Volcanoes I. Molten rock

Volcanoes
I.
Molten rock a.
Magma - beneath the Earth’s surface b.
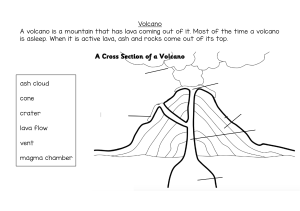
Lava - magma that extrudes onto the surface of the Earth i.
Pahoehoe - (pa-hoy-hoy)- freely flowing lava that forms a thin skin with wrinkles and then looks like twisted rope when solid ii.
Aa - (ah-ah)- rough, jagged surface with dangerously sharp edges
II.
Different types of Cones a.
Shield Volcanoes -built by a steady supply of very fluid basaltic lava.
Have a broad, gently sloping cone that resembles a shield. i.
Mauna Loa in Hawaii- largest volcano on earth b.
Cinder Cones -very steep, but not high, formed from explosive eruptions from a single vent. i.
Sunset Crater- Arizona ii.
Paricutin- Mexico c.
Composite Cone - (Stratovolcano) erupts both lava and ash with a steep summit and gently sloping sides i.
Erupts explosively ii.
Mt. Vesuvius, Mount Pele Mnt. St Helens, Mt. Pinatubo
III.
Craters - formed at the central vent of an erupting volcano. Increase in size during eruptions i.
Calderas -very large crater > 5km in diameter
1.
Yellowstone National Park- a.
Remnant of a volcano that erupted 600,000 yrs ago. i.
Hot springs, bubbling mud, steaming pools, geysers