Ch 25 Capacitance
advertisement

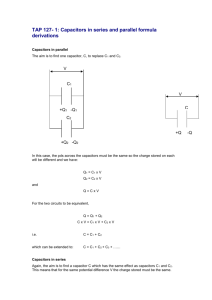
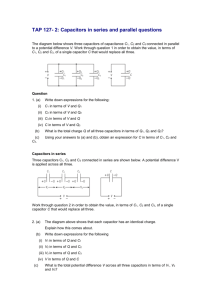
Ch 25 Capacitance , ⁄ , , 2 Capacitance. Charging a capacitor. Definition of capacitance: . Units: [ ] Checkpoint 1 3 Calculating the Capacitance. Calculating the electric field. Calculating the potential difference. Parallel-Plate capacitor. If the area of the plates is , their separation is , and the charge on each plate is , then the electric field is and Cylindrical capacitor: Spherical capacitor: , where the cylinder has length , radii , where the radii are Isolated sphere capacitor: . and . and . , where the radius is . Checkpoint 2 Sample Problem: Charging the plates in a parallel-plate capacitor 4 Capacitors in Parallel and in Series. Capacitors in parallel. When a potential difference V is applied across several capacitors connected in parallel, that potential difference V is applied across each capacitor. The total charge Q stored on the capacitors is the sum of the charges stored on all the capacitors. Capacitors connected in parallel can be replaced with an equivalent capacitor that has the same total charge Q and the same potential difference V as the actual capacitors. Parallel combination: Capacitors in series. When a potential difference V is applied across several capacitors connected in series, the capacitors have identical charge Q. The sum of the potential differences across all the capacitors is equal to the applied potential difference V. Capacitors connected in series can be replaced with an equivalent capacitor that has the same charge Q and the same total potential difference V as the actual series capacitors. Series combination: Checkpoint 3 Sample Problem: Capacitors in parallel and in series Sample Problem: One capacitor charging up another capacitor 5 Energy Stored in an Electric Field. Explosions in airborne dust. Energy density. The potential energy of a charged capacitor may be viewed as being stored in the electric field between its plates. The energy stored in a capacitor is ( ) The energy density (energy/volume) of any electric field is ( ) Units: [ ] Sample Problem: Potential energy and energy density of an electric field. ----------------Material below is not covered in this course----------------------------------------------------6 Capacitor with a Dielectric 7 Dielectrics: An Atomic View 8 Dielectrics and Gauss’ Law ⁄