I. Chemical level A. Basic definitions has mass
advertisement

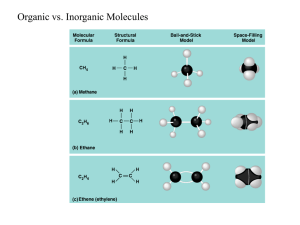
I. Chemical level A. Basic definitions 1. matter – anything that occupies space and has mass 2. element – basic unit of all matter (109 total) a. 92 natural elements b. 4 basic – H, C, O, N, -96% of human mass Ca, P -> 99% (3%) K, S, Cl, Mg, I, FE, (16 other)1% -> 100% c. atomic structure 1. nucleus – p+ and n0 (inside) e- - (outside) 2. #e- = #p+ d. atomic number is the number of protons e. atomic mass =p+ + n0 f. electrons in energy levels – 2,8,18, etc… 1.electrons jump – light releases 2.atom – attempts to fill outer levels (valence) and bonding is the result 3.bonding – sharing, or giving/ receiving of valence electrons – chemical reaction B. Molecule – 2 or more atoms chemically combined C. Compound – combination of 2 or more elements D. Bonding 1. ionic – giving or receiving of e- (bond) transfer e- results in a change in charge ions – anions, cation electrolytes – ionic solution 2. covalent - more common in human body more stable sharing of e-, 1-4 pair H2, H2O, CO2, O2, N2 a. H, O, N, C 3. Hydrogen bond – a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one O or one N H – O or H – N – may also be attracted to other O or H Weak bridges between molecules a. only 5% as strong as a covalent bond b. break and form easily c. found in H2O, proteins, and nucleic acids E. synthesis reaction – anabolic (anabolism) A + B AB (reactants) (products) amino acids proteins *energy required F. decomposition – catabolism AB A + B breakdown of food energy released G. exchange (replacement) – single or double replacement AB + C AC + B AB + CD AD + CB II. Chemical compounds and life processes A. inorganic compounds– usually lack carbon – small 1. H2O – most abundant inorganic substance in a human a. 60% red blood cells b. 75% muscle c. 92% plasma d. solvent – universal – liquid or gas that something dissolves into e. absorbs and releases heat slowly – maintains homeostasis f. lubricant – saliva, mucous g. suspension medium 2. acids – dissociates into H+ and an anion 3. bases – dissociates into OH- and a cation 4. salts – ionize to form anions and cations NaCl Na+ + Cl5. pH – degree of acidity or alkalinity of a soln H+ > more acidic OH- > more basic a. pH scale – 0-14 0------------------7----------------14 many H+ neutral many OHfew OHfew H+ acidic basic 6. buffer system – maintains the body’s pH by replacing strong acids and bases with weak acids and bases D. Organic compounds – always contain carbon – covalent 1. Carbohydrate – C:H:O =1:2:1 ratio a. sugars – 1. monosaccharide (3-7 carbons) glucose, fructose, ribose, and pentose (deoxyribose) 2. disaccharides – sucrose dehydration synthesis of 2 monosaccharides (H2O stripped) b. starches 1. polysaccharides – starch, glycogen broken by hydrolysis 2. Lipids (fats) – C, H, O, - no fixed ratio and most are not water soluable a.two basic components are glycerol and fatty acids b. harder to break down than carbons but actually provide 2x the energy of carbo’s or protein c. saturated, unsaturated, polyunsaturated o saturated – single control bonds between carbons – all C are bonded to a maximum number of H beef, pork, butter, whole milk, eggs and cheese the liver produces cholesterol from the breakdown of sat. fats o monounsaturated - 1 double covalent bond between C olive oil, peanut oil help reduce cholesterol o polyunsaturated – more than 1 double covalent bond corn oil, safflower oil, sunflower oil, cottonseed oil, sesame oil, soybean oil help reduce cholesterol 3.Proteins - C, H, O, N body structure, physiological activities ( catalysts) amino acids – 20 different and are the building blocks - amino group NH2 - carboxyl group COOH - side chain – R group peptide bonds - dipeptide – two amino acids - tripeptide – three - polypeptides – more than three 4. Nucleic acids – large organic molecules - C, H, O, and P DNA – double helix - nitrogenous bases, pentose, and phosphate 1000 rungs of a DNA form a gene RNA – single strand 5. Enzymes – normal body temp and pressure are too low for chemical reactions to occur rapidly enough enzymes are regulators (catalysts) specificity – specific - substrates – molecule on which enzymes react 1. efficiency 2. control 6. ATP – energy – short term molecule adenine + sugar + phosphate