Loops and Curves
advertisement
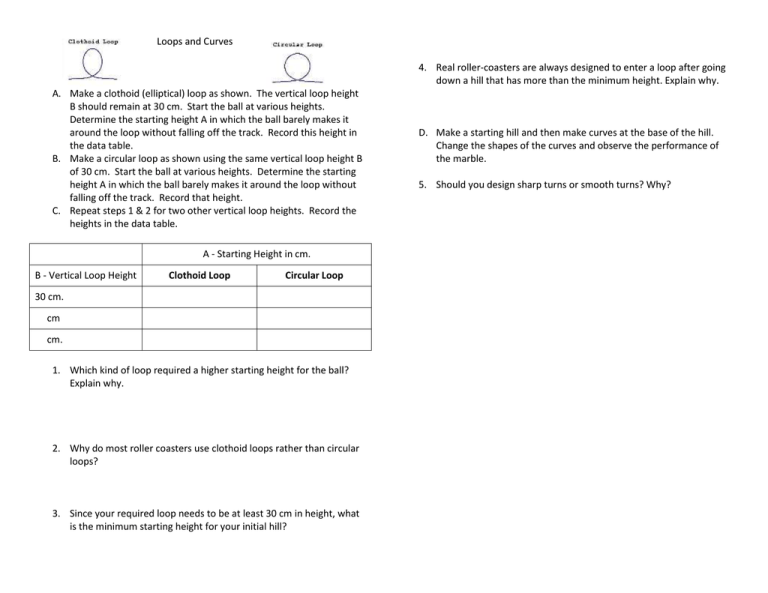
Loops and Curves 4. Real roller-coasters are always designed to enter a loop after going down a hill that has more than the minimum height. Explain why. A. Make a clothoid (elliptical) loop as shown. The vertical loop height B should remain at 30 cm. Start the ball at various heights. Determine the starting height A in which the ball barely makes it around the loop without falling off the track. Record this height in the data table. B. Make a circular loop as shown using the same vertical loop height B of 30 cm. Start the ball at various heights. Determine the starting height A in which the ball barely makes it around the loop without falling off the track. Record that height. C. Repeat steps 1 & 2 for two other vertical loop heights. Record the heights in the data table. A - Starting Height in cm. B - Vertical Loop Height Clothoid Loop Circular Loop 30 cm. cm cm. 1. Which kind of loop required a higher starting height for the ball? Explain why. 2. Why do most roller coasters use clothoid loops rather than circular loops? 3. Since your required loop needs to be at least 30 cm in height, what is the minimum starting height for your initial hill? D. Make a starting hill and then make curves at the base of the hill. Change the shapes of the curves and observe the performance of the marble. 5. Should you design sharp turns or smooth turns? Why?