Science SCI.III.1.2
advertisement

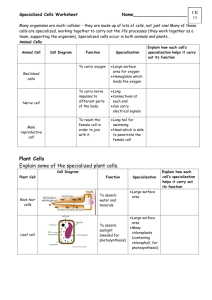
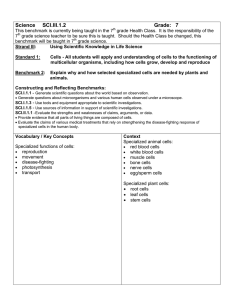
Science SCI.III.1.2 Grade: 6 Strand III: Using Scientific Knowledge in Life Science Standard 1: Cells - All students will apply and understanding of cells to the functioning of multicellular organisms, including how cells grow, develop and reproduce. Benchmark 2: Explain why and how selected specialized cells are needed by plants and animals. Constructing and Reflecting Benchmarks: SCI.I.1.1 Generate scientific questions about the world based on observation. • Generate questions about microorganisms and various human cells observed under a microscope. SCI.I.1.3 Use tools and equipment appropriate to scientific investigations. SCI.I.1.5 Use sources of information in support of scientific investigations. SCI.II.1.1 Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of claims, arguments, or data. • Provide evidence that all parts of living things are composed of cells. • Evaluate the claims of various medical treatments that rely on strengthening the disease-fighting response of specialized cells in the human body. Vocabulary / Key Concepts Context Specialized functions of cells: • reproduction • photosynthesis • transport • movement • disease-fighting Specialized plant cells: • root cells • leaf cells • stem cells Specialized animal cells: • red blood cells • white blood cells • muscle cells • bone cells • nerve cells • egg/sperm cells Knowledge and Skills Students will explain that plants and animals are made of specialized cells that make up different tissues, organs, and organ systems. Each organ or organ system is made of specialized cells that carry out the functions of that organ or system. Examples: • Reproduction: egg (ovule) and sperm (pollen) carry instructions for creating a new organism • Transport: root and stem cells transport water, minerals, and food • Photosynthesis: leaf cells are where this occurs • Disease-fighting: White blood cells fight disease • Movement: Muscles and bones are specialized for movement and support Resources Coloma Resources CO2 & O2 meters from Vernier Software – located in the classroom Laser Disk on Diversity of Life – in Library The Power Plant (booklet) written by K Roth and C Anderson Other Resources: • Microworlds – NSRC – p. 67 “Looking Inside an Onion” • The Lives of Plants – MDE, New Directions Unit – p. 79 • Magnificient Microworld Adventures – AIMS • The Budding Botanist – AIMS • Kids Growlab – National Gardening Association • The Private Eye • Franklin Institute online – Anatomy and Physiology - EXCELLENT cell and plant links • Life Science - Plants http://www.utm.edu/departments/ed/cece/fif th/5F2.shtml • Scope Unit - Cell Theory and Biological Organization 6th Grade Science Curriculum Technology Resources III.1.MS.2 Explain why and how selected specialized cells are needed by plants and animals. Instruction Focus Question: Why are specialized cells needed by plants? Working in small groups, students will examine a common small plant, such as a marigold. Looking at the plant, students will draw the entire plant and label the three basic organs (leaf, stem and roots). Next to each organ, the students will: • describe the function/purpose of each part • draw what the cells might look like in each part Students will continue investigating plant cells by: • collecting actual cell samples • examining cell samples to determine their functions • analyzing the similarities/differences between their predicted and actual drawings Assessment Optional Assessment Students will select an organism and one of its specialized cells to research. They will prepare a summary of their research, including information about its structure (visual representation) and function (written summary) that could be used on a class web site. (Give students rubric before activity.) Scoring Rubric Criteria: Accuracy of visual representation: Apprentice - Shows a sketchy visual of a cell. Basic - Displays a visual of a cell structure. Meets - Designs an accurate visual of specialized cells. Exceeds - Designs a detailed, comprehensive visual(s) of several specialized cells. Criteria: Completeness of description: Apprentice - Provides a vague description of cell function. Basic - Describes briefly the cell’s function. Meets - Describes the function(s) accurately of the specialized cell. Exceeds - Describes in detail the function(s) of several specialized cells. Criteria: Correctness of format: Apprentice - Explains with inappropriate vocabulary or grammar. Basic - Explains with partially correct vocabulary and grammar. Meets - Explains with appropriate vocabulary and grammar. Exceeds - Explains with extended vocabulary and exceptional grammar. Teacher Notes: See III.2.MS.4 (link) Systems and processes functioning to provide/remove materials to/from cells