Unit 2 Day 1 – Definition & Determination of Capacitance
advertisement

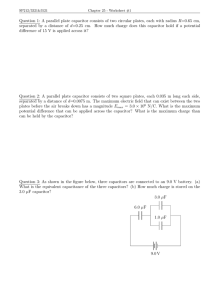
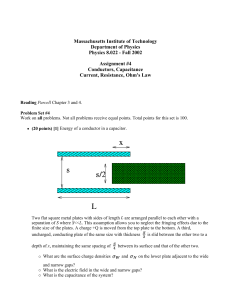
Definition & Determination of Capacitance • Definition of Capacitance • Uses for Capacitors • Capacitor Symbology • Properties of a Capacitor • Determination of Capacitance Capacitors • A capacitor is a device which stores electric charge on two conducting plates, separated by a finite gap. • Electric potential energy is stored in a uniform electric field, generated by the charge distribution on the two plates Uses for Capacitors • Capacitors are used to dissipate electric energy to run a camera flash • A capacitor can provide energy to back-up computer power supplies • Capacitors can block low frequency AC signals, and act as power supply filters Capacitor Symbology • Capacitor schematic symbols • vs. Battery schematic symbol Properties of a Capacitor • When a capacitor is connected to a source of potential difference (battery), the electrons are drawn to the (+) terminal of the battery & flow to the other plate, until equilibrium has been reached Properties of a Capacitor • The electron debt on the LH plate leaves the plate with a net (+) charge. The excess electrons on the RH plate leaves the plate with a net (-) charge. • +Q -Q • The establishment of this charge distribution leads to the development of a uniform electric field between the plates Capacitance Parameters • The amount of potential difference (ΔV) that can be applied across the plates is limited by the amount of charge that can be accumulated on the plates & is given by the relationship: Q C V • SI Units: Farads (1μF = 1.0 x 10-6 F) Determination of Capacitance • The electric field between the plates Is mostly uniform 1 Q ch arg e E where is 0 0 A area Qd V E d 0 A Q A C 0 V d • The capacitance does not depend on Q or ΔV but only on the geometry of the device The Coaxial Capacitor 20l C Ra ln Rb Capacitance of Parallel Conducting Wires • 2 conducting wires, of radius R, and length l C 0l d ln R