Study guide part II
advertisement

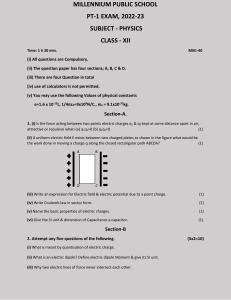
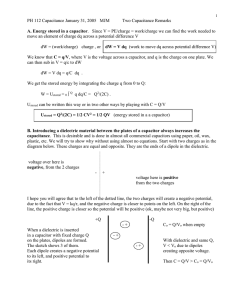
Study Guide Part II - Modern Physics Mrs. Ashley College Physics Name ____________________________________________ The following concepts will be covered on the test: Static electricity Unlike charges attract and like charges repel Insulators and conductors semiconductors Coulomb's Law F = k Q1Q2 r2 K = 8.988 X 109 N m/C2 Permittivity of free space, K = 1/40 0 = 8.85 X 10 -12 C2/N m2 Electric charge is quantized Remember that the electrostatic force between charged particles at rest is a vector When working with the vectors of force between charged particles, sum components of the x and y axis separately. Fx = F1cos an Fy = F1sin You find the magnitude of the resultant force using Pythagorean formula You find the direction by finding the angle that F makes with the x axis by tan = Fy Fx Remember to draw a picture in doing your problems Electric Field F = qE E = F/q E = kqQ/r2 q For Uniform Electric Field Field lines Electric dipole Electric potential W = fd Vba = -Ed PEa - PEb =qEd Electric potential is the electric potential energy per unit charge V = PEa/ q Potential difference is often called Voltage and is measured in Volts, only differences in potential energy can be measured. E = - Vba/d Electron volts Potential can be positive or negative Potential due to electric dipole V = kpcos (formula for dipole moment) r2 Capacitance and capacitor C = 0 A/d (finding the capacitance of a capacitor) Finding the area of the capacitor is A = Cd 0 Electric Currents, chapter 18 Know the parts of a battery What makes a battery produce a charge Know parallel and series circuits Know when a circuit is closed or open Ohms law R = V/I V = IR Modern Physics You will not need to memorize all the formulas below, concepts and understanding the example problems/how to solve is all that is needed. Relativity principle Reference frames Inertial reference frame Simultaneity Time dilation Length contraction proper length relativistic momentum and mass rest mass E = mC2 KE = moC2 1-v2/c2 Wien's Law T = 2.90 X 10-3 m K E = hf h is Planks Constant; f is the frequency and E is the energy hf = KEmax + W0 Use this formula when electrons are ejected from a substance. f = c/ hf = hc/ Photon momentum is found: p = h/ Know the photon interactions and pair production = hc/E Know the wave particle duality Understand principle of complementarity de Broglie wave nature of mater = h/p Rutherford's model of the atom Bohr model of the atom n2 r Z Atomic spectra Energy levels, ground state and excited states Quantum mechanics of atoms The relationship between wave and particle Heisenberg Uncertainty principle Δx =ħ/Δp