STEREO (Solar Terrestrial RElations Observatory) as a Mars Space Weather Resource p Janet Luhmann, SSL
advertisement

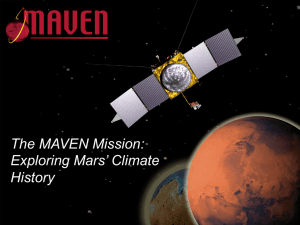
STEREO (Solar Terrestrial RElations Observatory) p as a Mars Space Weather Resource Janet Luhmann, SSL May 2013 The twin spacecraft STEREO mission was instrumented for these science objectives: 1. 2. 3. 4. To Understand the causes and mechanisms of CME initiation To Characterize the propagation of CMEs through the heliosphere To Discover the mechanisms and sites of energetic particle acceleration in the low corona and the interplanetary medium To Develop a 3D time‐dependent model of the magnetic topology, temperature, density, and velocity structure of the ambient solar wind Each STEREO spacecraft contains a full suite of both imaging and in-situ data capability p y ((though g no magnetographs) g g p ) UCLA Russell Group processes and serves MAG data and science While STEREO SECCHI images the Sun, IMPACT and PLASTIC measure all the in‐situ signatures of space weather‐ including the ICMEs and SEP events Mars Atmosphere and Volatile E l i N (MAVEN) Mi EvolutioN Mission i MAVEN is the last Mars Scout Mission (PI Bruce Jakosky, Jakosky LASP) Scheduled for launch in Nov 2013 MAVEN Science Questions MAVEN Science Questions MAVEN will determine the role that loss of volatiles to space has played through time, providing definitive answers about Mars climate history: • What is the current state of the upper atmosphere and what processes control it? • What is the escape rate at the present epoch and how does it relate to the controlling p processes? • What has the total loss to space been through time? The MAVEN spacecraft also contains a full particles and fields package, p g ,p plus a UV spectrometer p and solar EUV flux monitor • 3-axis attitude control (wheel based) • Mono-propellant propulsion system • Single-fault tolerant during all critical events • Launch (Wet) Mass: 2550 kg max • Spacecraft Dry Mass: 903 kg max • Power: 1135 W at Mars Aphelion LPW (2) SWEA Electra (behind) SWIA SEP “Gull-Wing” Solar Arrays Fixed HGA MAG (2) SEP Articulated Payload Platform (IUVS/STATIC/NGIMS) The PF Package Solar Wind Ion Analyzer (SWIA) – SSL EUV Solar Wind Electron Analyzer (SWEA) – IRAP(CESR) / SSL SWEA LPW 2 PLCS SWIA Langmuir g Probe and Waves (LPW) – LASP / SSL LPW/Extreme Ultra-Violet (LPW-EUV) – LASP Solar Energetic Particle Detector (SEP) – SSL SEP 2 PLCS STATIC MAG 2 PLCS Magnetometer (MAG) – GSFC Supra-Thermal and Thermal Ion Composition (STATIC) SSL MAVEN Will Measure the Energetic Drivers, Reservoirs, and Escape Rates • MAVEN will determine the present state of the upper atmosphere and today’s rates of loss to space. • Measurements will allow determination of the net integrated loss to space through time. MAVEN Mission Architecture Launch on Atlas V-401 Ten-Month Ballistic Cruise to Mars 20-Day Launch Period: November 18 – December 7, 2013 Orbit Insertion: 22 Sept 2014 One Year of Science Operations MAVEN Orbit and Primary Science Mission Science Mission • Elliptical orbit to provide coverage of all altitudes • The orbit precesses in both latitude and local solar time • One-Earth-year mission allows thorough coverage of near-Mars space The STEREO orbits at ~1 AU provide changing perspectives on the Sun and multipoint p in-situ sampling p g STEREO +ACE real‐time multipoint measurements at 1 AU give the latest state of space weather (NOAA RT data plots, images from SOHO, SDO) NOAA SWPC plots SOHO/LASCO, SDO/AIA images http://stereo.ssl.berkeley.edu/multistatus.php l i li i S Real‐time multipoint SEP events in early April 2013 -and here are some Multipoint ‘reconstructions’ of coronal mass ejection j magnetic g flux ropes p in Interplanetary space in August 2010 Moestl et al., ApJ 2012-from magnetometer data Sometime in 2015 the STEREO Spacecraft will ‘flip over’ and continue their mission. They have enough fuel to operate for ~100 years. STEREO location on November 15, 2014, just after MAVEN arrives STEREO goes behind the Sun (Earth perspective) and is occulted (=no data): STEREO-A dates: Mar 17-Jul 14, 2015 STEREO-B dates: Jan 20-Mar 28 and Aug 25-Oct 19, 2015 Bottom Line: STEREO provides an incredibly lucky opportunity to enhance the capability of the MAVEN mission toward understanding solar activity effects at Mars.