World Health Organization (WHO) International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF)
advertisement

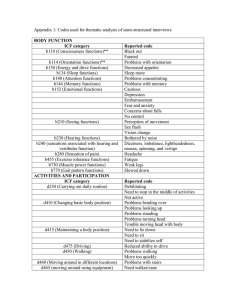
World Health Organization (WHO) International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) Disablement models • Interrelationship among – Disease, impairments, functional limitations, disabilities, handicapps, and the environment • Nagi – Active pathology, impairment, functional limitations and disability • ICF – Alters the perspective of disability models from framework of causes of disability and health to a framework that describes the impact the changes in health has on person‐ does not focus on cause but captures a descriptive assessment of the disability – Individual function is complex dynamic relationship between • Health condition • Environment and personal factors – Body Functions and Structures, Activities and Participation World Health Organization (WHO) • Family of Classifications‐ describe the health status of an individual at a point in time • International Classification of Function – Classify function and disability • ICD‐9 (ICD 10 coming)‐ classify diagnosis disease and disorders • Combination of 2 is meant to describe a patient in combining the diagnosis with the corresponding disability 1 ICF • Health Condition – Disorder, disease, injury, trauma , aging or congenital abnormality (ICD‐9 and 10 codes) • Body function‐ physiological and neuromuscular function • Body Structure‐ anatomical parts of body • Impairments – problems in body function or structure that are perm or temporary • Activity‐ execution of a task or action • Activity limitation‐ difficulty executing activities • Participation‐ involvement with life situations • Participation restriction‐ problems in involvement with life situations • Environmental Factors‐ physical, social and attitudinal environment in which people live and conduct life ICF • Personal – Background of Life – age, gender , race, habits , lifestyle and social background • Environmental Factors – Physical, social, attitudinal environment in which people live and conduct life • These 2 Interact and Impact Function ICF Model Disability and function are Interactions between health Conditions and contextual factors Health Condition (disorder/disease) Body functions and structure Environmental Factors Activity Participation Personal Factors 2 ICF Model: Body Functions • Impairments of: – Mental functions – Sensory functions – Functions of the cardiovascular, and respiratory systems – Neuromusculoskeletal and movement related functions • Mobility of joint, muscle power, muscle tone, involuntary movements ICF Model: Body Structures • Impairments of: – Structure of the nervous system – Structure of the cardiovascular and respiratory system – Skin and related structures – Structure related to movement • Head and neck, shoulder, UE, pelvis, LE, trunk ICF Model: Body Structures and Function • Both use qualifiers to describe extent – No impairment – Mild impairment – Moderate impairment – Severe impairment – Complete Impairment – Not specified – Not applicable 3 ICF: Activity Limitations and Participation Restrictions Learning and applying knowledge General tasks and demands – Communication – Mobility – Self care Domestic life Interpersonal interactions and relationships Major life areas Community social and civic life Qualifiers • ICF becomes a classification when qualifiers are used • Performance qualifier – What individual does in current environment – Involvement in life situation‐ includes assistive devices • Capacity qualifier – Ability to execute a task or action – Highest probable level of functioning in a standard environment • If capacity >performance than environment is barrier to performance • If performance > capacity than environment has facilitated performance ICF: Environmental Factors • Products and technology • Natural environment and human made changes (climate, light, sound, terrain) • Support and relationships • Legal and social structures • Attitudes • Services, systems and policies • Described in barriers or facilitators 4 ICF: Personal Factors • • • • • • • Lifestyle Habits Social background Education Life events Race/ethnicity Sexual orientation Why the ICF model over others? 1. Accepted/endorsed by APTA, international community, and across health professions 2. Interaction between areas/non‐causal relationships 3. Inclusion of contextual factors 4. Uses neutral language to allow us to talk about enabling and disabling factors. ICF Definitions • Function= Non‐problematic or neutral aspects of health • Disability= – Body function and structures – Activity Limitation – Participation Limitation 5 ICF • Validated cross culturally in over 40 countries • Describes components of functioning impacted by a health condition • Unifies the medical and social models of disablement – Function is associated with and not just a consequence of a health condition 6 What ICF is Not • NOT Classify People ‐ – Unit of Classification is function of person in relation to health • Not Clinical Assessment or Measurement Tool – Framework and set of classifications on which assessments and measurements may be based – Professionals develop the tools to measure the function • Not just for people with disability – Health related state for all people • Not Describes the Patient – Describes the function at one point in time or over time 7