Lecture 29 CSE 331 Nov 11, 2009
advertisement

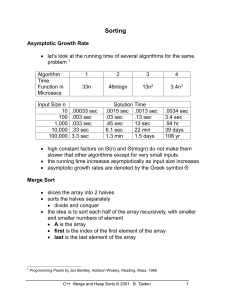
Lecture 29 CSE 331 Nov 11, 2009 To be strictly enforced For the rest of the semester on Fridays SUBMIT your HOMEWORKS by 1:10 PM Extra Q sessions next week Monday and Tuesday 4-6pm CSE 242 Mergesort algorithm Input: a1, a2, …, an Output: Numbers in sorted order MergeSort( a, n ) If n = 2 return the order min(a1,a2); max(a1,a2) aL = a1,…, an/2 aR = an/2+1,…, an return MERGE ( MergeSort(aL, n/2), MergeSort(aR, n/2) ) An example run 51 1 100 19 2 8 1 51 19 100 2 8 1 19 51 100 2 1 2 3 4 8 4 3 3 19 MergeSort( a, n ) If n = 2 return the order min(a1,a2); max(a1,a2) aL = a1,…, an/2 aR = an/2+1,…, an return MERGE ( MergeSort(aL, n/2), MergeSort(aR, n/2) ) 3 4 4 51 8 100 Correctness Input: a1, a2, …, an Output: Numbers in sorted order MergeSort( a, n ) If n = 2 return the order min(a1,a2); max(a1,a2) aL = a1,…, an/2 aR = an/2+1,…, an return MERGE ( MergeSort(aL, n/2), MergeSort(aR, n/2) ) Inductive step follows from correctness of MERGE By induction on n Today’s agenda Show that Mergesort runs in O(n log n) time Solve recurrences To be strictly enforced For the rest of the semester on Fridays SUBMIT your HOMEWORKS by 1:10 PM