Physics 2C Summer Session I Quiz #4
advertisement

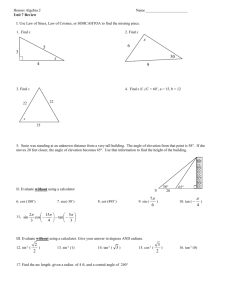
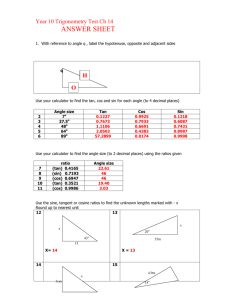
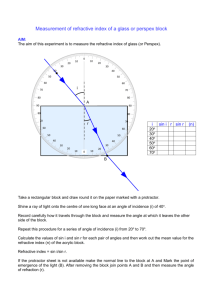
Physics 2C Summer Session I Quiz #4 1. A plane wave of randomly polarized light is incident on a stack 3 linear polarizers. The polarization axes are all rotated through an angle of =6 relative to the polarization of the light incident upon it. The intensity of the light as it emerges from the stack relative to the incident light, S=So ; is given by A) 0 B) :281 C) :375 D) :422 From the law of Malus S=So = E) :650 1 cos2 ( =6) 2 2 = :281 ! B 2. Consider an incident light ray that is propagating in the plane of the page with an angle of incidence of 65 to the …rst of two mirrors as shown in the …gure for problem 2. Determine the angle of re‡ection from the second mirror, M2 : Problem 2 A) 55 B) 60 C) 65 D) 35 E) 25 The initial acute angle in the triangle is = 90 65 = 25 : Hence the second acute angle is = 180 120 = 35 : This means that M2 = 35 = 55 ! A 90 3. An alarm in your dorm room goes o¤ one morning with an annoying 600Hz buzz, and your roommate throws it out the window. Your dorm room is on the sixth ‡oor 20m above the ground. Assuming that the outside temperature is such that the speed of sound is v = 330m=s; and that g = 10:0m=s2 ; what frequency do you hear just before the alarm hits the ground? A) 560Hz B) 636Hz C) 600Hz 1 D) 639Hz E) 566Hz p p The velocity of the alarm just before it hits the ground is u = 2gh = 2 (10) 20 = 20:0m=s: From the Doppler shift the frequency at the moment of contact with the ground is f0 = f 600 = = 566Hz ! E 1 + us =v 1 + 20=330 4. Light is incident upon an air-water interface (nair = 1), and the refracted light inside the water makes a 52 angle as measured from the air-water interface. If the water has a refractive index of n = 4=3; the incident angle of the light is A) 61:2 B) 27:5 C) 36:2 D) 55:2 E) 34:8:0 Since the angle as measured from the interface is 38 ; the refracted angle inside the zirconium is 90 52 = 38 . From Snell’s law n1 sin 1 = n2 sin 1 = 2 ! sin 1 = 4 sin 38 = :8209 3 55:2 ! D 5. Standing in air (n = 1), you look down the center of a right circular cylinder of transparent material whose height is 2=3 times its diameter. If your line of sight makes a 53:13 angle with the normal to the top surface, what is the minimum refractive index of this material for which you will be able to see through the bottom surface of the cylinder? Problem 5 A) 1:25 B) 1:33 C) 1:67 D) 2:00 E) 2:67 To see the right corner at the bottom cylinder requires nair sin 53:13 n 1=2 n = n sin = n p =p = :6n 1=4 + 4=9 1 + 16=9 = :8=:6 = 4=3 ! B 2 For an index less than this the ray of light will have a refracted angle greater than sin 1 :6 and exit the side of the cylinder. 6. A block of diamond with n = 2:42 is submerged in a liquid. If perfect internal re‡ection is observed for all incident angles (inside the diamond) greater than i = 36:87 ; the index of refraction for the ‡uid is A) 1:33 B) 1:45 C) 1:49 D) 1:52 The critical angle is determined from n1 sin c E) 1:66 = n2 ! nliq = 2:42 (:6) = 1:452 ! B 7. What is the refractive index of a material for which the polarizing angle in water (nwater = 4=3) is 57 ? A) 1:12 B) 1:15 C) 1:54 D) 1:89 E) 2:05 The expression that determines the polarizing angle is tan leads to 4 n2 = nwater tan = tan 57 = 2:05 ! E 3 = n2 =n1 : This 8. A virtual image is located 32cm behind a concave mirror with a focal length of 16cm. How much is the image magni…ed (include sign to determine if the image is inverted or upright)? A) M = 3 B) M = 1 C) M = 1:5 D) M = 2 E) M = 2:0 From the mirror equation the location of the object is determined via 1 f 1 1 1 1 1 `0 f + 0 ! = = ` ` ` f `0 `0 f 0 `f 32 (16) 32 = = cm `0 f 32 16 3 = ` = The magni…cation is found from M= h0 = h `0 = ` 32 =3!A 32=3 9. A beaker is …lled to a depth of 6cm with benzene (n = 1:5). How deep does the bottom of the beaker appear to be when looking straight down? A) 2cm B) 3cm C) 4cm D) 6cm The apparent depth is determined from `0 = E) 9cm 6 ` = = 4cm ! C n 1:5 3 10. How far from a page should you hold a lens with a 30cm focal length in order to see the print magni…ed 2 times? A) 40cm B) 45cm C) 20cm D) 15cm The expression for the magni…cation yields M= h0 =2= h `0 ! `0 = ` E) 60cm 2`: From the lens equation 1 1 1 1 1 1 = + 0 = = f ` ` ` 2` 2` ` = f =2 = 15cm ! D Some useful formulas f0 n1 sin 1 = 1 1 uo =v f; f 0 = f us =v = n2 sin 2; s 1 1 u=c f; tan u=c 1 1 1 = + 0; M = f ` ` 4 = n2 =n1 `0 =` = h0 =h