Quadrilaterals Item Bank from Geo Test Bank
advertisement

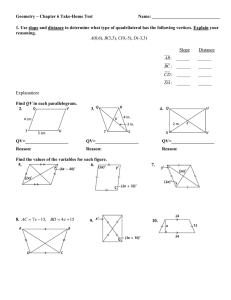
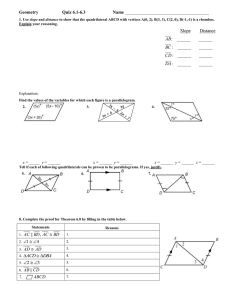
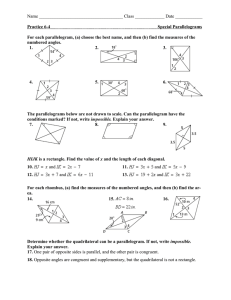
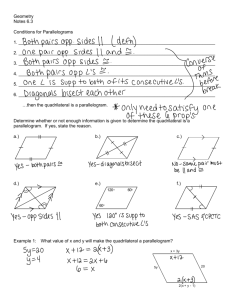
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ ID: A Quadrilaterals Item Bank from Geo Test Bank Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Judging by appearance, classify the figure in as many ways as possible. ____ a. rectangle, square, quadrilateral, parallelogram, rhombus b. rectangle, square, parallelogram c. rhombus, trapezoid, quadrilateral, square d. square, rectangle, quadrilateral 2. What is the most precise name for quadrilateral ABCD with vertices A(–5, 2), B(–3, 6), C(6, 6), and D(4, 2)? a. quadrilateral b. rectangle c. parallelogram d. rhombus 3. ABCD is a parallelogram. If m∠CDA = 66, then m∠BCD = ? . The diagram is not to scale. ____ a. 66 b. 124 c. 114 4. ABCD is a parallelogram. If m∠DAB = 115, then m∠BCD = ____ a. 125 b. 65 c. 1 75 ? d. 132 . The diagram is not to scale. d. 115 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 5. For the parallelogram, if m∠2 = 5x − 28 and m∠4 = 3x − 10, find m∠3. The diagram is not to scale. ____ a. 9 b. 17 c. 173 d. 163 6. In the parallelogram, m∠KLO = 68 and m∠MLO = 61. Find ∠KJM. The diagram is not to scale. ____ ____ a. 119 b. 61 c. 129 d. 68 7. In parallelogram DEFG, DH = x + 3, HF = 3y, GH = 4x – 5, and HE = 2y + 3. Find the values of x and y. The diagram is not to scale. a. x = 6, y = 3 b. x = 2, y = 3 c. x = 3, y = 2 d. x = 3, y = 6 8. Find AM in the parallelogram if PN =9 and AO = 4. The diagram is not to scale. a. 8 b. 4 c. 2 9 d. 4.5 Name: ________________________ ____ ID: A 9. If ON = 5x − 5, LM = 4x + 4, NM = x − 9, and OL = 2y − 5, find the values of x and y for which LMNO must be a parallelogram. The diagram is not to scale. 2 5 c. x = 0, y = 5 2 2 5 b. x = 0, y = d. x = 9, y = 5 2 ____ 10. If m∠B = m∠D = 41, find m∠C so that quadrilateral ABCD is a parallelogram. The diagram is not to scale. a. x = 9, y = a. 41 b. 139 c. 82 d. 278 ____ 11. DEFG is a rectangle. DF = 5x – 5 and EG = x + 11. Find the value of x and the length of each diagonal. a. x = 4, DF = 13, EG = 13 c. x = 4, DF = 15, EG = 15 b. x = 4, DF = 15, EG = 18 d. x = 2, DF = 13, EG = 13 ____ 12. m∠R = 130 and m∠S = 80. Find m∠T. The diagram is not to scale. a. 65 b. 70 c. 3 35 d. 80 Name: ________________________ ID: A Short Answer 13. Find the values of the variables and the lengths of the sides of this rectangle. The diagram is not to scale. 14. Isosceles trapezoid ABCD has legs AB and CD, and base BC. If AB = 4y – 3, BC = 3y – 4, and CD = 5y – 10, find the value of y. 15. One side of a kite is 6 cm less than 4 times the length of another. The perimeter of the kite is68 cm. Find the length of each side of the kite. Essay 16. Given: SV ≅ TU and SV Ä TU Prove: VX = XT 17. Explain how you can determine, without measuring any angles, whether a quadrilateral is a rectangle. 4 Name: ________________________ ID: A 18. Verify that quadrilateral ABCD with vertices A(–5, –1), B(–9, 6), C(–1, 5), and D(3, –2) is a rhombus by showing that it is a parallelogram with perpendicular diagonals. Other 19. Is the quadrilateral a parallelogram? Explain. The diagram is not to scale. 20. Can this quadrilateral be a parallelogram? Explain. 5