PES 1120 General Physics II
advertisement

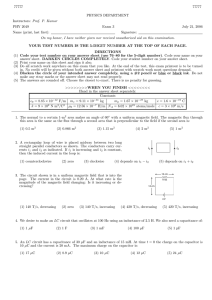
PES 1120 General Physics II Practice Exam 2 One (4” x 6”) index card may be used for formulas or other notes or diagrams. Definitions & Concepts (2 pts each) 1. What units will result from multiplying Amperes by Volts? 2. Magnetic force on an electron traveling through a uniform magnetic field, B, as shown in the given diagram. What direction is the electron traveling? a. Up b. Right c. Into page d. Out of page B F 3. What units result from multiplying ohms and farads? Applications 4. If 5 mA of current flow through a wire of diameter 1 mm, what is the current density through the wire? 5. (removed) 6. What is the equivalent capacitance of the combination shown? 7. Air-filled parallel plate capacitor a. The capacitor is constructed with a capacitance of 6F. If the plates are 0.1 mm apart, what is the area of one of the plates? b. A voltage source of 12 V is connected across the capacitor. How much charge eventually moves onto the positive plate? c. How much energy is now contained in the capacitor? d. Some Pyrex glass (dielectric constant of 5.6) is inserted between the plates and the capacitor is again connected to the same voltage source. What is the new capacitance? R. Gist 1 of 3 Short Semester Ver. A, Rev 2 PES 1120 General Physics II Practice Exam 2 8. A rod of 2.0-m length and a square (2.0 mm x 2.0 mm) cross section is made of a material with –8 a resistivity of 6.0 x 10 m at 20o Celcius. a. What is the resistance of the rod at this temperature? b. If a potential difference of 0.50 V is placed across the ends of the rod, what is the initial current? c. At what rate is heat generated (i.e. power used) in the rod the instant current begins to flow? d. The material then heats up to an operating temperature of 500 degrees Celcius. The temperature coefficient of the material is 0.5 x 10-3 Kelvin-1. What is the operating resistance? 9. Determine the voltage and current for the 8 resistor. 10. A capacitor of capacitance 12F and a resistor of 50 and a switch are connected in series with a battery of voltage 10V. How long after the switch is closed does it take for the charge in the capacitor to reach half of its maximum amount? 11. What is the equivalent resistance between a and b in the diagram? 12. A charged particle (charge = 5.0 µC) moves in a region of a 9 mT magnetic field directed along the vector (2/3 i +1/3 j – 2/3 k). The particle’s velocity is specified by (3000 m/s)i + (4000 m/s)j. What is the magnetic force vector on the particle? R. Gist 2 of 3 Short Semester Ver. A, Rev 2 PES 1120 General Physics II Practice Exam 2 13. The figure shows the orientation of a rectangular loop consisting of 80 closely wrapped turns each carrying a current of 8.0 A. The magnetic field in the region is 50 mT along the x-axis. The loop is hinged so that it can turn about the y axis. If = 30, a = 0.40 m, and b = 0.30 m, what is the magnitude of the torque exerted on the loop? 14. What will be the radius of curvature (cyclotron radius) of the path of a proton (mass=1.67 x 10-27 kg, charge=1.602 x 10-19 C) with a kinetic energy of 3.0-keV (1eV=1.602 x 10-19 J) in a perpendicular magnetic field of magnitude 0.40 T? Constants o kE R. Gist Permittivity of free space Coulomb’s constant 3 of 3 8.854 x 10-12 C2/(N*m2) 8.98 x 109 N*m2/C2 Short Semester Ver. A, Rev 2