Internet Graphics 1
advertisement

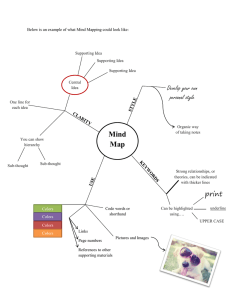
Internet Graphics 1 Representing Images Raster Image: Images consist of “dots” of color, not lines Pixel: Picture element-tiny rectangle Resolution: Number of pixels SVGA: 1280 x 1024 = 1,310,720 VGA: 640 x 480 Your monitor can be modified 2 Representing Images RGB: monitor, each pixel Intensity: 0 (dark) – 255 (bright) Representing Color: # - # - # 255-255-255 = white 100-0-0 = scarlet 16,777,216 = 16 million colors 3 Representing Images Light media: RGB Opaque media: paint Red, blue, yellow Printers Cyan, yellow, magenta Must have conversion software for translating monitor to printer 4 Storage of Images 1 byte = 8 bits = 255 values Images are memory hogs Causes problems with transmission e.g. Image: 5 million pixels = 14 Mb Solutions Less “accuracy” Compression 5 Reducing Color Depth Reduce the number of colors Depth: measured by bits/pixel True color = 3 bytes = 24 bits 6 8-bit Color 1 byte = 8 bits = 256 colors Color Palette – 256 colors Multiple palettes are available 8-bit number represents the particular color in the palette – not the mix of RGB Uses 1/3 storage space + 768 bytes to define the palette 7 Other Color Depths 1-bit - Black & White 4-bit = 16 colors Simple drawings, icons Windows, but can change palette Start; Settings; Control Panel; Display; Appearance; Scheme 8 Color Depth Tradeoff Color depth vs. Resolution Due to storage requirements, must reduce one 1280 x 1024 256 colors 16 M colors 640 x 480 Photos: need more than 256 colors 9 10