CHAPTER 1 VOCAB
advertisement

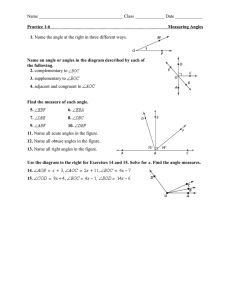
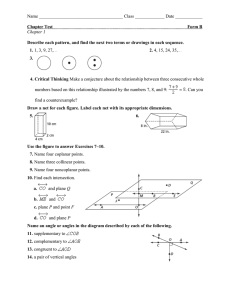
CHAPTER 1 VOCAB 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Inductive Reasoning: reasoning that is based on patterns you observe. Conjecture: a conclusion you reach using inductive reasoning. Counterexample: An example that is used to prove conjectures false. Net: a 2-D pattern that forms a 3-D figure. Point: Location represented by a dot and named with a capital letter. Space: the set of all points. Line: A series of points that extend in opposite directions with no end. Collinear Points: Points that lie on the same line. Plane: Flat surface that contains lines and extends in all directions named by a single capital letter or 3 noncollinear points. 10. Coplanar: Points and lines in the same plane. 11. Postulate/Axiom: Math facts. 12. Segment: the part of a line with 2 endpoints containing all the points between them. 13. Ray: part of a line with one endpoint and extends to include all points on one side of that endpoint. 14. Opposite Rays: 2 collinear rays with the same endpoint. (forms a line!) 15. Parallel Lines: coplanar lines with no intersection. 16. Skew Lines: noncoplanar; not parallel but never intersect 17. Parallel Planes: planes that do not intersect 18. Coordinate: The distance and direction a point is from the origin on a number line. 19. Congruent Segment: Two segments with the same length. 20. Midpoint: A point that divides a segment into two congruent segments. 21. Angle : 2 rays with the same endpoint. Ways to name them!! 22. Acute Angle –less than 90 degrees 23. Right Angle – 90 degrees 24. Obtuse Angle – between 90 and 180 degrees 25. Straight Angle – 180 degrees 26. Congruent Angles - Angles with the same measure. 27. Vertical Angles: Two angles whose sides are opposite rays. 28. Adjacent angles - Two coplanar angles with a common side, a common vertex and no common interior points 29. Complimentary angles: 2 angles whose sum is 90 degrees 30. Supplementary angles: 2 angles whose sum is 180 degrees 31. Construction – formed by the use of a straightedge and compass. 32. Drawing- formed by a ruler and protractor. 33. Bisect- cut in 2 congruent parts 34. Perpendicular Bisector – A line, segment, or ray that is perpendicular to a segment at its midpoint. 35. Angle Bisector –A ray that divides an angle into two congruent coplanar angles.