Document 10787128
advertisement

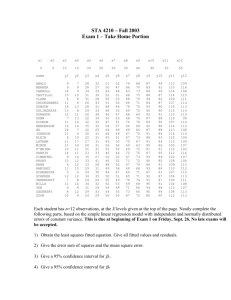
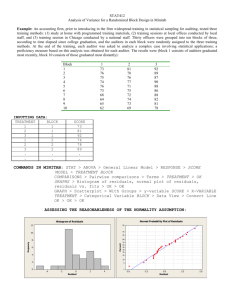
Things to know and formulas for Exam 1 Three decisions. Three sources of variability. Three types of variability. Control, Replication, and Randomization. How to use the sample size tables. How to interpret computer output. Two independent Sample Problem Equal Variance Condition s 2p t n1 1s12 n2 1s22 with df n1 n2 2 n1 n2 2 Y1 Y2 1 1 s p n1 n2 1 1 n1 n2 Y1 Y2 t * s p Analysis of Variance, 1-Factor with k levels Source df Sums of Squares Factor k–1 Error C. Total R2 SS Factor SS C.Total Mean Square F-Ratio ni Yi Y S SFactor k - 1 MS Factor MS Error N–k ni 1si2 S SError N - k N–1 Yij Y 2 ̂ 2 ̅ ̅ 1 Multiple Comparisons, LSD t * has df df Error and 95% confidence for each comparison 1 1 LSD t * MS Error ni n j Yi Y j LSD then the difference in sample means is statistically significan t Confidence interval for the difference in two means Yi Y j LSD Analysis of Residuals To check for equality of standard deviations, plot residuals versus treatments and compute the standard deviation of the residuals for each treatment. To check for normality, look at the distribution of residuals. 2