Document 10853706
advertisement
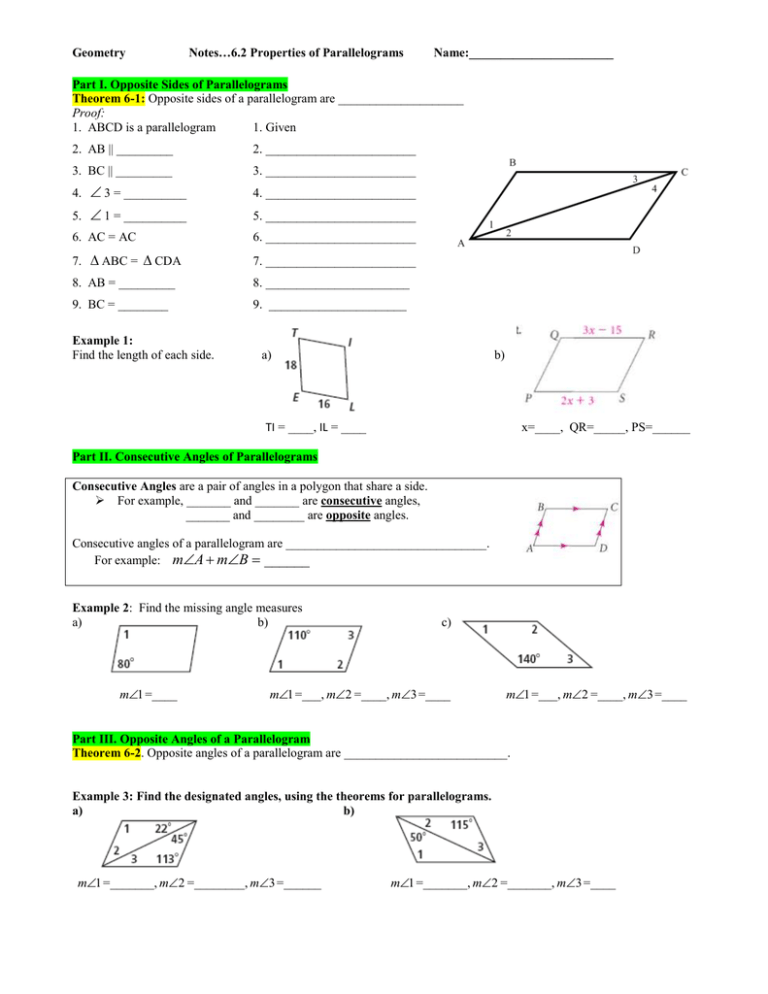
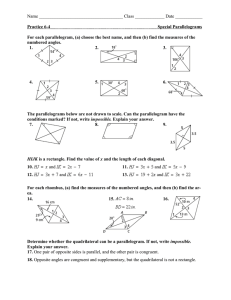
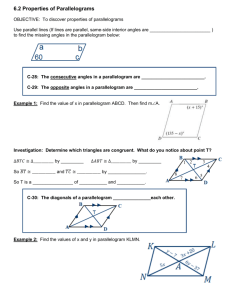
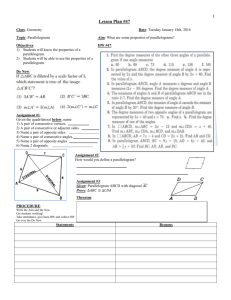
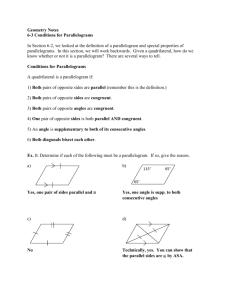
Geometry Notes…6.2 Properties of Parallelograms Name:_______________________ Part I. Opposite Sides of Parallelograms Theorem 6-1: Opposite sides of a parallelogram are ____________________ Proof: 1. ABCD is a parallelogram 1. Given 2. AB || _________ 2. ________________________ 3. BC || _________ 3. ________________________ 3 = __________ 5. 1 = __________ 4. 4. ________________________ 5. ________________________ 6. AC = AC 6. ________________________ 7. ABC = CDA 7. ________________________ 8. AB = _________ 8. _______________________ 9. BC = ________ 9. ______________________ Example 1: Find the length of each side. a) b) TI = ____, IL = ____ x=____, QR=_____, PS=______ Part II. Consecutive Angles of Parallelograms Consecutive Angles are a pair of angles in a polygon that share a side. For example, _______ and _______ are consecutive angles, _______ and ________ are opposite angles. Consecutive angles of a parallelogram are ________________________________. For example: mA mB ______ Example 2: Find the missing angle measures a) b) m1 =____ c) m1 =___, m2 =____, m3 =____ m1 =___, m2 =____, m3 =____ Part III. Opposite Angles of a Parallelogram Theorem 6-2. Opposite angles of a parallelogram are __________________________. Example 3: Find the designated angles, using the theorems for parallelograms. a) b) m1 =_______, m2 =________, m3 =______ m1 =_______, m2 =_______, m3 =____ c) d) y=_______, mE _____, mG _____ m1 =___, m2 =____, m3 =____ Part IV. Proving a parallelogram is a rectangle or a square. A Rectangle is a parallelogram with 4 ____________ angles A Square is a parallelogram with 4 ____________angles and __________ sides are congruent To show you have a square: Opposite Sides are __________ Two adjacent sides are ____________________. One angle is ________ degrees. To show you have a rectangle: Opposite Sides are ___________ One angle is __________ degrees. Example: Show the vertices R(-2, -3), S(4, 0), T(3, 2), V(-3, -1) 1. Parallel sides: Slope of RS=___________ Slope of TV= ________ Slope of ST=___________ Slope of VR=_________ ________ || _______ and ______ || _______, therefore RSTV is a parallelogram 2. Right angles: Show RS ST: (Slope of RS)(Slope of ST) = ______. Therefore mS _______ Applying the above Angle Theorems for Parallelograms: mT ______, mV ________, mR _________ Part V. Diagonals of a Parallelogram Theorem 6-3. The ________________ of a parallelogram _____________________ each other. AO = _____________ and BO = ______________ Example 4: a) x = ___________ d) b) c) EG = ______ x = ___________ e) IK = 46 x=___________ f) x =______________ y =______________ x=________________ g) a =_____________ b =_____________