Chapter 15 Overview
advertisement

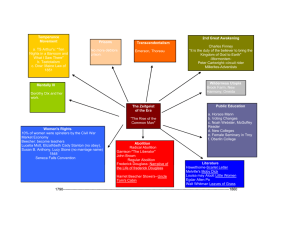
Chapter 15 Overview The Second Great Awakening • 1800s-1830s • Emphasized the importance of religion • Reaction against declining church membership and deism • Emphasized emotion over reason • Used camp meetings (revival meetings) • Emphasis on the ability of an individual to earn salvation (as opposed to predestination) • Led to the growing popularity of new denominations • Actively sought female participation Charles Grandison Finney • "America's foremost revivalist" • Encouraged women • Innovative techniques • Humans can earn salvation • Abolitionist Camp Meetings The camp meeting is a phenomenon of American frontier Christianity. The "camp meeting" was a response to the lack of established churches on the frontier. Word of mouth told that there was to be a religious meeting at a certain location. Due to the primitive means of transportation, if this meeting was to be more than a few miles' distance from those attending, it would necessitate their leaving home for its entire duration, or as long as they desired to remain, and camping out at or near its site. Unlike traditional religious events these meetings could provide their participants with almost continuous services; once one speaker was finished (often after several hours) another would often rise to take his place. New Sects & Denominations • Baptists & Methodists grew the most Other Examples: • Millerites (Adventists)—Jesus would return on October 22, 1844 • Unitarians—Jesus was not divine • Mormons—New American scriptures Reform Movements Partly inspired by the Second Great Awakening, Americans began to look for new ways to improve society. Temperance • Opposed excessive (and sometimes any) alcohol consumption • American Temperance Society (1826) • Northern states experimented with prohibition laws in the 1850s. Public Schools • Reformers believed that better organized schools were needed to cope with growing industrialism and immigration. • Horace Mann advocated 1) state funded schools, 2) assigning students to specific grades, 3) longer school years, 4) required attendance, and 5) standardized text books. • In 1852 Massachusetts passed the first compulsory school attendance law. Horace Mann Abolition • Sought the abolition of slavery • Some favored immediate, uncompensated abolition • Others favored gradual forms of abolition • William Lloyd Garrison • Frederick Douglass Abolitionists Women’s Rights • Lucretia Mott & Elizabeth Cady Stanton • Seneca Falls Convention (1848) Declaration of Sentiments We hold these truths to be self-evident: that all men and women are created equal. • The history of mankind is a history of repeated injuries and usurpations on the part of man toward woman, having in direct object the establishment of an absolute tyranny over her. To prove this, let facts be submitted to a candid world. • He has never permitted her to exercise her inalienable right to the elective franchise. • He has compelled her to submit to laws, in the formation of which she had no voice. • He has withheld from her rights which are given to the most ignorant and degraded men--both natives and foreigners. • Having deprived her of this first right of a citizen, the elective franchise, thereby leaving her without representation in the halls of legislation, he has oppressed her on all sides. • He has made her, if married, in the eye of the law, civilly dead. • He has taken from her all right in property, even to the wages she earns. • He has monopolized nearly all the profitable employments, and from those she is permitted to follow, she receives but a scanty remuneration. He closes against her all the avenues to wealth and distinction which he considers most honorable to himself. As a teacher of theology, medicine, or law, she is not known. • He has denied her the facilities for obtaining a thorough education, all colleges being closed against her. • He allows her in church, as well as state, but a subordinate position, claiming apostolic authority for her exclusion from the ministry, and, with some exceptions, from any public participation in the affairs of the church. • He has created a false public sentiment by giving to the world a different code of morals for men and women, by which moral delinquencies which exclude women from society, are not only tolerated, but deemed of little account in man. Things have changed… Asylums • Dorothea Dix: Champion of better treatment on the mentally ill. Prisons • Debtors prisons were being abolished • Capital punishment was being used less frequently • Brutal punishments (whipping, branding) were being eliminated • Prisons were to reform as well as punish Utopias • Experiments in cooperative communities • Over 40 utopian communities were set up