( ) Zarestky
advertisement

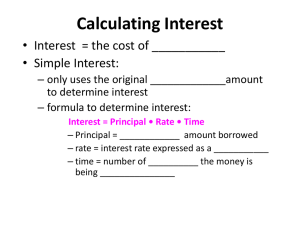
Zarestky Math 141 Chapter 5 Notes 5.1 Compound Interest Simple interest is earned/paid on the original principal only. • Formula: I = P ! r ! t o I represents the total amount of interest. o P represents the initial investment or principal. o r represents the annual interest rate in decimal form. o t represents time (usually in years). • Total earned: A = P (1 + rt ) Compound interest is interest earned/paid on both the interest and principal. • Different Compounding Periods: o annually: m=1 o semi-annually: m = 2 o quarterly: m=4 o monthly: m = 12 o weekly: m = 52 o daily: m = 365 Continuous Compound Interest • Formula: A = Pert o A is the accumulated amount at the end of t years o P is the principal o e = 2.71828... o r is annual interest rate in decimal form o t is time in years Effective Rate of Interest • This is the simple interest rate that would produce the same amount of accumulated interest in one year. • Used as a basis for comparing interest rates. • Equivalent to Annual Percentage Rate (APR) and Annual Percentage Yield (APY) • When paying interest we want the lowest effective rate, and when earning interest we want the highest effective rate. 5.2 Annuities 5.3 Amortization and Sinking Funds Annuities • An annuity is an account into which regular payments are made. Examples include monthly mortgages and deposits into savings accounts. Equity • How much of the item belongs to you and not the bank. • Equity = Value of the item – Amt owed to the bank Amortize – to liquidate a debt by installment payments • An amortization table can be used to summarize payments, equity, interest, principal, etc. Sinking Fund – a fund set up for a specific purpose at some future date