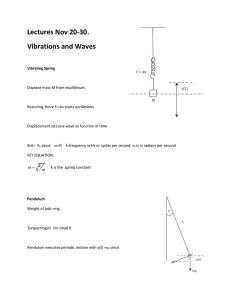
PHY-2464 Physical Basis of Music PHY -
advertisement

PHY2464 - The Physical Basis of Music PHY -2464 PHY-2464 Physical Basis of Music Presentation Presentation 22 Basics Basics of of Sound Sound Waves Waves –– Part Part A A An An edited edited Version Version of of Sam Sam Matteson’s Matteson’s Unit Unit 11 Session Session 22 Sam Sam Trickey Trickey Jan. Jan. 10, 10, 2005 2005 PHYPHY-2464 Pres. 2 Sound Waves - A So far we’ve seen that: • Sound is a longitudinal mechanical wave that originates from a vibration or vibrations and propagates in a (nearly elastic) material medium. • “Wave” = disturbance in material that doesn’t transfer mass; “Elastic” = springs back when deformed 1 PHY2464 - The Physical Basis of Music PHYPHY-2464 Pres. 2 Sound Waves - A Longitudinal waves →↔→ Transverse waves →↕→ Sound is a longitudinal mechanical wave in a material medium. (Stadium wave with people’s arms is transverse.) PHYPHY-2464 Pres. 2 Sound Waves - A Fact: Sound does not propagate (move from one place to another) in a vacuum. Why? True vacuum is empty space → NO matter → NO sound (Practical vacuum has so little matter that there also is no sound.) Sound is a mechanical wave: such waves require a material medium. 2 PHY2464 - The Physical Basis of Music PHYPHY-2464 Pres. 2 Sound Waves - A Aside: Radio (and TV) Radio waves are Electro-magnetic waves, not sound. EM waves are “a disturbance in the force” Sound information is coded in the amplitude modulation (AM) or frequency modulation (FM) of the radio waves. Radio waves are NOT sound. PHYPHY-2464 Pres. 2 Sound Waves - A • Lightning is a high energy electrical discharge • The superheated air expands explosively • A “shock wave” travels to your ear 3 PHY2464 - The Physical Basis of Music PHYPHY-2464 Pres. 2 Sound Waves - A Velocity (speed) of a wave = the distance a point on the wave travels divided by the time it takes to cover that distance v = d /t (clearly also d = v x t and t = d /v ) PHYPHY-2464 Pres. 2 Sound Waves - A Fact - Sound is non-dispersive: its velocity is independent of wavelength. Fact - The velocity of sound in air at room temperature (20 C) and normal atmospheric pressure is 343. m/s 4 PHY2464 - The Physical Basis of Music PHYPHY-2464 Pres. 2 Sound Waves - A FLASH! Rrrrumble PHYPHY-2464 Pres. 2 Sound Waves - A Recall Fact - The velocity of sound in air at room temperature (20 C) is 343. m/s d = v x t = (343m/s)x (3 seconds) = 1029 m ≈ 1 km 5 PHY2464 - The Physical Basis of Music PHYPHY-2464 Pres. 2 Sound Waves - A Summary: • • • • Sound is a longitudinal mechanical wave that originates from a mechanical vibration and propagates in an elastic material medium. Sound is non-dispersive. The velocity of sound in air is 343 m/s at 20 C. Radio waves are E-M waves, not sound. 6