South Fork Payette River
advertisement

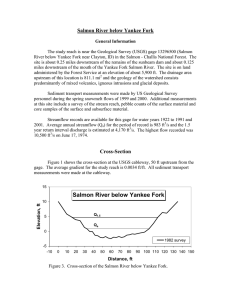
South Fork Payette River General Information The study reach is about a 1,320 ft length of river at the Geological Survey (USGS) gage 13235000 (South Fork Payette River at Lowman, Id.) in the Boise National Forest. The stream gaging station is approximately 0.5 miles downstream from Lowman, Idaho. The site is on land administered by the Forest Service at an elevation of about 3,790 ft. The drainage area upstream of this location is 449.3 mi2 and the geology of the watershed is predominantly intrusive igneous. Sediment transport measurements were made by USGS personnel predominantly during the spring snowmelt discharges of 1994 and 1995. Sediment transport was also measured on May 17, 1997 at a discharge that exceeded those of the previous two sampling years. Additional information collected at the site includes a survey of the stream reach, pebble counts of the surface substrate, core samples of the subsurface substrate material and samples of floodplain deposits. Figures 1 and 2 show photographs of the site looking upstream and downstream from the gaging station. Figure 1. South Fork Payette River looking downstream from the USGS gaging station. Figure 2. South Fork Payette River looking upstream from the USGS gaging station. Stream discharge has been recorded since May 1942. Average annual discharge (Qa) for the period of record is 862 ft3/s and bankfull discharge (Qb) is estimated at 3,050 ft3/s. The range of daily mean discharge for the period of record is 130 ft3/s to 8,900 ft3/s. The highest instantaneous discharge recorded was 8,980 ft3/s on June 16, 1974. Cross-Section Figure 3 shows the cross-section at the USGS gaging station. The average gradient for the study reach is 0.0040 ft/ft. Most sediment transport measurements were made from a bridge about 600 ft upstream of the gaging station. During lower discharges, wading measurements were made either 150 ft or 200 ft downstream of the gaging station. 60 South Fork Payette River at the USGS Gage Elevation, ft 50 40 30 20 10 Qa 0 1994 Survey 1998 Survey -10 -20 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 Distance, ft Figure 3. Cross-section of the South Fork Payette River at Lowman, ID at the USGS Gage. Channel Geometry The channel geometry relationships for the cross-section about 200 ft downstream of the gage where most wading sediment samples were collected in 1994 is shown in Figure 4. Information for 1994 through 1996 within the range of discharges for the sediment transport measurements were used to develop the power relationships with discharge (solid data symbols). Over the range of discharges when sediment transport was measured at this location (721 to 1,250 ft3/s) estimated stream width, estimated average depth and estimated average velocity varied from 156.0 to 177.9 ft, 1.55 to 1.85 ft, and 3.0 to 3.8 ft/s, respectively. The average reach slope is 0.0040 ft/ft. The channel geometry relationships for the bridge cross-section are shown in Figure 5. Sediment transport measurements during higher discharges in 1994 and for all measurements in 1995 and 1997 were made from the bridge (Figure 5). 10 1000 100 Width 0.216 y = 38.103x 2 R = 0.45 10 Average Velocity 0.462 y = 0.142x 2 R = 0.96 Average Velocity, ft/s Width and Depths, ft South Fork Payette River Wading Average Depth 0.322 y = 0.186x 2 R = 0.72 1 10 100 1000 1 10000 Discharge, ft3/s Figure 4. Width, average depth, and average velocity versus stream discharge at the wading cross section on the South Fork Payette River. (Open data symbols represent all data from 1941 to 1996 from cross-sections 150 ft to 200 ft below the gage; solid data symbols represent data from 1994 to 1996 used to develop the displayed power relationships.) 1000 10 100 Top Width y = 119.57x0.043 R2 = 0.16 Average Velocity, ft/s Width and Depth, ft South Fork Payette River at Bridge Mean Velocity y = 0.158x0.447 R2 = 0.97 10 Mean Depth y = 0.068x0.477 R2 = 0.97 1 100 1000 1 10000 Discharge, ft3/s Figure 5. Width, average depth, and average velocity versus stream discharge at the bridge cross section on the South Fork Payette River. (Open data symbols represent all data from 1971 to 1997 from the bridge cross-section about 600 ft upstream of the gage; solid data symbols represent data from 1994 to 1997 used to develop the displayed power relationships.) Channel Material A surface pebble count was made at a cross-section at the USGS gage in August 1994. Surface pebble counts were made at three cross-sections and three cores of subsurface material were collected, one at each cross-section, in October 1995. The average D50 and D90 for the surface material in the reach for the 1994 and 1995 samples are 55 mm and 175 mm and 110 mm and 258 mm, respectively (Figure 6). The average D50 and D90 for the 1995 subsurface material samples are 20 mm and 102 mm, respectively. About 8% of the surface material was sand (2 mm) size or smaller for both the 1994 and 1995 samples. The D50 of the floodplain samples ranged from 0.12 to 0.25 mm. 100 90 South Fork Payette River 80 Percent Finer 70 Floodplain Samples 60 50 40 30 20 Surface 1995 Subsurface 1995 Surface 1994 10 0 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000 Particle Size, mm Figure 6. Particle size distribution for surface and subsurface material and floodplain material samples in the South Fork Payette River study reach. Sediment Transport Sediment transport measurements made in 1994 and 1997 includes 72 measurements of bedload transport and 37 measurements of suspended sediment transport. Sediment transport measurements spanned a range of stream discharges from 721 ft3/s (0.83Qa; 0.24Qb) to 6,390 ft3/s (7.33Qa; 2.10Qb). Bedload transport ranged from 4.67 to 981 t/d and suspended transport ranged from 8.23 to 11,900 t/d. Over the range of measured discharges, suspended transport typically accounts for the majority of the material in transport with over an order of magnitude greater suspended transport than bedload transport at the highest discharges and about similar rates between suspended and bedload transport at the lowest discharges during which sediment transport was measured (Figure 7). 100000 South Fork Payette River Sediment Transport, tons/day 10000 1000 Suspended 3.174 y = 7.360E-09x 2 R = 0.90 BCF=1.238 100 10 Suspended Total Bedload - Wading Total Bedload -Bridge 6 in. Total Bedload - Bridge 3 in. 1 100 Qa Qb 1000 Total Bedload 2.020 y = 1.261E-05x 2 R = 0.70 BCF=1.353 10000 3 Discharge, ft /s Figure 7. Bedload and suspended load transport rate versus discharge (The power relationships include all data. Bedload data symbols code the data by sampling location and size of the bedload sampler.) The bedload transport rates by size class (Figure 8) shows that the larger rates are 1000 South Fork Payette River Bedload Rate, tons/day 100 <0.5mm 1.654 y = 3.207E-05x 2 R = 0.63 0.5-2mm 1.406 y = 5.806E-04x 2 R = 0.31 10 2-8mm 2.015 y = 7.583E-07x 2 R = 0.43 1 0.1 8-32mm 2.140 y = 3.559E-07x 2 R = 0.43 >32mm 1.381 y = 4.534E-04x 2 R = 0.42 0.01 100 Qb Qa <0.5mm 0.5-2mm 2-8mm 8-32mm >32mm 1000 10000 3/ Discharge, ft s associated with material 0.5 to 2 mm diameter. Figure 8. Bedload transport rate versus discharge for selected size classes. The largest particle in the bedload sample generally increased with discharge (Figure 9). The largest particle measured in a bedload sample was 128 mm at a discharge of 3,630 ft3/s. Although the largest particle size increased with discharge, the D50 for most bedload samples was less than 2 mm. However, for many of the bedload samples collected at discharges greater than bankfull discharge, the median diameter of the samples exceeded 2 mm and eight samples exceeded a D50 of 20 mm. The relationship between discharge and the largest particle in the bedload sample and the supporting observation of the largest particle moved in 1997, and associated instantaneous peak discharge for the respective snowmelt period suggest that some material about the median size of the surface material is in motion at discharges near the bankfull discharge. 1000 South Fork Payette River Bedload Size, mm 100 Largest Particle 1997 D50 for three surface pebble counts D50 for three subsurface cores R2 = 0.71 10 R2 = 0.17 1 Median Size Qa Qb Largest Particle 0.1 100 1000 10000 3 Discharge, ft /s Figure 9. Largest particle in the bedload sample and median size of the sample versus stream discharge for the South Fork Payette River.