Introduction Mario Fifić
advertisement

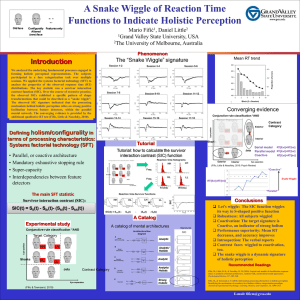
A Snake Wiggle of Reaction Time Functions to Indicate Holistic Perception Old face Configurally Features only Altered (new) face Mario Fifić Grand Valley State University, Michigan Phenomenon The “Snake Wiggle” signature Session 3-4 100 RT ms 150 200 0 50 100 RT ms 150 600 Session 9-10 0.2 0.2 0 SIC 0.2 SIC 0.4 0 0.2 0.2 0.4 0.4 0.4 100 RT ms 150 0 200 50 100 RT ms 150 200 50 SIC 0.2 SIC 0.2 0 0 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.4 0.4 0.4 0 200 50 100 RT ms 150 200 50 100 RT ms 150 200 0.1 HL 2 LH Lips-position HL HH HH HL Freq Sharks LL 0.002 0.002 0.001 0.001 LL L Freq Jets HL HL 0.005 0.005 0.004 0.004 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.002 0.002 Eye- separation 400. 400. 680 Exterior 660 LH 640 0.1 Interior 200. 200. 0.4 0.2 - 1000. 1200. 1400. 1000. 1200. 1400. 0.2 LL 800. 800. 1000. 1200. 1200. 1400. 1400. 1000. 460 0.0 0 LH 0.6 0.4 0.2 + LL 0.8 0.6 0.4 = 0.2 1 2 70 80 RT ms 90 100 110 SIC(t) = Shh(t) - 50 60 70 80 RT ms 50 90 100 110 Shl(t) - 60 70 80 RT ms 90 100 110 50 (Slh(t) 60 70 80 RT ms Serial Self-terminating Input Eyes Lips Decision OR Response B Serial Exhaustive Input Eyes Lips Decision AND Response Decision OR Response Analytic Analytic/ Holistic C Input Parallel Self-terminating LL L Contrast Category Input D Parallel Exhaustive Eyes Lips Input Eyes Input Lips Decision AND Response E Coactive Input Input Eyes Lips Joe’s face Decision Response Analytic Analytic/ Holistic Strong Holistic 8 10 12 Serial Block (2 x Session) model RT[Ext]<RT[Int] Jets Parallel model RT[Ext]=RT[Int] Participant Coactive 06 RT[Ext]>RT[Int] Eye- separation 0.3 -20 -40 4 5 6 7 8 -80 -100 “Coactive” 740 0.2 720 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 700 0.1 680 Snake Wiggle 660 640 0.0 0 2 4 6 8 10 “Parallel” Block (2 x Session) Conclusions 0 0.4 0 Architecture flow diagram 6 0.2 90 100 110 - Sll(t)) 3 Block (2 x Session) 0.2 60 0 -60 0.4 0.8 4 Interior 780 20 0.1 RT[Ext]-RT[Int] RT(ms) 480 S IC SIC 0.2 - 0.6 Exterior 0.3 1 P R O B A B IL IT Y 0.4 HL 500 600. 600. LL2 L (Fific, Little & Nosofsky, 2010; Psych Review) 760 540 400. 400. 0 H 0.0 800 0.001 0.001 200.200. 400.400. 600.600. 800.800. 1000. 1200. 1400. 1000. 1200. 1400. 1 P R O B A B IL IT Y 0.6 P R O B A B IL IT Y P R O B A B IL IT Y HH 800. 800. 580 Participant 05 520 RT(ms) 1 600. 600. Contrast 0.2 Category LH Errors RT(ms) 560 0.002 0.002 0.001 0.001 0.8 10 580 200. 200. 0.3 Sharks 620 LL HL Block (2 x Session) 600 0.004 0.004 0.002 0.002 0.004 0.004 0.8 8 0.006 0.006 0.003 0.003 LH H 6 0.008 0.008 0.006 0.006 0.005 0.005 HL 4 Reaction time histograms 640 620 LH HHHH LH HH HL Sharks LL (Fific & Townsend, 2010) Participant 04 720 RT (ms) HH 10 740 Conjunctive-rule classification “AND” 0.3 Sharks 0.0 0 A catalog of mental architectures Eye- separation 8 760 650 600 A Jets 6 Converging evidence 200 700 0.004 0.004 Sharks LH H 4 Errors RT(ms) 0.2 0 200. 200. 400. 400. 600. 600. 800. 800. 1000. 1000. 1200. 1200. 1400. 1400. LH HL 2 Block (2 x Session) Proportion of errors HH Target LH HH Category Sharks 150 550 Conjunctive-rule classification “AND”” Conjunctive-rule classification “AND” HL 0 HH Tutorial: how to calculate the survivor interaction contrast (SIC) function Experimental study HH HL 12 0.0 Target Category LH 700 10 20 30 40 RT ms 50 60 A Catalog HH 10 750 Tutorial 50 SIC(t) = Sll(t) - Slh(t)- (Shl(t) - Shh(t)) 500 600 1 Survivor interaction contrast (SIC): 8 Session 17-18 0.2 150 6 800 0.4 100 RT ms 4 100 RT ms 850 0.4 0.1 400 Participant 03 0 0.4 0 2 600 Block (2 x Session) Reaction time Survivor functions The main SFT statistic 0.1 0.0 0 Session 15-16 Session 13-14 50 200 560 0 0.2 0 150 Session 11-12 580 0.4 50 100 RT ms 620 0.4 0 640 50 0 200 Lips- position 50 660 Proportion of errors 0.4 0.2 Proportion of errors 0.4 700 Proportion of errors 0.4 0.2 680 RT (ms) 0.2 700 0.3 800 RT (ms) 0.2 Session 7-8 SIC 720 0 0.2 0 0.3 Proportion of errors 0 900 740 0.2 SIC SIC SIC 0 Parallel, or coactive architecture Mandatory exhaustive stopping rule Super-capacity Interdependencies between feature detectors Lips- position • • • • 0.2 MeanParticipant RT trend 02 760 0.4 RT (ms) Defining holism/configurality in terms of processing characteristics: Systems factorial technology (SFT) 0.4 0.2 SIC We analyzed the underlying fundamental processes engaged in forming holistic perceptual representations. The subjects participated in a face categorization task over multiple sessions. We applied the systems factorial technology (SFT) to analyze the properties of the observed response time (RT) distributions. The key statistic was a survivor interaction contrast function (SIC). Over the course of extensive practice, the observed SICs exhibited a specific pattern of shape transformations that could be described as a "snake wiggle". The observed SIC signature indicated that the processing mechanism behind holistic perception relies on strong positive facilitation between feature detectors, within the parallel mental network. The converging evidence is provided by the additional qualitative RT test (Fific, Little & Nosofsky, 2010). Session 5-6 780 RT (ms) 0.4 Participant 01 Proportion of errors Session 1-2 RT (ms) Introduction Errors RT(ms) Signatures 70 Let’s wiggle: The SIC function wiggles its way to S-shaped positive function Robustness: All subjects wiggled Coactivation: The target signature is Coactive, an indicator of strong holism Performance superiority: Mean RT decreases, and accuracy improves Introspection: The verbal reports Contrast faces wiggled to coactivation, too. The snake wiggle is a dynamic signature of holistic perception Recommended Readings Fific, M., Little, D. R., & Nosofsky, R. M. (2010). Logical-rule models of classification response times: A synthesis of mental-architecture, random-walk, and decision-bound approaches. Psychological Review, 117, 309–348. Fific, M., & Townsend, J. T. (2010). Information-processing alternatives to holistic perception: Identifying the mechanisms of secondary-level holism within a categorization paradigm. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 36, 1290-1313. E-mail: fificm@gvsu.edu