numbers up to four digits. Subtract whole numbers up to four digits. Multiply whole numbers up to four digits. Divide a four-digit number by at least a three-digit number. Compute using the correct order of operations to solve problems including multiply, divide, add, and subtract (M, D, A, S). Solve single-step, real-life word problems involving multiplication and division using up to three-digit whole numbers. M.3 FRACTIONS 3.3.1 3.3.2 3.3.3 3.3.4 4.3.2 4.3.3 M.6 APPLY MATH IN A FUNCTIONAL CONTEXT 6.3.1 6.3.2 6.3.3 9.3.1 9.3.2 9.3.3 Date & Initial Date & Initial Compare prices and recognize best buys. Interpret information on a payroll stub. Solve problems using money to write a check and balance a check register. M.9 UNITS OF TIME AND MEASUREMENT Identify and calculate equivalent fractions (fourths, thirds, halves, eighths, fifths, and tenths). Add and subtract fractions (fourths, thirds, halves, eighths, fifths, and tenths). Multiply fractions (fourths, thirds, halves, eighths, fifths, and tenths). Divide fractions (fourths, thirds, halves, eighths, fifths, and tenths). M.4 DECIMALS 4.3.1 Date & Initial Date & Initial Calculate units of time using a clock and calendar. Identify and select appropriate linear measurements (inches, feet, yards, and miles). Identify and select appropriate metric measurement (including meters, liters, and grams). M.10 TABLES, CHARTS, GRAPHS, AND MAPS Date & Initial 10.3.1 Measure and compute direct distances using scales/legends on a simple map. M.13 GEOMETRY Date & Initial Date & Initial 13.3.1 Recognize basic geometric shapes (triangle, square, circle, rectangle, hexagon, and pentagon). 13.3.2 Calculate perimeter of squares and rectangles using whole numbers. Identify place value for decimals (tenths, hundredths, and thousandths). Round decimals to whole numbers. Convert decimals to fractions and fractions to decimals (fourths, thirds, halves, eighths, fifths, and tenths). 37 Performance Descriptors MATHEMATICS – LOW INTERMEDIATE – LEVEL 3 Each IGO should be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Whole Numbers M.1.3.1 Complete a minimum of ten problems involving the addition of whole numbers up to four digits. M.1.3.2 Complete a minimum of ten problems involving the subtraction of whole numbers up to four digits. M.1.3.3 Complete a minimum of ten problems involving the multiplication of whole numbers up to four digits. M.1.3.4 Complete a minimum of ten problems involving the division of a four-digit number by at least a three-digit number. M.1.3.5 Compute using the correct order of operations to solve a minimum of ten problems including multiply, divide, add, and subtract (M, D, A, S). M.1.3.6 Solve a minimum of ten single-step, real-life word problems involving multiplication and division using up to three-digit whole numbers. Fractions M.3.3.1 Identify and calculate equivalent fractions (fourths, thirds, halves, eighths, fifths, and tenths) solving a minimum of five problems each that require (1) reducing, (2) raising fractions to higher terms, (3) changing improper fractions to whole or mixed numbers, and (4) changing mixed and whole numbers to improper fractions. M.3.3.2 Solve a minimum of ten fraction problems (fourths, thirds, halves, eighths, fifths, and tenths) that include addition of like and unlike denominators; subtract a minimum of ten similar fraction problems that include like and unlike denominators and borrowing from whole and mixed numbers. M.3.3.3 Solve a minimum of ten fraction problems (fourths, thirds, halves, eighths, fifths, and tenths) that include multiplication of fractions, whole numbers, and mixed fractions. M.3.3.4 Solve a minimum of ten fraction problems (fourths, thirds, halves, eighths, fifths, and tenths) that include division of fractions, whole numbers, and mixed fractions. Decimals M.4.3.1 Identify the place value for a minimum of five decimals each involving tenths, hundredths, and thousandths. M.4.3.2 Round a minimum of ten decimals to whole numbers. M.4.3.3 Convert a minimum of five decimals to fractions and five fractions to decimals (fourths, thirds, halves, eighths, fifths, and tenths). Apply Math in a Functional Context M.6.3.1 Compare prices and recognize best buys in a minimum of ten problems. M.6.3.2 Answer a minimum of eight questions that require the interpretation of a payroll stub. M.6.3.3 Write at least two checks and complete a check register that includes beginning and ending balances and at least five transactions (deposits and checks). Units of Time and Measurement M.9.3.1 Solve a minimum of five problems that require calculating units of time using a clock; solve a minimum of five similar problems using a calendar. M.9.3.2 Identify and select appropriate linear measurements (inches, feet, yards, and miles) in a minimum of ten examples. M.9.3.3 Identify and select appropriate metric measurement (including meters, liters, and grams) in a minimum of ten examples. Tables, Charts, Graphs, and Maps M.10.3.1 Measure and compute a minimum of ten direct distances using scales/legends on a simple map. Geometry M.13.3.1 Identify a minimum of one example of each of the following basic geometric shapes: triangle, square, circle, rectangle, hexagon and pentagon. M.13.3.2 Calculate the perimeter of five squares and five rectangles using whole numbers. 38 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST ABE MATHEMATICS Federal Functioning Level 4 – High Intermediate (6–8.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: NOTE: Essential IGOs related to the GED Tests are underlined. M.1 WHOLE NUMBERS 1.4.1 Solve real-life, multi-step whole number word problems. M.3 FRACTIONS 3.4.1 4.4.2 4.4.3 4.4.4 4.4.5 5.4.2 5.4.3 6.4.1 6.4.2 Solve problems relating to payroll stubs. Interpret and calculate sales tax, rebates, and discounts. 6.4.4 Compute and compare unit pricing using division of decimals. Interpret catalog order forms and calculate cost of multiple items, shipping and handling, and sales tax as required. M.9 UNITS OF TIME AND MEASUREMENT Date & Initial 10.4.1 10.4.2 Date & Initial 11.4.2 11.4.3 11.4.4 11.4.5 Date & Initial Date & Initial Identify positive and negative numbers on a number line. Add positive and negative numbers. Subtract positive and negative numbers. Multiply positive and negative numbers. Divide positive and negative numbers. M.12 ALGEBRA 12.4.1 Date & Initial Solve problems using maps to compute travel time, gas consumption, and travel costs. Develop and draw conclusions from tables and graphs using instructor or student selected information. M.11 INTEGERS 11.4.1 Date & Initial Solve problems using conversions of units of weight, length/width, and capacity. M.10 TABLES, CHARTS, GRAPHS, AND MAPS Convert percents to decimals and fractions. Compute percents by finding the part, the percent and the whole. Solve real-life word problems using percents. M.6 APPLY MATH IN A FUNCTIONAL CONTEXT 6.4.3 9.4.1 Add decimals; add decimals and whole numbers. Subtract decimals; subtract decimals and whole numbers. Multiply decimals; multiply decimals and whole numbers. Divide decimals; divide decimals and whole numbers. Solve real-life word problems using decimals. M.5 PERCENTS 5.4.1 Date & Initial Solve a minimum of ten real-life word problems using fractions. M.4 DECIMALS 4.4.1 Date & Initial Date & Initial Solve simple algebraic equations (e.g., 5x=40, 2x+4=10) 39 Performance Descriptors MATHEMATICS – HIGH INTERMEDIATE – LEVEL 4 Each IGO should be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Whole Numbers M.1.4.1 Solve a minimum of ten real life, multi-step whole number word problems. Fractions M.3.4.1 Solve a minimum of ten real-life word problems using fractions. Decimals M.4.4.1 Solve a minimum of five problems involving adding decimals; solve a minimum of five problems involving adding decimals and whole numbers, both vertically and horizontally. M.4.4.2 Solve a minimum of five problems involving subtracting decimals; solve a minimum of five problems involving subtracting decimals and whole numbers, both vertically and horizontally. M.4.4.3 Multiply a minimum of five problems involving decimals; multiply a minimum of five problems involving decimals and whole numbers, both vertically and horizontally. M.4.4.4 Divide a minimum of five problems involving decimals; divide a minimum of five problems involving decimals and whole numbers. M.4.4.5 Solve a minimum of ten real-life word problems using decimals that require addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Percents M.5.4.1 Convert a minimum of ten percents to decimals and fractions. M.5.4.2 Compute a minimum of five percent problems each involving (1) finding the part, (2) finding the percent, and (3) finding the whole. M.5.4.3 Solve a minimum of fifteen real-life word problems with five each involving the three operations in M.5.4.2. Apply Math in a Functional Context M.6.4.1 Solve a minimum of eight problems relating to payroll stubs. M.6.4.2 Interpret and calculate a minimum of five problems each involving sales tax, rebates, and discounts. M.6.4.3 Solve a minimum of ten problems that require computing and comparing unit pricing using division of decimals. M.6.4.4 Accurately complete a catalog order form that lists at least five items for sale. List unit prices, amount of money for purchases, calculate a subtotal, tax, shipping, and total costs. Units of Time and Measurement M.9.4.1 Convert a minimum of ten units of weight, length, and capacity that include ounces, pounds, tons, inches, feet, yards, cups, pints, quarts, and gallons; complete five reading problems that use conversions of weight, length, and capacity. Tables, Charts, Graphs, and Maps M.10.4.1 Solve a minimum of ten problems using maps to compute travel time, gas consumption and travel costs. M.10.4.2 Develop and draw conclusions from a table or graph (pictograph, circle graph, bar graph, or line graph). Integers M.11.4.1 M.11.4.2 M.11.4.3 M.11.4.4 M.11.4.5 Identify a minimum of ten positive and negative numbers on a number line. Add a minimum of ten problems involving positive and negative numbers. Subtract a minimum of ten problems involving positive and negative numbers. Multiply a minimum of ten problems involving positive and negative numbers. Divide a minimum of ten problems involving positive and negative numbers. Algebra M.12.4.1 Solve a minimum of ten simple algebraic equations (e.g., 5x = 40, 2x + 4 = 10). 40 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST ABE MATHEMATICS Federal Functioning Level 5 – Low Adult Secondary (9–10.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: NOTE: Essential IGOs related to the GED Tests are underlined. M.3 FRACTIONS 3.5.1 Date & Initial 10.5.1 Interpret information from multi-line graphs to solve problems. Perform multiple operations of fractions (review). M.11 INTEGERS 11.5.1 M.4 DECIMALS 4.5.1 Perform multiple operations of decimals (review). M.5 PERCENTS 5.5.1 Date & Initial 12.5.1 12.5.2 Perform multiple operations of percents (review). M.6 APPLY MATH IN A FUNCTIONAL CONTEXT 6.5.1 Date & Initial 13.5.1 Solve problems using averaging (mean) and median. 13.5.2 M.7 RATIO AND PROPORTION 7.5.1 7.5.2 7.5.3 Date & Initial 13.5.3 Solve problems with probability. Compute using ratio. Compute using proportion. 13.5.4 M.8 ESTIMATION 8.5.1 9.5.1 9.5.2 Date & Initial Date & Initial Convert between the standard and metric systems of measures; inch/cm, foot/meter; pound/kilogram; quart/liter; Fahrenheit/Celsius. Compute time using United States time zones. M.10 TABLES, CHARTS, GRAPHS, AND MAPS 13.5.5 13.5.6 Use estimation to solve real life problems. M.9 UNITS OF TIME AND MEASUREMENT Identify and plot ordered pairs on a rectangular/coordinate plane. M.12 ALGEBRA Solve powers and perfect square roots. Solve complex algebraic equations (for ex.: 5(x+2) = 3(x +6), 3 r = 6). M.13 GEOMETRY Date & Initial 13.5.7 13.5.8 Date & Initial Date & Initial Recognize and identify complex geometric words and shapes such as quadrilateral, polygon, hexagon, octagon, parallelogram, cube, trapezoid, cone, cylinder, and pyramid. Solve problems involving angles (right, complementary, supplementary, vertical, and corresponding) and triangles. Calculate circumference, perimeter, length, and width of selected geometric shapes (refer to current GED math formula page). Calculate area of geometric shapes (refer to current GED math formula page). Solve real-life problems using perimeter and area. Calculate volume of geometric shapes (refer to current GED math formula page). Solve real-life problems using volume. Solve problems using the Pythagorean Theorem with and without the aid of the calculator. M.14 TRIGONOMETRY Date & Initial Date & Initial Date & Initial 14.5.1 Identify components of trigonometric functions (adjacent, opposite, and hypotenuse). 41 Performance Descriptors MATHEMATICS – LOW ADULT SECONDARY – LEVEL 5 Each IGO should be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Fractions M.3.5.1 Review fractions as indicated in Level 3 (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) and solve a minimum of eight fraction reading problems. Decimals M.4.5.1 Review decimals including writing decimals from words, converting fractions to decimals and decimals to fractions, and estimation/rounding; solve a minimum of eight decimal word problems. Percents M.5.5.1 Review percents including changing percents to decimals, decimals to percents, fractions to percents, and percents to fractions. Find the part, whole, and percent of a given problem and solve a minimum of eight percent word problems. Apply Math in a Functional Context M.6.5.1 Solve a minimum of five problems each using averaging (mean) and median. Ratio and Proportion M.7.5.1 Solve a minimum of ten problems with probability. M.7.5.2 Compute a minimum of ten problems using ratio. M.7.5.3 Compute a minimum of ten problems using proportion. Estimation M.8.5.1 Use estimation to solve a minimum of ten real-life problems. Units of Time and Measurement M.9.5.1 Convert between the standard and metric systems of measures by solving a minimum of two problems each involving inch/cm; foot/meter; pound/kilogram; quart/liter; and Fahrenheit/Celsius. M.9.5.2 Solve a minimum of ten problems involving time using United States time zones. Tables, Charts, Graphs, and Maps M.10.5.1 Interpret information from multi-line graphs to solve a minimum of five problems. Integers M.11.5.1 Identify and plot a minimum of ten ordered pairs on a rectangular/coordinate plane. Algebra M.12.5.1 Solve a minimum of ten problems using powers and perfect square roots. M.12.5.2 Solve a minimum of ten complex algebraic equations (for ex.: 5(x+2) = 3(x +6), 3 r = 6). 4 Geometry M.13.5.1 Recognize and identify a minimum of ten complex geometric words and shapes such as quadrilateral, polygon, hexagon, octagon, parallelogram, cube, trapezoid, cone, cylinder, and pyramid. M.13.5.2 Solve a minimum of five problems each involving triangles and complementary, supplementary, vertical, and corresponding angles. M.13.5.3 Solve a minimum of ten problems involving the calculation of circumference, perimeter, length, and width of circles, triangles, square, rectangles, and parallelograms. M.13.5.4 Solve a minimum of ten problems involving the calculation of area of circles, triangles, squares, rectangles, and parallelograms. M.13.5.5 Solve a minimum of five real-life problems using perimeter and five problems using area. M.13.5.6 Solve a minimum of five problems each involving the volume of cubes and cylinders. M.13.5.7 Solve a minimum of ten real-life problems using volume. M.13.5.8 Solve a minimum of ten problems using the Pythagorean Theorem with and without the aid of the calculator using both hypotenuse and leg. Trigonometry M.14.5.1 Solve a minimum of ten problems that require the identification of trigonometric functions including adjacent, opposite, and hypotenuse. 42 WEST VIRGINIA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION SKILLS CHECKLIST ABE MATHEMATICS Federal Functioning Level 6 – High Adult Secondary (11.0-12.9) Student: Program: Instructor: Date Enrolled: NOTE: Essential IGOs related to the GED Tests are underlined. M.6 APPLY MATH IN A FUNCTIONAL CONTEXT 6.6.1 6.6.2 Use payroll stub information to construct a personal/family budget. Reconcile a bank statement. M.7 RATIO AND PROPORTION 7.6.1 7.6.2 Date & Initial Date & Initial Solve real-life word problems using proportion. Make predictions based on probability including possible outcomes. monomials. Multiply and divide binomials. Solve problems involving the slope of a line on a graph. 12.6.7 Solve problems involving the x and y intercepts on a graph. 12.6.8 Solve problems involving distance between points on a coordinate system. 12.6.9 Factor algebraic expressions. 12.6.10 Express numbers in scientific notation. 12.6.5 12.6.6 M.13 GEOMETRY M.9 UNITS OF TIME AND MEASUREMENT 9.6.1 Date & Initial 13.6.1 Use geometric formulas to solve reallife problems (review). Read and interpret information on scales, meters, and gauges. M.14 TRIGONOMETRY M.10 TABLES, CHARTS, GRAPHS AND MAPS 10.6.1 Compare and analyze tables and graphs. M.11 INTEGERS 11.6.1 Date & Initial Explain the relationship between length on a number line and absolute value. M.12 ALGEBRA 12.6.1 Date & Initial 12.6.2 12.6.3 Use algebra to solve real-life problems. Solve inequalities. Translate word phrases into algebraic expressions or word sentences into equations. 12.6.4 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide Date & Initial Date & Initial Date & Initial 14.6.1 Solve problems involving trigonometric ratios (sin, cos, tan) with right angles. ADDITIONAL GED IGOS (not required for completion of FFL) Date & Initial GED.6.1 Operate a scientific calculator to solve basic and advanced mathematical functions. GED.6.2 Evaluate insurance costs and benefits. GED.6.3 Calculate retirement and investment benefits. 43 Performance Descriptors MATHEMATICS – HIGH ADULT SECONDARY – LEVEL 6 Each IGO should be mastered with a minimum score of 80%. Apply Math in a Functional Context M.6.6.1 Use payroll stub information to construct a personal/family budget. M.6.6.2 Record at least ten transactions that include outstanding checks and deposits, debits/withdrawals and service charges. Balance should agree with check register (ending balance). Ratio and Proportion M.7.6.1 Solve a minimum of ten real-life word problems using proportion. M.7.6.2 Make a minimum of ten predictions based on probability including possible outcomes. Units of Time and Measurement M.9.6.1 Read and interpret information on a minimum of five scales, five meters, and five gauges. Tables, Charts, Graphs, and Maps M.10.6.1 Compare and analyze information from a minimum of five pairs of tables and graphs representing identical or similar data. Integers M.11.6.1 By drawing a number line, show the relationship between length on a number line and absolute value for a minimum of five given absolute values. Algebra M.12.6.1 M.12.6.2 M.12.6.3 Use algebra to solve a minimum of ten real-life problems. Solve a minimum of ten inequalities. Solve a minimum of ten problems that require the translation of word phrases into algebraic expressions or word sentences into equations. M.12.6.4 Solve a minimum of five problems each that require addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of monomials. M.12.6.5 Solve a minimum of five problems each that require the multiplication and division of binomials. M.12.6.6 Solve a minimum of five problems involving the slope of a line on a graph. M.12.6.7 Solve a minimum of five problems involving the x and y intercepts on a graph. M.12.6.8 Solve a minimum of five problems involving distance between points on a coordinate system. M.12.6.9 Factor a minimum of ten algebraic expressions. M.12.6.10 Express a minimum of five numbers in scientific notation. Geometry M.13.6.1 Use geometric formulas to solve a minimum of ten real-life problems. Trigonometry M.14.6.1 Solve a minimum of ten problems involving trigonometric ratios (sin, cos, tan) with right angles. 44