Popular Screens for Cognitive Impairment Test Name Brief Description
advertisement
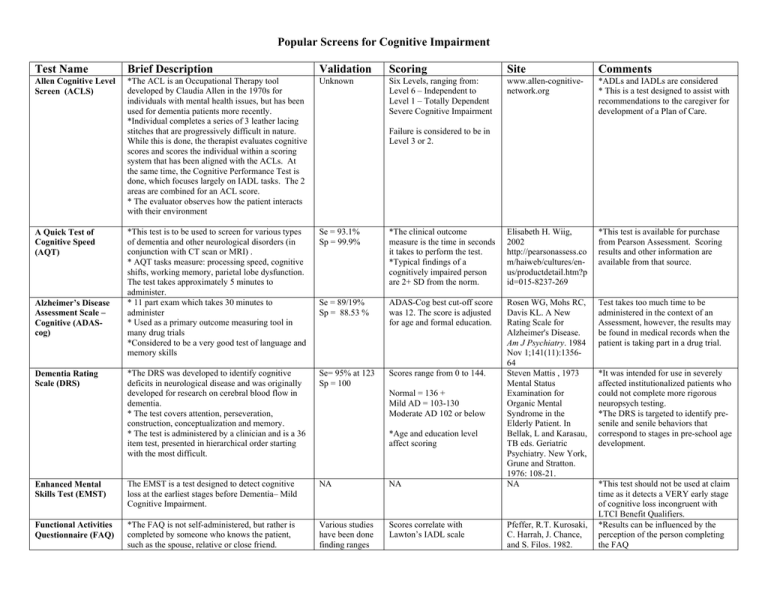
Popular Screens for Cognitive Impairment Test Name Brief Description Validation Scoring Site Comments Allen Cognitive Level Screen (ACLS) *The ACL is an Occupational Therapy tool developed by Claudia Allen in the 1970s for individuals with mental health issues, but has been used for dementia patients more recently. *Individual completes a series of 3 leather lacing stitches that are progressively difficult in nature. While this is done, the therapist evaluates cognitive scores and scores the individual within a scoring system that has been aligned with the ACLs. At the same time, the Cognitive Performance Test is done, which focuses largely on IADL tasks. The 2 areas are combined for an ACL score. * The evaluator observes how the patient interacts with their environment Unknown Six Levels, ranging from: Level 6 – Independent to Level 1 – Totally Dependent Severe Cognitive Impairment www.allen-cognitivenetwork.org *ADLs and IADLs are considered * This is a test designed to assist with recommendations to the caregiver for development of a Plan of Care. *This test is to be used to screen for various types of dementia and other neurological disorders (in conjunction with CT scan or MRI) . * AQT tasks measure: processing speed, cognitive shifts, working memory, parietal lobe dysfunction. The test takes approximately 5 minutes to administer. * 11 part exam which takes 30 minutes to administer * Used as a primary outcome measuring tool in many drug trials *Considered to be a very good test of language and memory skills Se = 93.1% Sp = 99.9% *The clinical outcome measure is the time in seconds it takes to perform the test. *Typical findings of a cognitively impaired person are 2+ SD from the norm. Elisabeth H. Wiig, 2002 http://pearsonassess.co m/haiweb/cultures/enus/productdetail.htm?p id=015-8237-269 *This test is available for purchase from Pearson Assessment. Scoring results and other information are available from that source. Se = 89/19% Sp = 88.53 % ADAS-Cog best cut-off score was 12. The score is adjusted for age and formal education. Test takes too much time to be administered in the context of an Assessment, however, the results may be found in medical records when the patient is taking part in a drug trial. *The DRS was developed to identify cognitive deficits in neurological disease and was originally developed for research on cerebral blood flow in dementia. * The test covers attention, perseveration, construction, conceptualization and memory. * The test is administered by a clinician and is a 36 item test, presented in hierarchical order starting with the most difficult. Se= 95% at 123 Sp = 100 Scores range from 0 to 144. Enhanced Mental Skills Test (EMST) The EMST is a test designed to detect cognitive loss at the earliest stages before Dementia– Mild Cognitive Impairment. NA NA Rosen WG, Mohs RC, Davis KL. A New Rating Scale for Alzheimer's Disease. Am J Psychiatry. 1984 Nov 1;141(11):135664 Steven Mattis , 1973 Mental Status Examination for Organic Mental Syndrome in the Elderly Patient. In Bellak, L and Karasau, TB eds. Geriatric Psychiatry. New York, Grune and Stratton. 1976: 108-21. NA Functional Activities Questionnaire (FAQ) *The FAQ is not self-administered, but rather is completed by someone who knows the patient, such as the spouse, relative or close friend. Various studies have been done finding ranges Scores correlate with Lawton’s IADL scale A Quick Test of Cognitive Speed (AQT) Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale – Cognitive (ADAScog) Dementia Rating Scale (DRS) Failure is considered to be in Level 3 or 2. Normal = 136 + Mild AD = 103-130 Moderate AD 102 or below *Age and education level affect scoring Pfeffer, R.T. Kurosaki, C. Harrah, J. Chance, and S. Filos. 1982. *It was intended for use in severely affected institutionalized patients who could not complete more rigorous neuropsych testing. *The DRS is targeted to identify presenile and senile behaviors that correspond to stages in pre-school age development. *This test should not be used at claim time as it detects a VERY early stage of cognitive loss incongruent with LTCI Benefit Qualifiers. *Results can be influenced by the perception of the person completing the FAQ Test Name Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) mini-cog Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE) aka Folstein Test of Mental Status Brief Description Validation * It is a 10-item questionnaire based largely on IADLs, social activities and current events *In 1984, the test was expanded to include 4 ADL questions and a question about initiative as follows: Sn = 85% to 94% Sp = 81% to 84% *Global Assessment of Functioning is for reporting the clinician's judgment of the individual's overall level of functioning and carrying out activities of daily living. This information is useful in planning treatment and measuring its impact, and in predicting outcome. *The Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) is a numeric scale (0 through 100) used by mental health clinicians and doctors to rate the social, occupational and psychological functioning of adults. GAF levels are commonly used by the Veterans Benefits Administration of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs in determining the appropriate level of disability compensation to be paid to veterans who suffer from service connected psychiatric disorders. The emphasis on using the GAF score has, however, decreased in recent years. *This instrument combines an uncued 3-item recall test with a clock drawing test (CDT). * The patient is given 3 words to recall. Then asked to draw a clock with the hands at a specific time. Instructions can be repeated, but no additional instructions given. The CDT serves as the recall distractor. *The test was developed to give a global impression of change in cognitive status in geriatric inpatients. *It covers the person’s orientation to time and place, recall ability, short-term memory and arithmetic ability. It has been found that the FAQ is a Sensitive as the MMSE unknown unknown *Sensitivity (at a cut score of 23/24) is 93%, *Specificity = 100% in the highly educated; specificity is 75% in the lower educated Scoring Site Comments Measurement of Functional Activities of Older Adults in the Community. Journal of Gerontology 37 (May): 323-9. *The original scale is largely IADL related. If this test is used, verify which components were administered – if ADLs were not included, thenthe test is less useful for LTCI. Scores 41 or below constitute Serious symptoms OR any serious impairment in social, occupational, or school functioning. http://ptsdhelp2000.co m/ptsd1.html This test is used in mental health functioning and therefore is not specifically related to dementia; it can include psychiatric diagnoses. *Relatively uninfluenced by age or education (according to authors) *Scoring: 0 = Positive Screen for Dementia 1 or 2 with abnormal CDT = Positive screen for dementia 1 or 2 with normal CDT = Negative screen for dementia 3 = Negative screen for dementia *Maximum score is 30. * Traditionally scores below 23 are considered to be indicative of cognitive impairment. *Scoring is affected by age and education. Borson S, Scanlon J, Brush M, Vitialiano P, Dokmak A. The minicog: a cognitive “vital signs” measure for dementia screening in multi-lingual elderly. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2000 15(11):1021-1027. * No validation score found. * No specific instructions as to how long the period between word introduction and recall are provided. Marshall Folstein, 1975 www.parinc.com *The test is quick and easy to administer. *It may be used as a screening test for cognitive loss. *It should not be used to diagnose dementia. Test Name Brief Description Minnesota Cognitive Acuity Screen (MCAS) The MCAS is a test designed to detect cognitive loss at the earliest stages before Dementia– Mild Cognitive Impairment. Neuropsychiatric Inventory Questionnaire (NPI-Q) *The Neuropsychiatric Inventory Questionnaire (NPI-Q) is a validated clinical instrument for evaluating psychopathology in dementia. * It is adapted from the NPI as a 2 page questionnaire. * 12 question survey of behaviors in dementia *The authors developed a brief questionnaire form of the NPI (NPI-Q), intended for use in routine clinical practice, and cross-validated it with the NPI in 60 Alzheimer’s patients. * The SPMSQ is intended to offer rapid screen for cognitive deficit in institutions and communitydwelling elderly persons. * 10-item screen covering memory, orientation to surroundings, knowledge of current events and ability to perform math. To make the test more challenging, an answer is scored correct if ALL parts of the question are answered correctly. The Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire (SPMSQ) Validation Scoring Site Comments group NA NA NA *Test-retest reliability was acceptable. *Each question is scored for present or absent *Present behaviors are scored for severity and distress A. Severity (1-Mild to 3Severe) B. Distress (0-No distress to 5-Extremely Distressing) Kaufer (2000) J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 12:233 *This test should not be used at claim time as it detects a VERY early stage of cognitive loss incongruent with LTCI Benefit Qualifiers. The NPI-Q is a self-administered tool in the form of a questionnaire Sensitivity = 88% Specificity = 78% *Scores are corrected for race and education, but generally are: *Mild CI = 3-4 errors Moderate CI = 5-7 errors Severe CI = 8+ errors Eric Pfeiffer, 1975 A Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire for the Assessment of Organic Brain Deficit in the Elderly. J AM Geriatric Soc. 1975; 23-440. * It detects organic intellectual impairment and determines its degree. * The test can be administered by a clinician in under 5 minutes